Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Extra Questions Science Chapter 8
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Science Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is Chandigarh unlikely to be affected by a cyclone? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Chandigarh is unlikely to be affected by a cyclone because it is not near to the sea or an ocean.
Question 2.
Discuss the major cause of winds.
Answer:
Wind currents are generated due to uneven heating on the earth. It may be between equator and pole and between land and water.
Question 3.
Name the ocean which is mainly responsible to bring rain bearing monsoon winds to Kerala coast in June every year. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
An Indian ocean is mainly responsible to bring rain bearing monsoon winds to Kerala coast in June every year.
Question 4.
Briefly describe the effect of heat on air pressure.
Answer:
The heat causes air to expand and occupies more space. It becomes lighter. That’s why, warm air is lighter than the cold air.
Question 5.
To expel hot air out of the kitchen, A has an exhaust fan fitted on the window of her kitchen and B has a similar exhaust fan fitted on the wall near the ceiling of her kitchen. Which of the exhaust fan will expel the hot air more effectively? Explain why. [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS]
Answer:
B’s exhaust fan will expel the hot air more effectively because hot air rises up and her fan is at greater height than A’s.
Question 6.
Enlist the other names of cyclone.
Answer:
Hurricane and typhoon are the other names of cyclone.
Question 7.
Suggest some precautions to be taken to prevent the roof of a tin sheet from flying away during a fierce wind storm. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Some precautions are
- Put heavy stones on it.
- Screw it tight.
Question 8.
Name the instrument which is used to measure the speed of wind.
Answer:
Anemometer is used to measure the speed of wind.
Question 9.
A flag mounted on a flag post near the sea coast flutters in the direction of sea. At what time of the day does this happen — at mid-night or in the afternoon? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
In the mid-night, the wind blows from land to sea. So, in the mid-night flag mounted on a flag post near the sea coast flutters in the direction of sea.
Question 10.
Figure shows a diagrammatic representation of trees in the afternoon along a sea coast. State on which side is the sea, A or B? Give reasons for your choice. [NCERT Exemplar]
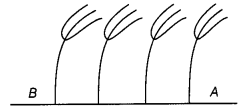
Answer:
In the afternoon, the wind blows from sea to land.
As pressure on the land is less than the pressure above sea, so the sea is on B side.
Question 11.
Name the factor responsible for the increase of speed of wind or cyclones.
Answer:
Factors like wind speed, wind direction, temperature and humidity contribute to the development of cyclones.
Question 12.
Name some cyclones that occurred in the past.
Answer:
Hugo, Katrina, Rita, Hud-Hud and Phailin are the various types of cyclones that occurred in the past.
Question 13.
Can you say why smoke always rises up?
Answer:
As we know that smoke is the combination of hot airs and hot air becomes light weight with respect to cold air. Thus, it always rises up.
Question 14.
In the wind flow pattern, it can be found that the wind shown is not in the exact North-South direction. Explain why.
Answer:
It is because the winds would have blown in the North-South direction either from North to South or from South to North. A change in direction is however caused by the rotation of the earth.
Question 15.
Monsoon winds are helpful. Do you agree?
Answer:
The monsoon winds carry water and it rains. Clouds bring rain and give us happiness. Farmers in our country depend mainly on rains for their harvests. So, monsoon winds are helpful.
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Science Extra Questions Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Paheli kept an empty bottle made of plastic inside a refrigerator. After few hours, when she opened the refrigerator, she found the bottle had collapsed. Explain the possible reason. [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS]
Answer:
On cooling the air, contraction of air takes place. The air inside the bottle contracts due to low temperature. Hence, the bottle collapses due to the outside pressure.
Question 2.
Mention an example when the cyclone hit a part of India and how much destruction was caused due to it.
Answer:
Orissa (a part of India) was hit by cyclone in 18th October 1999. The wind speed was 200 km/h and smashed 45000 houses making 700000 people homeless. Another cyclone hit the Orissa again an 29th October with the wind speed of 260 km/h. Thousands of people lost their lives and property worth crores of rupees was destroyed.
Question 3.
When strong/high speed wind blows, an umbrella held upright at times gets upturned. Explain the reason. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
High speed wind passing over the umbrella creates low pressure above the umbrella with respect to below of it. Therefore, the umbrella upturns.
