Creating New Social Orders_ Colonial Societies, 1500–1700
Explore the Creating New Social Orders_ Colonial Societies, 1500–1700 study material pdf and utilize it for learning all the covered concepts as it always helps in improving the conceptual knowledge.












































































Creating New Social Orders_ Colonial Societies, 1500–1700 PDF Download
Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , FIGURE John Smiths famous map of Virginia ( 1622 ) illustrates many geopolitical features of early colonization . In the upper left , who governed a powerful local confederation of Algonquian communities , sits above other local leaders , denoting his authority . Another native , who appears in the upper right , visually reinforces the message that the English did not control the land beyond a few outposts along the Chesapeake . CHAPTER OUTLINE Spanish Exploration and Colonial Society Colonial Rivalries Dutch and French Colonial Ambitions English Settlements in America The Impact of Colonization INTRODUCTION By the century , the geopolitical map of North America had become a patchwork of imperial designs and ambitions as the Spanish , Dutch , French , and English reinforced their claims to parts of the land . Uneasiness , punctuated by violent clashes , prevailed in the border zones between the Europeans territorial claims . Meanwhile , native peoples waged war to drive the invaders from the continent . In the Chesapeake Bay and New England colonies , conflicts erupted as the English pushed against their native neighbors ( The rise of colonial societies in the Americas brought Native Americans , Africans , and Europeans together for the time , highlighting the radical social , cultural , and religious differences that hampered their ability to
58 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , understand each other . European settlement affected every aspect of the land and its people , bringing goods , ideas , and diseases that transformed the Americas . Reciprocally , Native American practices , such as the use of tobacco , profoundly altered European habits and tastes . Spanish Exploration and Colonial Society LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end ofthis section , you will be able to main Spanish American colonial settlements of the and Discuss economic , political , and demographic similarities and differences between the Spanish colonies Jamestown King Philip Pope colonists ( leads and wages war Pueblo Spanish Indians fight against Revolt establish Puritan in Augustine Wars colonies Santa Fe 1565 . 1680 I 1607 1610 1620 1676 English Spanish English Nathaniel settle establish Puritans Bacon Jamestown Santa Fe draft leads , armed Compact ' rebellion and found against Plymouth Virginia Colony governor I During the , Spain expanded its colonial empire to the Philippines in the Far East and to areas in the Americas that later became the United States . The Spanish dreamed of mountains of gold and silver and imagined converting thousands of eager Native Americans to Catholicism . In their vision of colonial society , everyone would know his or her place . Patriarchy ( the rule of men over family , society , and government ) shaped the Spanish colonial world . Women occupied a lower status . In all matters , the Spanish held themselves to be atop the social pyramid , with Native peoples and Africans beneath them . Both Africans and native peoples , however , contested Spanish claims to dominance . Everywhere the Spanish settled , they brought devastating diseases , such as smallpox , that led to a loss of life among native peoples . European diseases killed far more native inhabitants than did Spanish swords . The world Native peoples had known before the coming of the Spanish was further upset by Spanish colonial practices . The Spanish imposed the encomienda system in the areas they controlled . Under this system , authorities assigned Native workers to mine and plantation owners with the understanding that the recipients would defend the colony and teach the workers the tenets of Christianity . In reality , the encomienda system exploited native workers . It was eventually replaced by another colonial labor system , the , which required Native towns to supply a pool of labor for Spanish overlords . AUGUSTINE , FLORIDA Spain gained a foothold in Florida , viewing that area and the lands to the north as a logical extension of their Caribbean empire . In 1513 , Juan Ponce de Leon had claimed the area around today Augustine for the Spanish crown , naming the land Florida ( Feast of Flowers , or Easter ) for the nearest feast day . Ponce de Leon was unable to establish a permanent settlement there , but by 1565 , Spain was in need of an outpost to confront the French and English privateers using Florida as a base from which to attack Access for free at .
Spanish Exploration and Colonial Society 59 Spanish ships heading from Cuba to Spain . The threat to Spanish interests took a new turn in 1562 when a group of French Protestants ( established a small settlement they called Fort Caroline , north of Augustine . With the authorization of King Philip 11 , Spanish nobleman Pedro Menendez led an attack on Fort Caroline , killing most of the colonists and destroying the fort . Eliminating Fort Caroline served dual purposes for the helped reduce the danger from French privateers and eradicated the French threat to Spain claim to the area . The contest over Florida illustrates how European rivalries spilled over into the Americas , especially religious between Catholics and Protestants . In 1565 , the victorious Menendez founded Augustine , now the oldest European settlement in the Americas . In the process , the Spanish displaced the local Natives from their ancient town of , which had stood for thousands of years ( Figure ) The suffered greatly from diseases introduced by the Spanish , shrinking from a population of around to fifty thousand in 1590 . By 1700 , only one thousand remained . As in other areas of Spanish conquest , Catholic priests worked to bring about a spiritual conquest by forcing the surviving , demoralized and reeling from catastrophic losses of family and community , to convert to Catholicism . FIGURE In this drawing by French artist Jacques le de Morgues , flee the Spanish settlers , who arrive by ship . Le lived at Fort Caroline , the French outpost , before the Spanish destroyed the colony in 1562 . Spanish Florida made an inviting target for Spain imperial rivals , especially the English , who wanted to gain access to the Caribbean . In 1586 , Spanish settlers in Augustine discovered their vulnerability to attack when the English pirate Sir Francis Drake destroyed the town with a of twenty ships and one hundred men . Over the next several decades , the Spanish built more wooden forts , all of which were burnt by raiding European rivals . Between 1672 and 1695 , the Spanish constructed a stone fort , Castillo de San Marcos Figure ) to better defend Augustine against challengers . FIGURE The Spanish fort of Castillo de San Marcos helped Spanish colonists in Augustine fend off marauding privateers from rival European countries .
60 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , CLICK AND EXPLORE Browse the National Park Service multimedia resources on Castillo de San Marcos ( castillo to see how the fort and gates have looked throughout history . SANTA FE , NEW MEXICO Farther west , the Spanish in Mexico , intent on expanding their empire , looked north to the land of the Pueblo Natives . Under orders from King Philip II , Juan de explored the American southwest for Spain in the late . The Spanish hoped that what we know as New Mexico would yield gold and silver , but the land produced little of value to them . In 1610 , Spanish settlers established themselves at Santa named La Villa Real de la Santa Fe de San Francisco de , or Royal City of the Holy Faith of Francis of many Pueblo villages were located . Santa Fe became the capital of the Kingdom of New Mexico , an outpost of the larger Spanish Viceroyalty of New Spain , which had its headquarters in Mexico City . As they had in other Spanish colonies , Franciscan missionaries labored to bring about a spiritual conquest by converting the Pueblo to Catholicism . At , the Pueblo adopted the parts of Catholicism that dovetailed with their own view of the world . However , Spanish priests insisted that natives discard their old ways entirely and angered the Pueblo by focusing on the young , drawing them away from their parents . This deep insult , combined with an extended period of drought and increased attacks by local Apache and Navajo in the that the Pueblo came to believe were linked to the Spanish the Pueblo to push the Spanish and their religion from the area . Pueblo leader demanded a return to native ways so the hardships his people faced would end . To him and to thousands of others , it seemed obvious that when Jesus came , the Corn Mothers went The expulsion of the Spanish would bring a return to prosperity and a pure , native way of life . In 1680 , the Pueblo launched a coordinated rebellion against the Spanish . The Pueblo Revolt killed over four hundred Spaniards and drove the rest of the settlers , perhaps as many as two thousand , south toward Mexico . However , as droughts and attacks by rival tribes continued , the Spanish sensed an opportunity to regain their foothold . In 1692 , they returned and reasserted their control of the area . Some of the Spanish explained the Pueblo success in 1680 as the work of the Devil . Satan , they believed , had stirred up the Pueblo to take arms against God chosen the Spanish , and their God , had prevailed in the end . Colonial Rivalries Dutch and French Colonial Ambitions LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end ofthis section , you will be able to Compare and contrast the development and character ofthe French and Dutch colonies in North America Discuss the economies of the French and Dutch colonies in North America French and Dutch colonies in North America were modest in comparison to colossal global empire . New France and New remained small commercial operations focused on the fur trade and did not attract an of migrants . The Dutch in New their operations to Manhattan Island , Long Island , the Hudson River Valley , and what later became New Jersey . Dutch trade goods circulated widely among the native peoples in these areas and also traveled well into the interior of the continent along preexisting native trade routes . French habitants , or , eked out an existence along the Lawrence River . French fur traders and missionaries , however , ranged far into the interior of North America , exploring the Great Lakes region and the Mississippi River . These pioneers gave France somewhat imperial claims to lands that nonetheless remained under the dominion of native peoples . FUR TRADING IN NEW The Dutch Republic emerged as a major commercial center in the . Its plied the waters of the Access for free at .
