Types Of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve the breaking of bonds present in reactant atoms and forming new bonds in products. Some of the important types of chemical reactions are described next:
Combination Reaction (A + B → AB)
Those reactions in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product are known as combination reactions.
In a combination reaction:
- Two or more elements can combine to form a compound.
- Two or more compounds can combine to form a new compound.
- An element and a compound can combine to form a new compound.
Examples of Combination Reactions
| Example of Combination Reaction | Chemical Equation |
| 1. Burning of hydrogen in air to form water | 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O |
| 2. Burning of carbon (coal) in air to form carbon dioxide | C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) |
| 3. Reaction of hydrogen with chlorine to form hydrogen chloride | H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g) |
| 4. Burning of sodium metal in chlorine to form sodium chloride. | 2Na(s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCl(s) |
| 5. Heating of iron with sulphur to form iron sulphide | Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS(s) |
Example 1.
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing.
(A) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
Answer:
The substance ‘X’ which is used in whitewashing is quick lime or Calcium Oxide. It’s chemical formula is CaO.
(B) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in above with water.
Answer:
Calcium oxide reacts with water to form slaked lime or calcium hydroxide and a large amount of heat is released in this process.
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions:
Chemical reactions are accompanied with a change in temperature of the reaction mixture. There can be either a rise in temperature or a fall in temperature.
Exothermic Reactions:
Reactant(s) → Produces + Heat
Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions. Some examples of exothermic reactions are:
- Burning of carbon in air to form carbon dioxide:
C(S) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat - Burning of natural gas:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + Heat - Reaction between calcium oxide with water to form slaked lime:
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Important
The reaction between calcium oxide with water to form slaked lime is used for whitewashing walls. The reaction taking place is:
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(S) + H2O(l)
- Respiration: It is the release of energy by the oxidation of glucose in the cells of our body.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy - Decomposition of vegetable matter into compost.
- All combustion reactions.
Endothermic Reactions: (Reactant(s) + Heat → Products(s))
Those reactions in which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions. Some examples of endothermic reactions are:
- Formation of nitrogen monoxide by heating nitrogen and oxygen to a temperature of about 3000°C.
N2(g) + O2(g) + Heat → 2NO(g) - All decomposition reactions are endothermic reactions since the decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat, light or electricity for breaking down the reactants.
For example, when calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide:
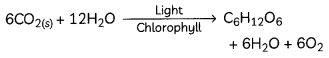
CaCO3(S) + Heat → CaO(s) + CO2(g) - Photosynthesis is an endothermic process as sunlight is absorbed by green plants during photosynthesis resulting in the formation of glucose, water and oxygen.

Decomposition Reaction (AB → A + B):
Those reactions in which a compound splits up into two or simpler substances are known as decomposition reactions.
Depending upon the form of energy required for the reaction, there are three types of decomposition reactions:
Thermal Decomposition Reactions:
When a decomposition reaction is carried out by heating, it is called thermal decomposition.
For example, decomposition of calcium carbonate to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide on heating is an important decomposition reaction used in various industries.

Example 2.
Case Based:
Two boiting tubes were taken, about 2 grams of a green coloured metal salt A’ was taken in the first tube and 2 grams of a white coloured metal salt ‘B’ was taken in the second tube. Both the tubes were heated by holding them with a pair of tongs. Smell of burning sulphur was observed in first test tube whereas brown gas was emitted in the second test tube.
(A) The salts ‘A’ and ‘B’ are:
(a) Ferrous nitrate and lead sulphate respectively
(b) Ferric oxide and Lead nitrate respectively
(c) Ferrous sulphate and lead nitrate respectively
(d) Ferric oxide and lead sulphate respectively
Answer:
(c) Ferrous sulphate and lead nitrate respectively
Explanation: The green coloured metal salt ‘A’ in the first test tube is ferrous sulphate as it is green in colour and when heated decomposes to form ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide, which smell of burning sulphur.
Equation for the reaction talcing place is:
![]()
The white coloured metal salt ‘B’ in the second test tube is lead nitrate as brown fumes of a gas is emitted when it is heated, which are of nitrogen dioxide.
Equation for the reaction talcing place is:
2Pb(NO3)2(S) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
(B) During the experiment of heating of ferrous sulphate, four students recorded their observation as
(I) Green colour changes to brown-black colour.
(II) Brownish-yellow gas is evolved.
(III) Blue colour changes to green colour.
(IV) Smell of burning sulphur is observed. Which of the above observations are incorrect?
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (IV)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (I) and (IV)
Explanation: Ferrous sulphate crystals are green in colour. When they are heated, they lose their molecules of water of crystallization and form ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide gases. The green colour of ferrous sulphate crystal changes to brown-black and smell of burning sulphur is observed.
(C) What are the products formed when ferrous sulphate is heated?
(a) SO3, SO2, FeO
(b) SO3, Fe2, O3
(c) SO3, SO2, FeO3
(d) SO2, FeO
Answer:
(c) SO3, SO2, FeO3
Explanation: When ferrous sulphate crystals are heated, it undergoes decomposition reaction to form ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
Equation for the reaction taking place is:
![]()
(D) On heating lead nitrate, two gases are evolved, one is colourless and the other is brown in colour. Which gases are they?
(a) Oxygen and nitrogen dioxide
(b) Hydrogen and lead oxide
(c) Hydrogen and oxygen
(d) Oxygen and nitrous oxide
Answer:
(a) Oxygen and nitrogen dioxide Explanation: When lead nitrate is heated, it undergoes decomposition reaction to form lead oxide, along with the evolution of gases nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
(E) In which of the following category will you put the reaction of heating of ferrous sulphate and lead nitrate?
(I) Decomposition Reaction
(II) Combination Reaction
(III) Endothermic Reaction
(IV) Exothermic Reaction
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) Both (I) and (III)
Explanation: As both ferrous sulphate and lead nitrate absorb heat and undergo decomposition, the reactions are endothermic reactions and are also known as thermal decomposition reactions.
The decomposition reactions that are carried out by using electricity are known as electrolytic decomposition reactions.
For example, the electrolysis of water to form hydrogen and oxygen gas.
![]()
Example 3.
Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
Answer:
When water undergoes electrolysis, it decomposes to form hydrogen gas and oxygen gas as per equation below:
2H2O → 2H2 + O2
As the electrolysis of water produces 2 volumes of hydrogen gas and 1 volume of oxygen gas, it can therefore be concluded that the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen elements in water is 2 :1 by volume.
Decomposition Reaction by Light Energy:
The decomposition reactions that occur in the presence of sunlight are known as photodecomposition reactions or photolysis.
For example, silver chloride (white) decomposes into silver (grey) and chlorine in the presence of sunlight.
![]()
A brief summary of some decomposition reactions is given below:
| Examples of Decomposition Reaction | Chemical Equation |
| 1. Heating of potassium chlorate in presence of manganese dioxide (catalyst) to give potassium chloride and oxygen | 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(S) + 3O2(g) |
| 2.Decomposition of molten sodium chloride on passing electric current to form sodium metal and chlorine gas | 2NaCl(l) → 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) |
| 3. Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of light to water (H2O) and oxygen gas (O2) | 2H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2 |
Example 4.
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for decomposition reactions.
Answer:
In a decomposition reaction, a single substance (reactant) splits into two or more products whereas in a combination reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a single product. Thus, decomposition reaction is the opposite of combination reaction.
Consider the reactions:
- ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
- 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Reaction (1) is a decomposition reaction as a single reactant (ZnCO3) splits into two products ZnO and CO2.
Reaction (2) is just the opposite of reaction (1) as two reactants H2 and O2 combine to form a single product (H2O).
Displacement Reaction (A + BC → AC + B):
Those reactions in which one element takes the place of another element in a compound, are known as displacement reactions. In general, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.