Question 4.
Give three precautions that should be taken to protect oneself from the thunderstorm. [Value Based Question]
Answer:
The following three precautions must be taken to protect oneself from the lightning of thunderstorm
- Do not take shelter under an isolated tree.
- Do not lie on the ground
- Do not take shelter under an umbrella with a metallic end.
Question 5.
Explain thunderstorm and how are they produced.
Answer:
The swift movement of the falling water along with the rising warm air producing sound, lightning, heavy rain and strong wind is called thunderstorm.
Question 6.
Name some effective safety measures against cyclone?
Answer:
On the part of government
- Cyclone forecast and warning system must be installed.
- Information about cyclone should be given to the people in time through rapid communication system.
- Construction of cyclone-shelter in cyclone-prone areas.
- Administrative arrangement should be taken to move people faster to safer places.
On the part of the people
- People should follow the essential guidelines provided by the agencies through TV radio, phones, etc.
- Proper arrangement should be made to shift the essential household goods, domestic animals, etc. to the safer places.
- Avoid driving on road which are under water because flood might have damaged the road.
- Phone numbers of all the emergency services like police, fire brigade, hospitals, etc. should be kept ready.
These are produced by the dark clouds which form at fairly low altitude in the atmosphere.
Question 7.
Tornado is different from a cyclone. Briefly explain Tornado. What destructions does it cause?
Answer:
These are formed over sea and are called water spouts. Tornado develops from thunderstorm and are formed mostly on the land. These are violent and can reach the speeds of more than 500 km/h destroying everything in their path. These are not very common in India but occurs in Canada and USA.
Most of the tornadoes are weak. When the warm air from the earth’s surface rises up, it whirls around it and causes very high speed winds. These are much smaller than cyclones, i.e. from a few metre to a few hundred metre but the wind speed can rise as high as 500 km/h. The funnel of tornado sucks up everything at its base like dust, debris, cars, trees and even houses.
Question 8.
The advanced technologies issue the alerts and warnings of unexpected storm. Comment.
Answer:
The technologies that include satellites and radars issue the information of expected storm in advance in the form of cyclone warnings. It is issued in two stages, i.e. a cyclone alert or cyclone watch is issued 48 h in advance of any expected storm and cyclone warning is issued 24 h in advance. The message is broadcasted every hour or half hour when a cyclone is nearest the coast.
Question 9.
Monsoon brings rain. Explain the formation of monsoon.
Answer:
During summer, when the land gets warmed and temperature of land becomes higher than that of water in ocean. The air above the land gets heated and rises. Therefore, the cold wind flows from the ocean towards the land. These are monsoon winds which bring water and cause rain.
Question 10.
Due to uneven heating of land and ocean water what happens in the following season?
(a) In winter season
(b) In summer season [HOTS]
Answer:
Due to uneven heating of land and ocean water
(a) In winter season The uneven heating of land and water generates winds from the North-West colder land which carry little water. It brings small amount of rain in winter season.
(b) In summer season The uneven heating of land and ocean water generates wind from the South-West direction. These winds carry lot of water from the Indian ocean.
Question 11.
Rohan was very happy that there was his birthday. He was decorating the room by blowing balloons. He was wondered that most of his balloons burstd. He rushed to his father and asked the reason. His father smiled and explained.
(a) Can you explain the region that why his balloons get burst?
(b) What can be conclude from the condition mentioned?
(c) What are the values shown by Rohan? [Value Based Question]
Answer:
(a) When Rohan blows air into the balloon, the balloon gets inflated due to the pressure exerted by air. But, Rohan observed that most of his balloons burstd. The reason behind it was, he overfilled the air into the balloon. The warm air gets expanded inside the balloon and exerted more and due to the more pressure on the walls of the balloon, balloons burstd.
(b) From the condition mentioned above, it can be concluded that air expands on heating.
(c) Curiosity to learn and scientific attitude.
Question 12.
How are the pressure difference created in nature?
Answer:
Pressure difference is created in the nature by the heat of the sun. When it falls on the earth surface, the surface of the earth gets heated and air above it also gets warm and becomes light weight and moves upward. Thus, the pressure difference is created.
Question 13.
Describe the following terms briefly.