Colonial Rivalries Dutch and French Colonial Ambitions 61 Atlantic , while other Dutch ships sailed to the Far East , returning with prized spices like pepper to be sold in the bustling ports at home , especially Amsterdam . In North America , Dutch traders established themselves on Manhattan Island . One of the Dutch of the North American settlement , Peter Stuyvesant , served from 1647 to 1664 . He expanded the outpost of New east to Long Island , and for many miles north along the Hudson River . The resulting elongated colony served primarily as a post , with the powerful Dutch West India Company controlling all commerce . Fort Amsterdam , on the southern tip of Manhattan Island , defended the growing city of New Amsterdam . In 1655 , Stuyvesant took over the small outpost of New Sweden along the banks of the Delaware River in New Jersey , Pennsylvania , and Delaware . He also defended New Amsterdam from Native American attacks by ordering enslaved Africans to build a protective wall on the city northeastern border , giving Wall Street its name ( Figure . i FIGURE The Plan is the only extant map of 1660 New Amsterdam ( New York City ) The line with spikes on the right side of the colony is the northeastern wall for which Wall Street was named . New failed to attract many Dutch colonists by 1664 , only nine thousand people were living there . with Native peoples , as well as dissatisfaction with the Dutch West India Company trading practices , made the Dutch outpost an undesirable place for many migrants . The small size of the population meant a severe labor shortage , and to complete the arduous tasks of early settlement , the Dutch West India Company imported some 450 enslaved Africans between 1626 and 1664 . The company had involved itself heavily in the slave trade and in 1637 captured , the post on the west coast of Africa , from the Portuguese . The shortage of labor also meant that New welcomed immigrants , including Protestants from Germany , Sweden , Denmark , and England , and embraced a degree of religious tolerance , allowing Jewish immigrants to become residents beginning in the . Thus , a wide variety of people lived in New from the start . Indeed , one observer claimed eighteen different languages could be heard on the streets of New Amsterdam . As new settlers arrived , the colony of New stretched farther to the north and the west Figure .
62 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , FIGURE This 1684 map of New shows the extent of Dutch settlement . The Dutch West India Company found the business of colonization in New to be expensive . To share some of the costs , it granted Dutch merchants who invested heavily in it , or large tracts of land and the right to govern the tenants there . In return , the shareholder who gained the patroonship promised to pay for the passage of at least thirty Dutch farmers to populate the colony . One of the largest was granted to van , one of the directors of the Dutch West India Company it covered most of Albany and Counties . This pattern of settlement created a yawning gap in wealth and status between the tenants , who paid rent , and the wealthy . During the summer trading season , Native Americans gathered at trading posts such as the Dutch site at ( Albany ) where they exchanged furs for guns , blankets , and alcohol . The furs , especially beaver pelts destined for the lucrative European millinery market , would be sent down the Hudson River to New Amsterdam . There , enslaved laborers or workers would load them aboard ships bound for Amsterdam . CLICK AND EXPLORE Explore an interactive map of New Amsterdam in 1660 ( that shows the city plan and the locations of various structures , including houses , businesses , and public buildings . Rolling over the map reveals relevant historical details , such as street names , the identities of certain buildings and businesses , and the names of residents of the houses ( when known ) COMMERCE AND CONVERSION IN NEW FRANCE After Jacques Cartier voyages of discovery in the , France showed little interest in creating permanent colonies in North America until the early , when Samuel de established Quebec as a French outpost . Although the fur trade was lucrative , the French saw Canada as an inhospitable frozen wasteland , and by 1640 , fewer than four hundred settlers had made their home there . The sparse French presence meant that colonists depended on the local native Algonquian people without them , the French would have perished . French , explorers , and fur traders made extensive contact with the Algonquian . The Algonquian , in turn , tolerated the French because the colonists supplied them with Access for free at .
Colonial Rivalries Dutch and French Colonial Ambitions 63 for their ongoing war with the Iroquois . Thus , the French found themselves escalating native wars and supporting the Algonquian against the Iroquois , who received weapons from their Dutch trading partners . These centered on the lucrative trade in beaver pelts , earning them the name of the Beaver Wars . In these wars , between rival native peoples spread throughout the Great Lakes region . A handful of French Jesuit priests also made their way to Canada , intent on converting the native inhabitants to Catholicism . The Jesuits were members of the Society of Jesus , an elite religious order founded in the to spread Catholicism and combat the spread of Protestantism . The Jesuits arrived in Quebec in the , and for the next century , their numbers did not exceed forty priests . Like the Spanish Franciscan missionaries , the Jesuits in the colony called New France labored to convert the native peoples to Catholicism . They wrote detailed annual reports about their progress in bringing the faith to the Algonquian and , beginning in the , to the Iroquois . These documents are known as the Jesuit Relations Figure 347 , and they provide a rich source for understanding both the Jesuit view of the Native Americans and the Native response to the colonizers . One Native convert to Catholicism , a Mohawk woman named , so impressed the priests with her piety that a Jesuit named Claude attempted to make her a saint in the Church . However , the effort to canonize faltered when leaders of the Church balked at elevating a savage to such a high status she was eventually canonized in 2012 . French colonizers pressured the native inhabitants of New France to convert , but they virtually never saw Native peoples as their equals . DEFINING AMERICAN A Jesuit Priest on Native Healing Traditions The Jesuit Relations ( Figure 37 provide incredible detail about Native life . For example , the 1636 edition , written by the Catholic priest Jean de , addresses the devastating effects of disease on Native peoples and the efforts made to combat it . RELATION DE CE PASSE nu MISSIONS DES . FRANCE . ua Au . up lint FIGURE French Jesuit missionaries to New France kept detailed records of their interactions
64 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , observations Algonquian and Iroquois that they converted to Catholicism . credit Project ) Let us return to the feasts . The is a remedy which is only for one particular kind of disease , which they call also , from the name of a little Demon as large as the , which they say is in the body of the sick man , especially in the part which pains him . They out that they are sick of this disease , by means of a dream , or by the intervention of some Sorcerer . Of three kinds of games especially in use Peoples , the games of crosse lacrosse , dish , and straw , two are , they say , most healing . Is not this worthy of compassion ?
There is a poor sick man , fevered of body and almost dying , and a miserable Sorcerer will order for him , as a cooling remedy , a game of crosse . Or the sick man himself , sometimes , will have dreamed that he must die unless the whole country shall play crosse for his health and , no matter how little may be his credit , you will see then in a beautiful , Village contending against Village , as to who will play crosse the better , and betting against one another Beaver robes and Porcelain collars , so as to excite greater interest . According to this account , how did Native Americans attempt to cure disease ?
Why did they prescribe a game of lacrosse ?
What might these games have for the sick ?
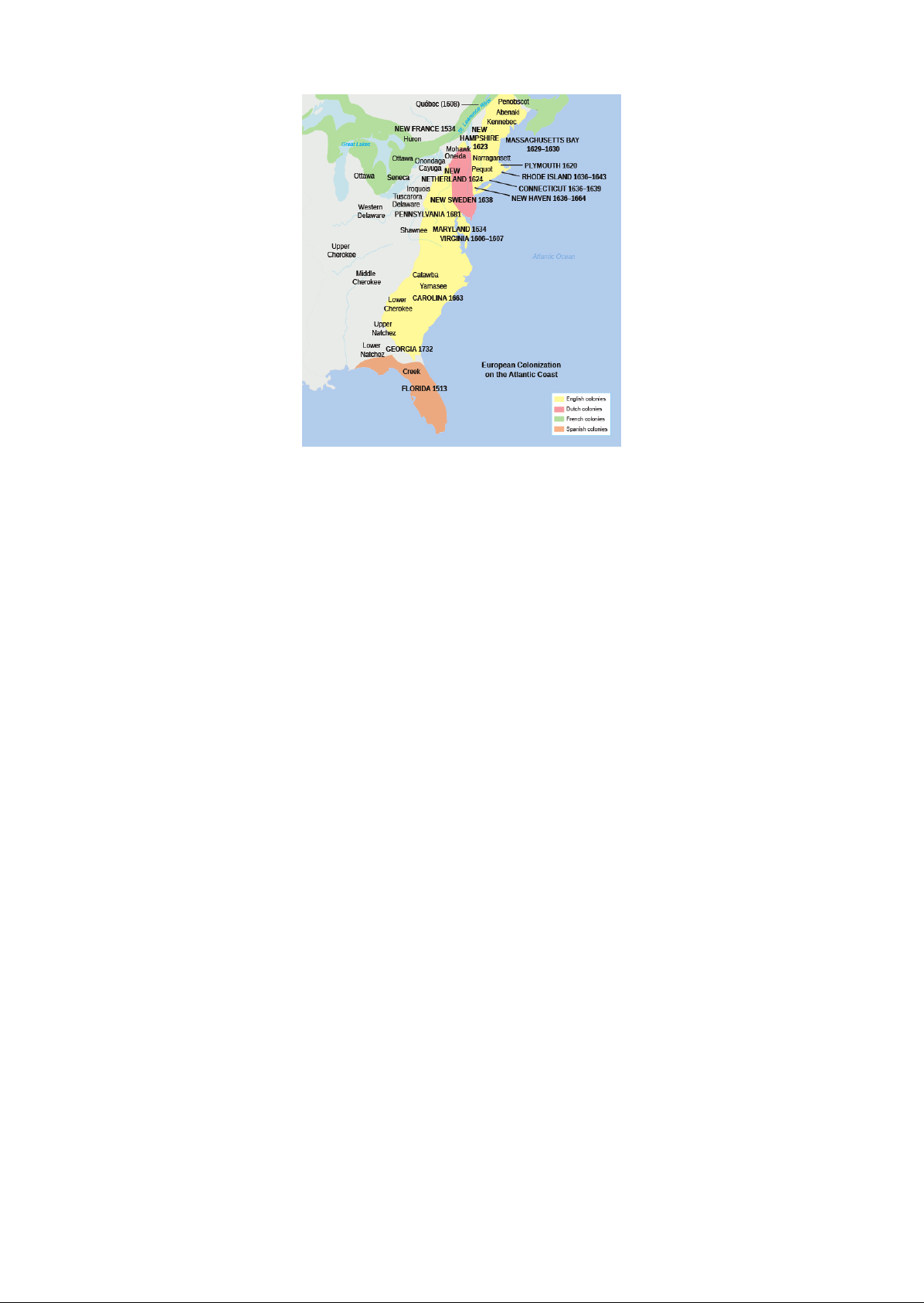
English Settlements in America LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end ofthis section , you will be able to English settlements in America Describe the differences between the Chesapeake Bay colonies and the New England colonies Compare and contrast the wars between Native inhabitants and English colonists in both the Chesapeake Bay and New England colonies Explain the role of Bacon Rebellion in the rise of chattel slavery in Virginia At the start of the seventeenth century , the English had not established a permanent settlement in the Americas . Over the next century , however , they outpaced their rivals . The English encouraged emigration far more than the Spanish , French , or Dutch . They established nearly a dozen colonies , sending swarms of immigrants to populate the land . England had experienced a dramatic rise in population in the sixteenth century , and the colonies appeared a welcoming place for those who faced overcrowding and grinding poverty at home . Thousands of English migrants arrived in the Chesapeake Bay colonies of Virginia and Maryland to work in the tobacco . Another stream , this one of pious Puritan families , sought to live as they believed scripture demanded and established the Plymouth , Massachusetts Bay , New Haven , Connecticut , and Rhode Island colonies of New England Figure ) Access for free at .
English Settlements in America 65 we DEW . new my , A ?
mum ' Nam Seneca ' RHODE ISLAND mum mums ' Delaware 1681 Shawnee ma Quebec ( 1508 ) Grail um Cherokee Middle Cherokee , Lawer 1732 339 an lhe mu mime FIGURE In the early seventeenth century , thousands of English settlers came to what are now Virginia , Maryland , and the New England states in search of opportunity and a better life . THE DIVERGING CULTURES OF THE NEW ENGLAND AND CHESAPEAKE COLONIES Promoters of English colonization in North America , many of whom never ventured across the Atlantic , wrote about the bounty the English would there . These boosters of colonization hoped to turn a by importing raw resources or providing new markets for English spread Protestantism . The English migrants who actually made the journey , however , had different goals . In Chesapeake Bay , English migrants established Virginia and Maryland with a decidedly commercial orientation . Though the early Virginians at Jamestown hoped to gold , they and the settlers in Maryland quickly discovered that growing tobacco was the only sure means of making money . Thousands of unmarried , unemployed , and impatient young Englishmen , a ong with a few , pinned their hopes for a better life on the tobacco of these two colonies . A very different of English men and women to the cold climate and rocky soil of New England , spurred by religious motives . Many of the Puritans crossing the Atlantic were people who brought families and children . Often they were following their ministers in a migration beyond the seas , envisioning a new English Israel where reformed Protestantism would grow and thrive , providing a model for the rest of the Christian world and a Counter what they saw as the Catholic menace . While the English in Virginia and Maryland worked on expanding their tobacco , the English in New England built towns focused on the church , where each congregation decided what was best for itself . The Congregational Church is the result of the Puritan enterprise in America . Many historians believe the fault lines separating what later became the North and South in tie United States originated in the profound differences between the Chesapeake and New England colonies . The source of those lay in England domestic problems . Increasingly in the early , the English state Church of England , established in the conformity , or compliance with its practices , bu Puritans pushed for greater reforms . By the , the Church of England began to see leading Puritan ministers and their followers as outlaws , a national security threat because of their opposition to its power . As the noose of conformity tightened around them , many Puritans decided to remove to New England . By 1640 , New England had a population of thousand . Meanwhile , many loyal members of the Church of England , who ridiculed and mocked Puritans both at home and in New England , to Virginia for economic opportunity . The troubles in England escalated in the 16405 when civil war broke out , pitting Royalist supporters of King
66 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , Charles I and the Church of England against Parliamentarians , the Puritan reformers and their supporters in Parliament . In 1649 , the Parliamentarians gained the upper hand and , in an unprecedented move , executed Charles I . In the , therefore , England became a republic , a state without a king . English colonists in America closely followed these events . Indeed , many Puritans left New England and returned home to take part in the struggle against the king and the national church . Other English men and women in the Chesapeake colonies and elsewhere in the English Atlantic World looked on in horror at the mayhem the Parliamentarians , led by the Puritan insurgents , appeared to unleash in England . The turmoil in England made the administration and imperial oversight of the Chesapeake and New England colonies , and the two regions developed divergent cultures . THE CHESAPEAKE COLONIES VIRGINIA AND MARYLAND The Chesapeake colonies of Virginia and Maryland served a vital purpose in the developing century English empire by providing tobacco , a cash crop . However , the early history of Jamestown did not suggest the English outpost would survive . From the outset , its settlers struggled both with each other and with the Native inhabitants , the powerful , who controlled the area . Jealousies and among the English destabilized the colony . One member , John Smith , whose famous map begins this chapter , took control and exercised powers , which furthered aggravated the squabbling . The settlers inability to grow their own food compounded this unstable situation . They were essentially employees of the Virginia Company of London , an English company , in which investors provided the capital and assumed the risk in order to reap the , and they had to make a for their shareholders as well as for themselves . Most initially devoted themselves to gold and silver instead of ways to grow their own food . Early Struggles and the Development of the Tobacco Economy Poor health , lack of food , and with Native peoples took the lives of many of the original Jamestown settlers . The winter of , which became known as the starving time , came close to annihilating the colony . By June 1610 , the few remaining settlers had decided to abandon the area only the arrival of a supply ship from England prevented another failed colonization effort . The supply ship brought new settlers , but only twelve hundred of the hundred who came to Virginia between 1607 and 1624 survived . MY STORY George Percy on The Starving Time George Percy , the youngest son of an English nobleman , was in the group of settlers at the Jamestown Colony . He kept a journal describing their experiences in the excerpt below , he reports on the privations of the colonists third winter . Now all of us at James Town , beginning to feelthat sharp prick of hunger which no man truly describe but he which has tasted the bitterness thereof , a world of miseries ensued as the sequel will express unto you , in so much that some to satisfy their hunger have robbed the store for the which I caused them to be executed . Then having fed upon horses and other beasts as long as they lasted , we were glad to make shift with vermin as dogs , cats , rats , and mice . All was that came to net to satisfy cruel hunger as to eat boots , shoes , or any other leather some could come by , and , those being spent and devoured , some were enforced to search the woods and to feed upon serpents and snakes and to earth for wild and unknown roots , where many of our men were cut off of and slain by the savages . And now famine beginning to look ghastly and pale in every face that nothing was spared to maintain life and to do those things which seem incredible as to dig up dead corpses out of graves and to eat them , and some have licked up the blood which has fallen from their weak fellows . Percy , A True Relation of the Proceedings and of Moment which have happened in Virginia from the Time Sir Thomas Gates shipwrecked upon the anno 1609 until my departure out of the Access for free at .