(a) Trade winds
(b) Wester lies
(c) Polar winds
Answer:
(a) The permanent wind that blows towards the equator from North to South are called trade winds.
(b) The wind blowing towards 60° N and 60° S latitudes are called wester lies.
(c) The set of wind blowing from the cold polar regions towards 60° N and 60° S latitudes are called polar winds.
Question 14.
A flat in Mumbai with a balcony facing the sea has some clothes hung on a clothes line in the balcony. Towards which direction, the clothes will be blown in the afternoon? Explain it. [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS]
Answer:
As during the afternoon, the land becomes hot which ultimately creates hot air above it and we know that hot air rises up and there is low pressure created. Thus, winds from sea start blowing towards the land and the clothes will be blown towards the house because sea breeze blowing towards the land.
Question 15.
Briefly explain what are cyclones and how are they formed.
Answer:
High speed winds and air pressure difference can cause cyclones.They are formed when water vapour changes back to liquid by the release of heat. This heat warms air around and it rises to move up and more air rushes to the vacant place. Thus, a cycle is formed which have low pressure and very high speed of air.
Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Science Extra Questions Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
The picture in figure shows tree line along the sea coast on an tops are permanently bent in one direction. Are the trees bendisland near the equator. As shown, the tree towards the sea or away from it? Explain. [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer:
In the given figure, the tree line along the sea coast on an island near the equator shows that tree tops are permanently bent in one direction. The reason behind this movement of tree is that during the day time the wind blows from sea to land because land gets warmer more quickly than sea.
This makes the air of land, warm and lighter which is raised up in the sky. Therefore, the top of the bent trees shows the moving direction of wind from sea to land.
Question 2.
Describe an activity to demonstrate that warm air is lighter than cool air. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Take two paper bags of same size and hang them in the inverted position at the two ends of metal or wooden stick. Now, tie a piece of strong thread in the middle of the stick. Now, hold the stick by thread. The wooden stick with two paper bags tied to its two ends will hang like a common beam balance. Initially, the wooden stick is perfectly horizontal showing that the two paper bags contain an equal mass of the air.

Caution Perform the experiment with the help of a teacher.
Now, put the burning candle below the open mouth of one side paper bag. We will see that after sometime, the left side of wooden stick goes up showing that it has become lighter than the right side and the balance of the cup is disturbed. The reason for this is that when a burning candle is placed below the one side paper bag, the air above the candle flame gets heated. The hot air being lighter rises up and fills the paper bag above it. Therefore, this side of wooden stick becomes lighter and moves up.
This experiment shows that the air becomes lighter and moves up.
This fact of air is utilised in launching hot air balloons. In nature, there are several situations where warm air rises at a place. The air pressure at that place is lowered. The cold air from the surrounding areas rushes in to fill its place.
Question 3.
State the importance of air pressure. Give reasons for air pressure.
Answer:
The importance of air pressure can be discussed as follows:
- It creates wind The difference in atmospheric pressure gives rise to the wind on the earth.
- It influences weather Air movement, i.e. downward or upward movement of air, caused due to differences in pressure creates cloudy and clear sky, brings rain or fine weather.
- Weather forecasting The changes in air pressure give important clues for weather forecasting. The air pressure is measured by an instrument called barometer.
Question 4.
A cyclone is generated from a thunderstorm. How a thunderstorm becomes a cyclone? Explain.
Answer:
When air moves gently (low speed), it is called a breeze while when it moves violently (high speed), it is called a storm. When the pressure of air drops, it indicates the possibility of a storm.
The swift movement of the falling water along with the rising warm air producing sound, lightning, heavy rain and strong wind is called thunderstorm. It develops in hot and humid tropical areas like India and is accompanied by heavy rains or hail. Thunderstorms are produced by the dark clouds which form at fairly low altitude in the atmosphere. In the tropical area, the air gets warmed up and makes it to rise, whereas humidity provides the water vapour for the formation of cloud.
Therefore, it can be said that to occur a thunderstorm, it requires moisture, rapidly rising warm air and sea breeze or mountains.
Question 5.
Advanced technology has helped people to save them from natural calamities like thunder storm and cyclone. Explain how.