English Settlements in America 67 Country which was in anno Domini 1612 , London 1624 What is your reaction to George Percy story ?
How do you think Jamestown managed to survive after such an experience ?
What do you think the Jamestown colonists learned ?
By the , Virginia had weathered the worst and gained a degree of permanence . Political stability came slowly , but by 1619 , the colony was operating under the leadership of a governor , a council , and a House of Burgesses . Economic stability came from the lucrative cultivation of tobacco . Smoking tobacco was a practice among native peoples , and English and other European consumers soon adopted it . In 1614 , the Virginia colony began exporting tobacco back to England , which earned it a sizable and saved the colony from ruin . A second tobacco colony , Maryland , was formed in 1634 , when King Charles I granted its charter to the Calvert family for their loyal service to England . Calvert , the second Lord Baltimore , conceived of Maryland as a refuge for English Catholics . Growing tobacco proved very ( Figure ) and the Chesapeake colonists needed a steady workforce to do the hard work of clearing the land and caring for the tender young plants . The mature leaf of the plant then had to be cured ( dried ) which necessitated the construction of drying barns . Once cured , the tobacco had to be packaged in ( large wooden barrels ) and loaded aboard ship , which also required considerable labor . AL AL FIGURE In this 1670 painting by an unknown artist , enslaved people work in sheds . To meet these labor demands , early Virginians relied on indentured servants . An indenture is a labor contract that young , impoverished , and often illiterate Englishmen and occasionally signed in England , pledging to work for a number of years ( usually between and seven ) growing tobacco in the Chesapeake colonies . In return , indentured servants received paid passage to America and food , clothing , and lodging . At the end of their indenture , servants received freedom clues , usually food and other provisions , including , in some cases , land provided by the colony . The promise of a new life in America was a strong attraction for members of England underclass , who had few if any options at home . In the , some indentured servants traveled to the Chesapeake Bay . Most were poor young men in their early twenties . Life in the colonies proved harsh , however . Indentured servants could not marry , and they were subject to the will of the tobacco planters who bought their labor contracts . Treated much like property , the contracted servants could be essentially sold or traded among those with means to purchase them . Some contract holders did not feed or house their servants well . If an indentured servant committed a crime or disobeyed those who held their contracts , they found their terms of service lengthened , often by several years . Female indentured servants faced special dangers in what was essentially a bachelor colony . Many were exploited by unscrupulous tobacco planters who seduced them with promises of marriage . If the women became pregnant , the planters would then sell them to other tobacco planters to avoid the costs of raising a child .
68 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , Nonetheless , those indentured servants who completed their term of service often began new lives as tobacco planters . To entice even more migrants to the New World , the Virginia Company also implemented the headright system , in which those who paid their own passage to Virginia received acres plus an additional for each servant or family member they brought with them . The headright system and the promise of a new life for servants acted as powerful incentives for English migrants to hazard the journey to the New World . CLICK AND EXPLORE Visit Virtual Jamestown ( to access a database of contracts of indentured servants . Search it by name to an ancestor or browse by occupation , destination , or county of origin . The Wars By choosing to settle along the rivers on the banks of the Chesapeake , the English unknowingly placed themselves at the center of the Empire , a powerful Algonquian confederacy of thirty native groups with perhaps as many as thousand people . The territory of the equally impressive people also bordered English settlements at the north end of the Chesapeake Bay . Tensions ran high between the English and the , and war prevailed . The First War ( resulted not only from the English colonists intrusion onto land , but also from their refusal to follow cultural protocol by giving gifts . English actions infuriated and insulted the . In 1613 , the settlers captured Pocahontas ( also called ) the daughter of a headman named , and gave her in marriage to Englishman John Rolfe . Their union , and her choice to remain with the English , helped quell the war in 1614 . Pocahontas converted to Christianity , changing her name to Rebecca , and sailed with her husband and several other to England where she was introduced to King James I ( Figure . Promoters of colonization publicized Pocahontas as an example of the good work of converting the to Christianity . FIGURE This 1616 engraving by Simon van de Passe , completed when Pocahontas and John Rolfe were presented at court in England , is the only known contemporary image of Pocahontas . Note her European garb and pose . What message did the painter likely intend to convey with this portrait of Pocahontas , the daughter of a powerful Native American leader ?
Access for free at .
English Settlements in America 69 CLICK AND EXPLORE Explore the interactive exhibit Changing Images of Pocahontas ( on website to see the many ways artists have portrayed Pocahontas over the centuries . Peace in Virginia did not last long . The Second War ( broke out because of the expansion of the English settlement nearly one hundred miles into the interior , and because of the continued insults and friction caused by English activities . The attacked in 1622 and succeeded in killing almost 350 English , about a third of the settlers . The English responded by annihilating every village around Jamestown and from then on became even more intolerant . The Third War ( began with a surprise attack in which the killed around five hundred English colonists . However , their ultimate defeat in this conflict forced the to acknowledge King Charles I as their sovereign . The Wars , spanning nearly forty years , illustrate the degree of native resistance that resulted from English intrusion into the confederacy . The Rise of Slavery in the Chesapeake Bay Colonies The transition from indentured servitude to slavery as the main labor source for some English colonies happened first in the West Indies . On the small island of Barbados , colonized in the , English planters first grew tobacco as their main export crop , but in the , they converted to sugarcane and began increasingly to rely on African enslaved people . In 1655 , England wrestled control of Jamaica from the Spanish and quickly turned it into a lucrative sugar island , run on forced labor , for its expanding empire . While slavery was slower to take hold in the Chesapeake colonies , by the end of the seventeenth century , both Virginia and Maryland had also adopted chattel legally Africans as property and not the dominant form of labor to grow tobacco . Chesapeake colonists also enslaved Native people . When the Africans arrived in Virginia in 1619 , did not exist in not yet become an institution in colonial America . Many Africans worked as servants and , like their White counterparts , could acquire land of their own . Some Africans who converted to Christianity became free landowners with White servants . The change in the status of Africans in the Chesapeake to that of enslaved people occurred in the last decades of the seventeenth century . Bacon Rebellion , an uprising of both White people and Black people who believed that the Virginia government was impeding their access to land and wealth and seemed to do little to clear the land of Native Americans , hastened the transition to African slavery in the Chesapeake colonies . The rebellion takes its name from Nathaniel Bacon , a wealthy young Englishman who arrived in Virginia in 1674 . Despite an early friendship with Virginia royal governor , William Berkeley , Bacon found himself excluded from the circle of friends and councilors . He wanted land on the Virginia frontier , but the governor , fearing war with neighboring tribes , forbade further expansion . Bacon marshaled others , especially former indentured servants who believed the governor was limiting their economic opportunities and denying them the right to own tobacco farms . Bacon followers believed Berkeley frontier policy did protect English settlers enough . Worse still in their eyes , Governor Berkeley tried to keep peace in Virginia by signing treaties with various local Native peoples . Bacon and his followers , who saw all Native peoples as an obstacle to their access to land , pursued a policy of extermination . Tensions between the English and the Native peoples in the Chesapeake colonies led to open . In 1675 , war broke out when warriors attacked settlements on Virginia frontier , killing English planters and destroying English plantations , including one owned by Bacon . In 1676 , Bacon and other Virginians attacked the without the governor approval . When Berkeley ordered arrest , Bacon led his followers to Jamestown , forced the governor to to the safety of Virginia eastern shore , and then burned the city . The civil war known as Bacon Rebellion , a vicious struggle between supporters of the governor and those who supported Bacon , ensued . Reports of the rebellion traveled back to
Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , England , leading Charles II to dispatch both royal troops and English commissioners to restore order in the tobacco colonies . By the end of 1676 , Virginians loyal to the governor gained the upper hand , executing several leaders of the rebellion . Bacon escaped the hangman noose , instead dying of dysentery . The rebellion in 1676 , but Virginians remained divided as supporters of Bacon continued to harbor grievances over access to Native land . Bacon Rebellion helped to catalyze he creation of a system of racial slavery in the Chesapeake colonies . At the time of the rebellion , indentured servants made up the majority of laborers in the region . Wealthy White people worried over the presence of this large class of laborers and the relative freedom they enjoyed , as well as the alliance that Black and White servants had forged in the course of the rebellion . Replacing indentured servitude with Black slavery ied these risks , alleviating the reliance on White indentured servants , who were often and troublesome , and creating a caste of racially laborers whose movements were strictly controlled . also lessened the possibility of further alliances between Black and White workers . Racial slavery even served to heal some of the divisions between wealthy and poor White people , who could now unite as mem of a superior racial group . While colonial laws in the tobacco co had made slavery a legal institution before Bacon Rebellion , new laws passed in the wake of the rebellion severely curtailed Black freedom and laid the foundation for racial slavery . Virginia passed a law in 1680 prohibiting free Black people and enslaved people from bearing arms , banning Black people from ing in large numbers , and establishing harsh punishments for enslaved people who assaulted Christians or sought freedom . Two years later , another Virginia law stipulated that all Africans brought to the colony would be enslaved for life . Thus , the increasing reliance on enslaved people in the tobacco the draconian laws instituted to control only helped planters meet labor demands , but also served to assuage English fears of further uprisings and alleviate class tensions between rich and poor White people . DEFINING AMERICAN Robert on Servants and Enslaved People Robert was a wealthy Jamestown planter and enslaver . This excerpt from his History and Present State of Virginia , published in 1705 , clearly illustrates the contrast between White servants and enslaved Black people . Their Servants , they distinguish by the Names of Slaves for Life , and Servants for a time . Slaves are the Negroes , and their Posterity , condition of the Mother , accordingto the Maxim , status follows the womb . They are call Slaves , in respect of the time of their Servitude , because it is for Life . Servants , are those which serve only for a few years , according to the time of their , or the Custom of the Country . The Custom ofthe Country takes place upon such as have no Indentures . The Law in this case is , that if such Servants be under Nineteen years of Age , they must be brought into Court , to have their Age adjudged and from the Age they are to be of , they must serve until they reach four and twenty But if they be adjudged upwards of Nineteen , they are then only to be Servants for the term of Years . The , and Slaves of both Sexes , are employed together in Tilling and Ground , in Sowing and Planting Tobacco , Corn , Some Distinction indeed is made between them in their , and Food but the Work of both , is no other than what the Overseers , the Freemen , and the Planters themselves do . Sufficient Distinction is also made between the , and Slaves for a White Woman is rarely or never put to work in the Ground , if she be good for any thing else And to Discourage all Planters from using any Women so , their Law imposes the heaviest Taxes upon Female Servants working in the Ground , while it suffers all other White Women to be absolutely exempted Whereas on the other hand , it is a common thing to work a Woman Slave out of Doors nor does the Law make any Distinction in her Taxes , whether her Work be Abroad , or at Home . According to Robert , what are the differences between the servants and the enslaved ?
What protections Access for free at .
English Settlements in America 71 did servants have that enslaved people did not ?
PURITAN NEW ENGLAND The second major area to be colonized by the English in the half of the seventeenth century , New England , differed markedly in its founding principles from the commercially oriented Chesapeake tobacco colonies . Settled largely by waves of Puritan families in the , New England had a religious orientation from the start . In England , men and women had been calling for greater changes to the English national church since the . These reformers , who followed the teachings of John Calvin and other Protestant reformers , were called because of their insistence on purifying the Church of England of what they believed to be ural , especially Catholic elements that lingered in its institutions and practices . Many who provided leadership in early New England were learned ministers who had studied at Cambridge or Oxford but who , because they had questioned the practices of the Church , had been deprived of careers by the king anc his officials in an effort to silence all dissenting voices . Other Puritan leaders , such as the governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony , John Winthrop , came from the privileged class of English gentry . These Puritans and many thousands more left their English homes not to establish a land of religious freedom , but practice their own religion without persecution . Puritan New England offered them the opportunity to live as they believed the Bible demanded . In their New England , they set out to create a model of reformed Pro , a new English Israel . The generated by Puritanism had divided English society , because the Puritans demanded reforms that undermined the traditional festive culture . For example , they denounced popular pastimes like dogs at ack a chained were often conducted on Sundays when people had a few leisure hours . In the cu ture where William Shakespeare had produced his masterpieces , Puritans called for an end to the theater , censuring playhouses as places of decadence . Indeed , the Bible itself became part of the struggle between Puritans and James I , who headed the Church of England . Soon after ascending the throne , James commissioned a new version of the Bible in an effort to Puritan reliance on the Geneva Bible , which followed the teachings of John Calvin and placed God authority above the monarch . The King James Version , published in 1611 , instead emphasized the majesty . During the and , the escalated to the point where the state church prohibited Puritan ministers from preaching . In the Church view , Puritans represented a national security threat , because their demands for cultural , social , and religious reforms undermined the king authority . Unwilling to conform to the Church of England , many Puritans found refuge in the New World . Yet those who emigrated to the Americas were not united . Some called for a complete break with the Church of England , while others remained committed to reforming the national church . Plymouth The First Puritan Colony The group of Puritans to make their way across the Atlantic was a small contingent known as the Pilgrims . Unlike other Puritans , they insisted on a complete separation from the Church of England and had first migrated to the Dutch Republic in Europe seeking religious freedom . Although they found they could worship without hindrance there , they grew concerned that they were losing their as they saw their children begin to learn the Dutch language and adopt Dutch ways . In addition , the English Pilgrims ( and others in Europe ) feared another attack on the Dutch Republic by Spain . Therefore , in 1620 , they moved on to found the Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts . The governor of Plymouth , William Bradford , was a Separatist , a proponent of complete separation from the English state church . Bradford and the other Pilgrim Separatists represented a major challenge to the prevailing vision of a English national church and empire . On board the , which was bound for Virginia but landed on the tip of Cape Cod , Bradford and forty other adult men signed the Compact Figure , which presented a religious ( rather than an economic ) rationale for colonization . The compact expressed a community ideal of working together . When a
72 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , larger exodus of Puritans established the Massachusetts Bay Colony in the 16303 , the Pilgrims at Plymouth welcomed them and the two colonies cooperated with each other . AMERICANA The Mayflower Compact and Its Religious Rationale The Mayflower Compact , which Pilgrim men signed on board the Plymouth Harbor , has been called the first American governing document , Constitution by over 150 years . But was the Mayflower Compact a constitution ?
How much authority did it convey , and to whom ?
I . 15 ' I , A . Aa I ) I ( I , I now . lo I . a I ( FIGURE The original Mayflower Compact is no longer extant only copies , such as this transcription by William Bradford , remain . In the name of God , Amen . We , whose names are underwritten , the loyal subjects of our dread Sovereign Lord King James , by the Grace of God , of Great Britain , France , and Ireland , King , defender of the Faith , etc . Having undertaken , for the Glory of God , and advancements of the Christian faith and honor of our King and Country , a voyage to plant the first colony in the Northern parts of Virginia , do presents , solemnly and mutually , in the presence of God , and one another , covenant and combine ourselves together into a civil body politic for our better ordering , and preservation and furtherance of the ends aforesaid and by virtue hereof to enact , constitute , and frame , such just and equal laws , ordinances , acts , constitutions , and , from time to time , as shall be thought most meet and convenient for the general good ofthe colony unto which we promise all due submission and obedience . In witness whereof we have hereunto subscribed our names at Cape Cod the of November , in the year of the reign of our Sovereign Lord King James , of England , France , and Ireland , the eighteenth , and of Scotland the , 1620 Different labor systems also distinguished early Puritan New England from the Chesapeake colonies . Puritans expected young people to work diligently at their calling , and all members of their large families , including children , did the bulk of the work necessary to run homes , farms , and businesses . Very few migrants came to Access for free at .