Answer:
During the early part of the last century, the people residing in coastal regions have less than a day for the preparations or to evacuate their homes from an overcoming cyclone. But, the today’s situation is very different. Today we are much protected. We have satellites and radars which can issue the cyclone watch or cyclone alert before 48 hrs (in advance) of any expected storm and a cyclone warning is issued 24 hrs in advance.
Therefore, the coastal residents have sufficient time to prepare and evacuate their homes. The message related to cyclone is broadcasted over the ratio every hour or half hour when a cyclone is nearer the coast.
In this way, the advanced technology has helped us in giving better protection from cyclones. Several national and international organisations cooperate to monitor the cyclone related disasters.
Question 6.
The phenomenon of cloud formation, rain, storm and cyclone are inter linked. Do you agree? If yes, give a flow chart that explain this relation. [HOTS]
Answer:
Yes, the following flow chart explains the phenomenon leading to the formation of cloud, rain, stornrand cyclone.

Winds, Storms and Cyclones Class 7 Science Extra Questions Miscellaneous Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A fire alarm usually detects smoke in case of fire. Where should such an alarm be placed in a room? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Near the door
(b) On the floor
(c) On any wall
(d) On the ceiling
Answer:
(d) On the ceiling
Question 2.
Following are precautions, one must take in case a storm is accompanied by lightning. [NCERT Exemplar]
(i) Do not take shelter under tree.
(ii) Do not take shelter under an umbrella with a metallic end.
(iii) Do not take shelter in open garages, storage sheds, etc.
(iv) Do not take shelter in a bus in the open.
Which one of these is not correct?
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
Answer:
(d) (iv)
Question 3.
Orissa was hit by a cyclone with wind speed of 200 km/h on which date
(a) 18 Oct, 1998
(b) 18 Oct, 1999
(c) 18 Oct, 2001
(d) 18 Oct, 2000
Answer:
(b) 18 Oct, 1999
Question 4.
Four schematic diagrams are shown below to depict the direction of sea breez. Which of them gives the correct direction? [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer:
(c) In summer, near the equator the land becomes warm and the temperature of the air increases. This causes the air from the ocean to blow towards the land. These are known as summer monsoon winds.
Question 5.
The warning of cyclone can be issued
(a) 48 h in advance
(b) 12 h in advance
(c) 6 h in advance
(d) 24 h in advance
Answer:
(d) 24 h in advance
Question 6.
Wind is caused due to
(a) uneven heating of equator and poles
(b) difference in humidity
(c) even heating of land and water
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) uneven heating of equator and poles
Question 7.
Figure shows a child blowing air with a straw near the opening of another straw which has its other end in a soft drink bottle. It was observed that the level of the soft drink in the straw rises up as soon as air is blown over its open end. Which one of the following best explains the reason for rise in level of the drink? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Blowing of air decreases pressure over the opening of the straw
(b) The straw of the soft drink bottle collapses when air is blown over its open end
(c) Blowing of air warms up the air inside the straw
(d) Blowing of air increases the pressure on the surface of soft drink in the bottle
Answer:
(a) Blowing of air decreases pressure over the opening of the straw
Question 8.
Formation of thunderstorm requires
(a) moisture
(b) rapidly rising warm air
(c) sea breeze
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 9.
Which of the following place is most likely to be affected by a cyclone? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Mumbai
(b) Puri
(c) Goa
(d) Porbandar
Answer:
(b) Puri
Question 10.
Increased wind speed is accompanied with
(a) increased air pressure
(b) affected air pressure
(c) reduced air pressure
(d) lower humidity
Answer:
(c) reduced air pressure
Question 11.
A curtain is hanging at the entrance of a room. A long corridor runs at right angles to the door, that is parallel to the curtain. If a strong wind blows along the corridor, the curtain will [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) get pushed inside the room
(b) get pushed outside the room
(c) get collected towards one end/ swirled
(d) remain unaffected
Answer:
(b) get pushed outside the room
Question 12.
The calm centre of cyclone is called
(a) head
(b) eye
(c) water spout
(d) storm
Answer:
(b) eye
Question 13.
Which precaution among the following is not a correct precaution to protect from lightning during a thunderstorm?
(a) Do not sit near a window
(b) Do not lie on the ground
(c) Do not sit in a car
(d) Do not stand under a tall tree
Answer:
(c) Do not sit in a car
Question 14.