English Settlements in America 73 New England as laborers in fact , New England towns protected their disciplined homegrown workforce by refusing to allow outsiders in , assuring their sons and daughters of steady employment . New England labor system produced remarkable results , notably a powerful economy with scores of oceangoing ships and the crews necessary to sail them . New England mariners sailing New ships transported Virginian tobacco and West Indian sugar throughout the Atlantic World . A City upon a Hill A much larger group of English Puritans left England in the , establishing the Massachusetts Bay Colony , the New Haven Colony , the Connecticut Colony , and Rhode Island . Unlike the exodus of young males to the Chesapeake colonies , these migrants were families with young children and their ministers . Their aim , according to John Winthrop ( Figure , the first governor of Massachusetts Bay , was to create a model of reformed city upon a hill , a new English Israel . The idea of a city upon a hill made clear the religious orientation of the New England settlement , and the charter of the Massachusetts Bay Colony stated as a goal that the colony people may be soe religiously , and civilly governed , as their good Life and , wynn and incite the Natives of Country , to the and Obedience of the true God and of , and the Christian . To illustrate this , the seal of the Massachusetts Bay Company Figure shows a Native American who entreats more of the English to come over and help us . FIGURE In the 1629 seal of the Massachusetts Bay Colony ( a ) a Native American is shown asking colonists to Come over and help This seal indicates the religious ambitions of John Winthrop ( the colony first governor , for his city upon a hill . Puritan New England differed in many ways from both England and the rest of Europe . Protestants emphasized literacy so that everyone could read the Bible . This attitude was in stark contrast to that of Catholics , who refused to tolerate private ownership of Bibles in the vernacular . The Puritans , for their part , placed a special emphasis on reading scripture , and their commitment to literacy led to the establishment of the printing press in English America in 1636 . Four years later , in 1640 , they published the book in North America , the Bay Psalm Book . As Calvinists , Puritans adhered to the doctrine of predestination , whereby a few elect would be saved and all others damned . No one could be sure whether they were predestined for salvation , but through introspection , guided by scripture , Puritans hoped to a glimmer of redemptive grace . Church membership was restricted to those Puritans who were willing to provide a conversion narrative telling how they came to understand their spiritual estate by hearing sermons and studying the Bible . Although many people assume Puritans escaped England to establish religious freedom , they proved to be just
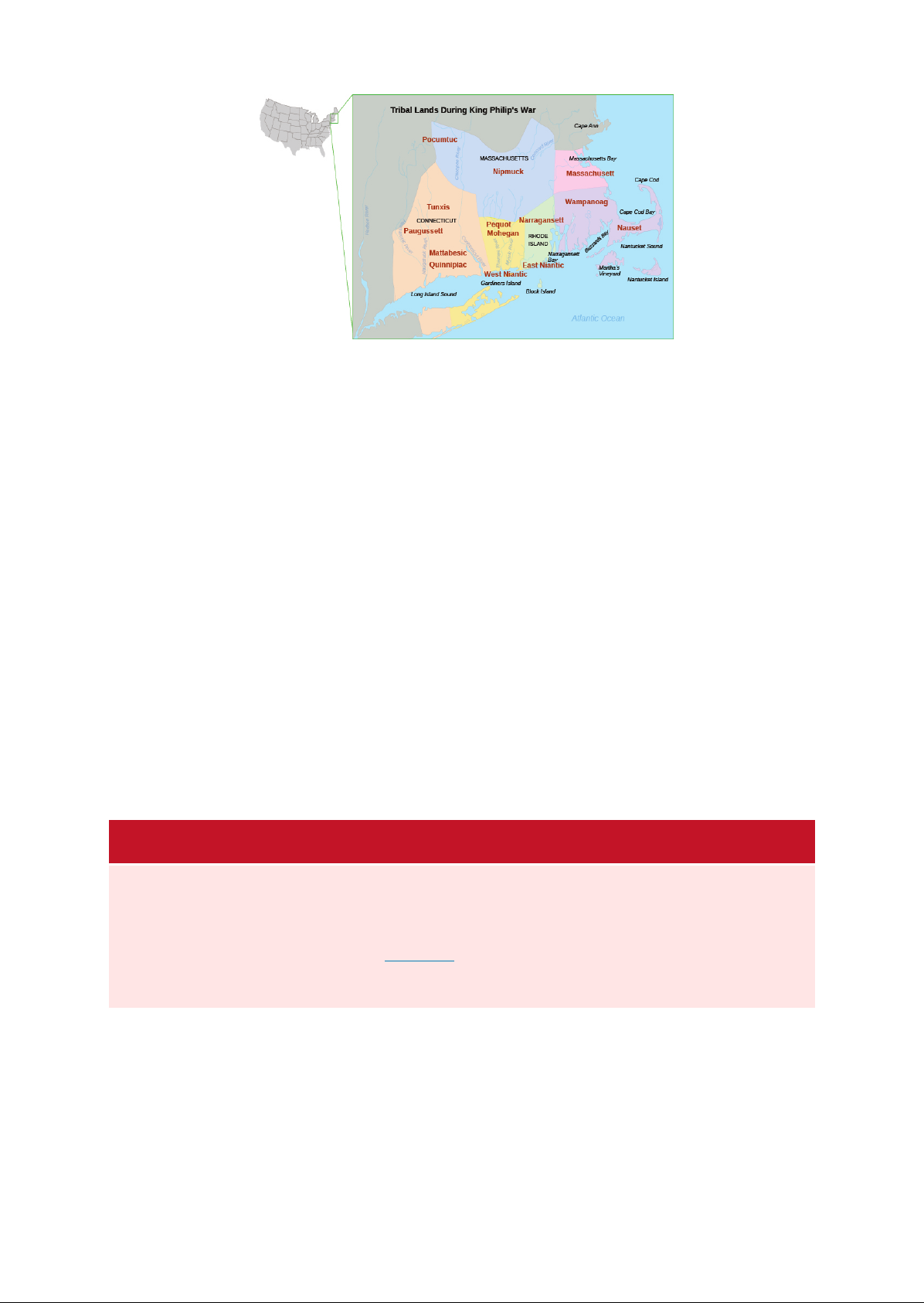
Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , as intolerant as the English state church . When dissenters , including Puritan minister Roger Williams and Anne Hutchinson , challenged Governor Winthrop in Massachusetts Bay in the , they were banished . Roger Williams questioned the Puritans taking of Native land . Williams also argued for a complete separation from the Church of England , a position other Puritans in Massachusetts rejected , as well as the idea that the state could not punish individuals for their beliefs . Although he did accept that nonbelievers were destined for eternal damnation , Williams did not think the state could compel true orthodoxy . Puritan authorities found him guilty of spreading dangerous ideas , but he went on to found Rhode Island as a colony that sheltered dissenting Puritans from their brethren in Massachusetts . In Rhode Island , Williams wrote favorably about native peoples , contrasting their virtues with Puritan New England intolerance . Anne Hutchinson also ran afoul of Puritan authorities for her criticism of the evolving religious practices in the Massachusetts Bay Colony . In particular , she held that Puritan ministers in New England taught a shallow version of Protestantism emphasizing hierarchy and covenant of works rather than a covenant of Literate Puritan women like Hutchinson presented a challenge to the male ministers authority . Indeed , her major offense was her claim of religious revelation , a type of spiritual experience that negated the role of ministers . Because of beliefs and her of authority in the colony , especially that of Governor Winthrop , Puritan authorities ried and convicted her of holding false beliefs . In 1638 , she was excommunicated and banished from the colony . She went to Rhode Island and later , in 1642 , sought safety among the Dutch in New . The following year , Algonquian warriors killed Hutchinson and her family . In Massachusetts , Governor noted her death as the righteous judgment of God against a heretic . Like many other Europeans , the Puritans believed in the supernatural . Every event appeared to be a sign of God mercy or judgment , and people be that witches allied themselves with the Devil to carry out evil deeds and deliberate harm such as the sickness or death of children , the loss of cattle , and other catastrophes . Hundreds were accused of witchcraft in New England , including townspeople whose habits or appearance bothered their neighbors or who appeared threatening for any reason . Women , seen as more susceptible to the Devil because of their supposedly weaker constitutions , made up the vast majority of suspects and those who were executed . he most notorious cases occurred in Salem Village in 1692 . Many of the accusers who prosecuted the ed witches had been traumatized by the Native wars on the frontier and by unprecedented political and cultural changes in New England . Relying on their belief in witchcraft to help make sense of their changing world , Puritan authorities executed nineteen people and caused the deaths of several others . CLICK AND EXPLORE Explore the Salem Witchcraft Trials ( I to learn more about the prosecution of witchcraft in New England . Puritan Relationships with Native Peoples Like their Spanish and French Catholic rivals , English Puritans in America took steps to convert native peoples to their version of Christianity . John Eliot , the leading Puritan missionary in New England , urged natives in Massachusetts to live in praying towns established by English authorities for converted Native Americans , and to adopt the Puritan emphasis on the centrality of the Bible . In keeping with the Protestant emphasis on reading scripture , he translated the Bible into the local Algonquian language and published his work in 1663 . Eliot hoped that as a result of his efforts , some of New England native inhabitants would become preachers . Tensions had existed from the beginning between the Puritans and the native people who controlled southern New England Figure . Relationships deteriorated as the Puritans continued to expand their settlements aggressively and as European ways increasingly disrupted native life . These strains led to King Philip War ( a massive regional that was nearly successful in pushing the English out of New England . Access for free at .