Thunderstorm develops very frequently in areas having
(a) polar climate
(b) tropical climate
(c) desert climate
(d) temperate climate
Answer:
(b) tropical climate
Question 15.
A cyclone is
(a) winds from the oceans carrying water
(b) very low pressure system with very high speed wind revolving around it.
(c) dark funnel shaped cloud that reaches from the sky to the ground
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) very low pressure system with very high speed wind revolving around it.
Question 16.
The word monsoon is derived from the word
(a) mausam
(b) monsoon
(c) museum
(d) storm
Answer:
(a) mausam
Fill in the Blanks
1. It is ……………….. row boat in the moving direction of wind.
2. The bicycle tube ……………….. when it is overfilled with ……………….. .
3. Air ……………….. on heating and ……………….. on cooling.
4. The ……………….. the difference in ……………….. the ……………….. the air moves.
5. A change in the direction of wind is caused due to ……………….. of earth.
6. The wind from the ocean carry ……………….. and bring rain which is a part of ……………….. .
7. Uneven heating of land generates monsoon winds from ……………….. direction in ……………….. .
8. factors like ……………….., ……………….., ……………….. and ……………….. contribute to the development of cyclones.
9. A violent Tornado can travel at the speeds of about ……………….. .
10. A whole ……………….. of India in vulnerable to
11. Air around us exerts ……………….. . [NCERT Exemplar]
12. The moving air is called ……………….. . [NCERT Exemplar]
13. The main cause of wind movement is uneven ……………….. . [NCERT Exemplar]
14. High speed wind can cause cyclone in regions of ……………….. pressure. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answers:
1. easier
2. bursts, air
3. expands, contracts
4. greater, pressure, faster
5. rotation
6. water, water cycle
7. South-West, summer
8. Wind speed, wind direction, temperature, humidity
9. 300 km/h
11. pressure
12. wind
13. heating
14. low
True/False
1. The layer of air surrounding the earth is called atmosphere.
2. Air gets contracted on the heating.
3. Cyclone develops in the polar region.
4. Hud-Hud and Katrina are Typhoon.
5. Tornado is frequently observed in India.
6. Cyclone appears a dark funnel shaped structure.
7. Falling water droplets and rising air move vigorously to produce thunderstorm.
8. Monsoon winds do not carry water with them.
9. The wind speed during cyclone is 150-250 km/h.
10. Uneven heating of land and water in winter (North-West and colder land) brings little rain in winter.
11. If wind flows from land to the ocean, then it is day time. [NCERT Exemplar]
12. A very high pressure system with very high speed wind surroundings, it forms a cyclone.
13 . The coast line of India is not vulnerable to cyclones. [NCERT Exemplar]
14 . Warm air is lighter than cool air. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answers:
1. True
2. False, air expands on heating.
3. False, cyclone develops in tropical region.
4. True
5. False, tornado does not occur in India.
6. False, tornado is dark funnel shaped structure.
7. True
8. False, monsoon wind carry water with them
9. True
10. True
11. False, if wind flows from land to the ocean, then it is night time.
12. False, a very low pressure system with very high speed wind revolving around it forms a cyclone.
13. False, the whole coastline of India is vulnerable to cyclone.
14. True
Match the Columns
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II. There can be more than one.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) On heating air | (i) descends |
| (b) On cooling air | (ii) expands |
| (iii) contracts | |
| (iv) rises |
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Tornado | (i) Occurs in Western Pacific region |
| (b) Anemometer | (ii) Reduces soil fertility |
| (c) Cyclone | (iii) Dark funnel shaped cloud |
| (d) Meteorologist | (iv) Measures the speed of wind |
| (e) Typhoon | (v) Study weather |
Question 3.
Match the Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) North-West wind | (i) Before 48 h |
| (b) Uneven heating of earth | (ii) Found the direction of wind |
| (c) Wind vane | (iii) Wind carrying water |
| (d) Monsoon | (iv) Bring little rainfall |
| (e) Cyclone watch | (v) Generates wind |
Answers:
1.
(a)-(ii) and (iv)
(b)-(i) and (iii)
2.
(a)-(iii)
(b)-(iv)
(c)-(ii)
(d)-(v)
(e)-(i)
3.
(a)-(iv)
(b)-(v)
(c)-(ii)
(d)-(iii)
(e)-(i)