English Settlements in America 75 Tribal um During King Philip war Cine Bil Nam , a , a West ( slings ham mum FIGURE This map indicates the domains of New England native inhabitants in 1670 , a few years before King Philip War . When the Puritans began to arrive in and , local Algonquian peoples had viewed them as potential allies in the already simmering between rival Native groups . In 1621 , the , led by , concluded a peace treaty with the Pilgrims at Plymouth . In the , the Puritans in Massachusetts and Plymouth allied themselves with the and people against the , who had recently expanded their claims into southern New England . In May 1637 , the Puritans attacked a large group of several hundred along the Mystic River in Connecticut . To the horror of their Native allies , the Puritans massacred all but a handful of the men , women , and children they found . By the century , the Puritans had pushed their way further into the interior of New England , establishing outposts along the Connecticut River Valley . There seemed no end to their expansion . leader or , also known as King Philip among the English , was determined to stop the encroachment . The , along with the , and , took up arms to drive the English from the land . In the ensuing , called King Philip War , Native forces succeeded in destroying half of the frontier Puritan towns however , in the end , the English ( aided by and Christian Native Americans ) prevailed and sold many captives into slavery in the West Indies . The severed head of King Philip was publicly displayed in Plymouth . The war also forever changed the English perception of Native peoples from then on , Puritan writers took great pains to vilify the Native people as bloodthirsty savages . A new type of racial hatred became a feature of relationships in the Northeast . MY STORY Mary Captivity Narrative Mary was a Puritan woman whom Native tribes captured and imprisoned for several weeks during King Philip War . After her release , she wrote The Narrative of the Captivity and the Restoration of Mary , which was published in 1682 ( Figure . The book was an immediate sensation that was reissued in multiple editions for overa century .
Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , or was MA RI ON A I in IS mun , am . hung . a ) FIGURE Puritan woman Mary wrote her captivity narrative , the front cover of which is shown here ( a ) after her imprisonment during King Philip War . In her narrative , she tells of her treatment by the Native Americans holding her as well as of her meetings with the leader ( shown in a contemporary portrait . But now , the next morning , I must turn my back upon the town , and travel with them into the vast and desolate wilderness , I knew not whither . It is not my tongue , or pen , can express the sorrows of my heart , and bitterness of my spirit that I had at this departure but God was with me in a wonderful manner , carrying me along , and bearing up my spirit , that it did not quite fail . One of the Indians carried my poor wounded babe upon a horse it went moaning all along , I shall die , I shall die . I went on foot after it , with sorrow that can not be expressed . At length it off the horse , and carried it in my arms till my strength failed , and down with it . Then they set me upon a horse with my wounded child in my lap , and there being no furniture upon the horse back , as we were going down a steep hill we both fell over the horse head , at which they , like inhumane creatures , laughed , and rejoiced to see it , though I thought we should there have ended our days , as overcome with so many . But the Lord renewed my strength still , and carried me along , that I might see more of His power yea , so much that I could never have thought of , had I not experienced it . What sustains her during her ordeal ?
How does she characterize her captors ?
What do you think made her narrative so compelling to readers ?
CLICK AND EXPLORE Access the entire text of Mary narrative ( at the Project . The Impact of Colonization LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end ofthis section , you will be able to Explain the reasons for the rise of slavery in the American colonies Describe changes to Native life , including warfare and hunting Contrast European and Native American views on property Assess the impact of European settlement on the environment As Europeans moved beyond exploration and into colonization of the Americas , they brought changes to virtually every aspect of the land and its people , from trade and hunting to warfare and personal property . Access for free at .
The Impact of Colonization ' European goods , ideas , and diseases shaped the changing continent . As Europeans established their colonies , their societies also became segmented and divided along religious and racial lines . Most people in these societies were not free they labored as servants or enslaved people , doing the work required to produce wealth for others . By 1700 , the American continent had become a place of stark contrasts between slavery and freedom , between the haves and the . THE INSTITUTION OF SLAVERY Everywhere in the American colonies , a crushing demand for labor existed to grow New World cash crops , especially sugar and tobacco . This need led Europeans to rely increasingly on Africans , and after 1600 , the movement of Africans across the Atlantic accelerated . The English crown chartered the Royal African Company in 1672 , giving the company a monopoly over the transport of enslaved African people to the English colonies . Over the next four decades , the company transported around Africans from their homelands . By 1700 , the tiny English sugar island of Barbados had a population of thousand enslaved people , and the English had encoded the institution of chattel slavery into colonial law . This new system of African slavery came slowly to the English colonists , who did not have slavery at home and preferred to use servant labor . Nevertheless , by the end of the seventeenth century , the English everywhere in particularly in the Chesapeake Bay come to rely on enslaved Africans . While Africans had long practiced slavery among their own people , it had not been based on race . Africans enslaved other Africans as war captives , for crimes , and to settle debts they generally used enslaved people for domestic and agricultural work , not for growing cash crops on large plantations . Additionally , African slavery was often a temporary condition rather than a lifelong sentence , and , unlike New World slavery , it was typically not heritable ( passed from an enslaved mother to her children ) The growing slave trade with Europeans had a profound impact on the people of West Africa , giving prominence to local chieftains and merchants who traded enslaved people for European textiles , alcohol , guns , tobacco , and food . Africans also charged Europeans for the right to trade in enslaved people and imposed taxes on enslaved people purchases . Different African groups and kingdoms even staged raids on each other to meet the demand for enslaved people . Once sold to traders , all captured people sent to America endured the hellish Middle Passage , the transatlantic crossing , which took one to two months . By 1625 , more than Africans had been shipped to the New World , though many thousands perished during the voyage . An astonishing number , some four million , were transported to the Caribbean between 1501 and 1830 . When they reached their destination in America , Africans found themselves trapped in shockingly brutal slave societies . In the Chesapeake colonies , they faced a lifetime and processing tobacco . Everywhere , Africans resisted slavery , and running away was common . In Jamaica and elsewhere , escaped enslaved people created maroon communities , groups that resisted recapture and eked out a living from the land , rebuilding their communities as best they could . When possible , they adhered to traditional ways , following spiritual leaders such as Vodun priests . CHANGES TO NATIVE LIFE While the Americas remained under the control of native peoples in the decades of European settlement , increased as colonization spread and Europeans placed greater demands upon the native populations , including expecting them to convert to Christianity ( either Catholicism or Protestantism ) Throughout the seventeenth century , the native peoples and that retained control of the land waged war against the invading Europeans , achieving a degree of success in their effort to drive the newcomers from the continent . At the same time , European goods had begun to change Native life radically . In the , some of the earliest objects Europeans introduced to Native Americans were glass beads , copper kettles , and metal utensils . Native
78 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , people often adapted these items for their own use . For example , some cut up copper kettles and refashioned the metal for other uses , including jewelry that conferred status on the wearer , who was seen as connected to the new European source of raw materials . As European settlements grew throughout the , European goods Native communities . Soon Native people were using these items for the same purposes as the Europeans . For example , many Native inhabitants abandoned their clothing in favor of European textiles . Similarly , clay cookware gave way to metal cooking implements , and Native Americans found that European and steel made starting much easier ( Figure . FIGURE In this 1681 portrait , the leader wears a combination of European and Native American goods . Which elements of each culture are evident in this portrait ?
The abundance of European goods gave rise to new artistic objects . For example , iron made the creation of shell beads among the native people of the Eastern Woodlands much easier , and the result was an astonishing increase in the production of Wampum , shell beads used in ceremonies and as jewelry and currency . Native peoples had always placed goods in the graves of their departed , and this practice escalated with the arrival of European goods . Archaeologists have found enormous caches of European trade goods in the graves of Native Americans on the East Coast . Native weapons changed dramatically as well , creating an arms race among the peoples living in European colonization zones . Native Americans refashioned European brassware into arrow points and turned axes used for chopping wood into weapons . The most prized piece of European weaponry to obtain was a musket , or light , European gun . In order to trade with Europeans for these , Native peoples their harvesting of beaver , commercializing their traditional practice . The of European materials made warfare more lethal and changed traditional patterns of authority among tribes . Formerly weaker groups , if they had access to European metal and weapons , suddenly gained the upper hand against groups . The Algonquian , for instance , traded with the French for muskets and gained power against their enemies , the Iroquois . Eventually , native peoples also used their new weapons against the European colonizers who had provided them . CLICK AND EXPLORE Explore the complexity of relationships ( in the series of primary source documents on the National Humanities Center site . ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES The European presence in America spurred countless changes in the environment , setting into motion chains Access for free at .
The Impact of Colonization 79 of events that affected native animals as well as people . The popularity of hats in Europe , coupled with Native Americans desire for European weapons , led to the of beaver in the Northeast . Soon , beavers were extinct in New England , New York , and other areas . With their loss came the loss of beaver ponds , which had served as habitats for as well as water sources for deer , moose , and other animals . Furthermore , Europeans introduced pigs , which they allowed to forage in forests and other . Pigs consumed the foods on which deer and other indigenous species depended , resulting in scarcity of the game native peoples had traditionally hunted . European ideas about owning land as private property clashed with natives understanding of land use . Native peoples did not believe in private ownership of land instead , they viewed land as a resource to be held in common for the of the group . The European idea of right to common land use and close to the native understanding , but colonists did not practice usufruct widely in America . Colonizers established , fences , and other means of private property . Native peoples who moved seasonally to take advantage of natural resources now found areas off limits , claimed by colonizers because of their insistence on rights . The Introduction of Disease Perhaps European colonization single greatest impact on the North American environment was the introduction of disease . Microbes to which native inhabitants had no immunity led to death everywhere Europeans settled . Along the New England coast between 1616 and 1618 , epidemics claimed the lives of 75 percent of the native people . In the , half the Huron and Iroquois around the Great Lakes died of smallpox . As is often the case with disease , the very young and the very old were the most vulnerable and had the highest mortality rates . The loss of the older generation meant the loss of knowledge and tradition , while the death of children only compounded the trauma , creating devastating implications for future generations . Some native peoples perceived disease as a weapon used by hostile spiritual forces , and they went to war to exorcise the disease from their midst . These mourning wars in eastern North America were designed to gain captives who would either be adopted ( as a replacement for a deceased loved one ) or ritually tortured and executed to assuage the anger and grief caused by loss . The Cultivation of Plants European expansion in the Americas led to an unprecedented movement of plants across the Atlantic . A prime example is tobacco , which became a valuable export as the habit of smoking , previously unknown in Europe , took hold Figure 316 ) Another example is sugar Columbus brought sugarcane to the Caribbean on his second voyage in 1494 , and thereafter a wide variety of other herbs , seeds , and roots made the transatlantic voyage .
80 Creating New Social Orders Colonial Societies , FIGURE van , a Dutch artist , painted An Apothecary Smoking in an Interior in 1646 . The large European market for American tobacco strongly influenced the development of some of the American colonies . Just as pharmaceutical companies today scour the natural world for new drugs , Europeans traveled to America to discover new medicines . The task of cataloging the new plants found there helped give birth to the science of botany . Early botanists included the English naturalist Sir Hans Sloane , who traveled to Jamaica in 1687 and there recorded hundreds of new plants ( Figure . Sloane also helped popularize the drinking of chocolate , made from the cacao bean , in England . i A To , AND JAMAICA I ! TH Herb and , i Billy , iI , 852 of thole ISLANDS INTRODUCTION . I ICE , I , of the Thin i ib , which have not . Sir , Bar In Two Volumes Vol II . I ! 172 . FIGURE English naturalist Sir Hans Sloane traveled to Jamaica and other Caribbean islands to catalog the flora of the new world . Native Americans , who possessed a vast understanding of local New World plants and their properties , would have been a rich source of information for those European botanists seeking to and catalog potentially useful plants . Enslaved Africans , who had a tradition of the use of medicinal plants in their native land , adapted to their new surroundings by learning the use of New World plants through experimentation or from Access for free at .
The Impact of Colonization 81 the native inhabitants . Native peoples and Africans employed their knowledge effectively within their own communities . One notable example was the use of the peacock to induce abortions Native American and enslaved African women living in oppressive colonial regimes are said to have used this herb to prevent the birth of children into slavery . Europeans distrusted medical knowledge that came from African or native sources , however , and thus lost the of this source of information .
82 Key Terms Key Terms headright system a system in which parcels of land were granted to settlers who could pay their own way to Virginia indenture a labor contract that promised young men , and sometimes women , money and land after they worked for a set period of years Jesuits members of the Society of Jesus , an elite Catholic religious order founded in the to spread Catholicism and to combat the spread of Protestantism maroon communities groups of escaped enslaved people who resisted recapture and eked a living from the land Middle Passage the perilous , often deadly transatlantic crossing of ships carrying captured Africans from the African coast to the New World musket a light , European gun large tracts of land and governing rights granted to merchants by the Dutch West India Company in order to encourage colonization a Spanish colonial system requiring Native American towns to supply workers for the colonizers the native people of Florida , whom the Spanish displaced with the founding of Augustine , the Spanish settlement in North America Wampum shell beads used in ceremonies and as jewelry and currency Summary Spanish Exploration and Colonial Society In their outposts at Augustine and Santa Fe , the Spanish never found the fabled mountains ofgold they sought . They did many native people to convert to Catholicism , but their zeal nearly cost them the colony of Santa Fe , which they lost for twelve years after the Pueblo Revolt . In truth , the grand dreams of wealth , conversion , and a social order based on Spanish control never came to pass as Spain envisioned them . Colonial Rivalries Dutch and French Colonial Ambitions The French and Dutch established co in the northeastern part of North America the Dutch in day New York , and the French in Canada . Both colonies were primarily trading posts for furs . While they failed to attract many colonists from their respective home countries , these outposts nonetheless imperial rivalries in North America . Both the Dutch and the French relied on native peoples to harvest the pelts that proved in Europe . English Settlements in America The English came late to colonization of the Americas , establishing stable settlements in the after several unsuccessful attempts in the . After Roanoke Colony failed in 1587 , the English found more success with the founding in 1607 and Plymouth in 1620 . The two colonies were very different in origin . The Virginia Company of London founded Jamestown with the express purpose of making money for its investors , while Puritans founded to practice their own brand of Protestantism without interference . Both colonies battled circumstances , including poor relationships with neighboring Native American tribes . repeatedly in tie Chesapeake Bay tobacco colonies and in New England , where a massive uprising against the English in 1675 to Philip succeeded in driving the intruders back to the sea . The Impact of Colonization The development of the Atlantic slave trade forever changed the course of European settlement in the Access for free at .
Review Questions 83 Americas . Other transatlantic travelers , including diseases , goods , plants , animals , and even ideas like the concept of private land ownership , further life in America during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries . The exchange for European goods including copper kettles , knives , and guns played a role in changing the material cultures of native peoples . During the seventeenth century , native peoples grew increasingly dependent on European trade items . At the same time , many native inhabitants died of European diseases , while survivors adopted new ways of living with their new neighbors . Review Questions . Which of the following was a goal of the Spanish in their destruction of Fort Caroline ?
establishing a foothold from which to battle the claiming a safe place to house the New World treasures that would be shipped back to Spain reducing the threat of French privateers locating a site for the establishment of Santa Fe . Why did the Spanish build Castillo de San Marcos ?
to protect the local to defend against imperial challengers as a seat for visiting Spanish royalty to house visiting delegates from rival imperial powers . How did the Pueblo attempt to maintain their autonomy in the face of Spanish settlement ?
What was patroonship ?
a Dutch ship used for transporting beaver furs a Dutch system of patronage that encouraged the arts a Dutch system of granting tracts of land in New to encourage colonization a Dutch style of hat trimmed with beaver fur from New . Which religious the French settlement in Canada and tried to convert the natives to Christianity ?
Franciscans Calvinists Anglicans Jesuits . How did the French and Dutch colonists differ in their religious expectations ?
How did both compare to Spanish colonists ?
What was the most lucrative product of the Chesapeake colonies ?
corn tobacco gold and silver enslaved people . What was the primary cause of Bacon Rebellion ?
former indentured servants wanted more opportunities to expand their territory Enslaved Africans wanted better treatment Natives wanted the Jamestown settlers to pay a fair price for their land Jamestown politicians were jockeying for power 84 Critical Thinking Questions . The founders of the Plymouth colony were Puritans Catholics Anglicans Jesuits 10 . Which of the following is not true of the Puritan religion ?
A . It required close reading of scripture . Church membership required a conversion narrative . Literacy was crucial . Only men could participate . 11 . How did the Chesapeake colonists solve their labor problems ?
12 . What was the Middle Passage ?
the fabled sea route from Europe to the Far East the land route from Europe to Africa the transatlantic journey that enslaved Africans made to America the line between the northern and southern colonies 13 . Which of the following is not an item Europeans introduced to Native Americans ?
wampum glass beads copper kettles metal tools 14 . How did European muskets change life for native peoples in the Americas ?
15 . Compare and contrast European and Native American views on property . Critical Thinking Questions 16 . Compare and contrast life in the Spanish , French , Dutch , and English colonies , differentiating between the Chesapeake Bay and New England colonies . Who were the colonizers ?
What were their purposes in being there ?
How did they interact with their environments and the native inhabitants of the lands on which they settled ?
17 . Describe the attempts of the various European colonists to convert native peoples to their belief systems . How did these attempts compare to one another ?
What were the results of each effort ?
18 . How did chattel slavery differ from indentured servitude ?
How did the former system come to replace the latter ?
What were the results of this shift ?
19 . What impact did Europeans have on their New World peoples and their communities as well as land , plants , and animals ?
Conversely , what impact did the New World native inhabitants , land , plants , and animals have on Europeans ?
How did the interaction of European and Native American societies , together , shape a world that was truly new ?
Access for free at .