In this reaction, iron has displaced or removed another element, copper, from copper sulphate solution. This reaction is known as the displacement reaction.
The reaction between most metals and acids is also a displacement reaction as the metal displaces hydrogen from the acid.
For example. Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2
The hydrogen gas is collected by the downward displacement of water as it is lighter than water. Moreover, it is also insoluble in water.
| Examples of Displacement Reaction | Chemical Equation |
| 1. When a strip of lead metal is placed in a solution of copper chLoride, the green colour of copper chloride solution fades due to the formation of a colourless solution of lead chloride. Lead is able to displace copper from copper chloride solution because lead is more reactive than copper. | CuCl2(aq) + Pb(s) → PbCl2(aq) + Cu(s) |
| 2. When iron (III) oxide is heated with aluminium powder, then aluminium oxide and iron metal are formed as a more reactive metal aluminium displaces a less reactive metal iron from its oxide | Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → Al2O3(s) + 2Fe(l) |
Example 5.
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer:
When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution as iron is more reactive than copper. Therefore, the colour of the copper sulphate solution changes from blue to green. The reaction taking place is:
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Example 6.
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings? Tick the cor¬rect answer.
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) iron salt and water are produced.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced
Explanation: As iron is more reactive than hydrogen, it displaces chlorine from dil hydrochloric acid and forms hydrogen gas and a salt, iron chloride.
The equation for the reaction taking place is:
2HCl(aq) + Fe(s) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Double Displacement Reaction (AB + CD → AD + CB)
Those reactions in which there is an exchange of ions between two compounds to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions. For example, when silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution, a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed along with sodium nitrate solution.
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
Precipitation Reaction:
Any reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction.
For example, when ammonium hydroxide solution is added to aluminium chloride solution, a white precipitate of aluminium hydroxide: formed along with ammonium chloride solution.
AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
Neutralization Reactions:
The reactions in which acids or acidic oxides (oxides of non-metals) react with bases or basic oxides (oxides of metals) to form salt and water are called neutralization reactions. For example,
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
| Example of Double Displacement Reaction |
Chemical Equation |
| 1. Lead (II) nitrate reacts with sodium chloride to produce sodium nitrate and a white precipitate of lead (II) chloride | Pb(N03)2(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) → 2NaN03(aq) + PbCl2(s) |
| 2. Aluminium sulphate reacts with calcium hydroxide solution to produce a white precipitate of aluminium hydroxide and calcium sulphate solution. | Al2(S04)3(aq) + 3Ca(OH)2(aq) → 2Al(OH)3(s) +3CaSO4(aq) |
Example 7.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(A) Potassium bromide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) → Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide(s)
Answer:
2KBr(aq) + Bal2(oq) → 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(s)
(It is a double Displacement reaction as there is an exchange of K+ and Ba2+ ions between the reactants)
(B) Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide(s) + Carbon dioxide(g)
Answer:
ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
(It is a decomposition reaction as a single reactant splits to form two products)
(C) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) → Hydrogen chloride(g)
Answer:
H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
(It is a combination reaction as two reactants combine to form a single product)
(D) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Answer:
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(oq) + H2(g)
(It is a displacement reaction as Mg displaces hydrogen from HCl as it is more reactive than H)
Example 8.
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write relevant equations for the above.
Answer:
In a displacement reaction a more reactive substance displaces a less reactive substance from its compound or salt solution whereas in a double displacement reaction exchange of ions takes place between the two reactant compounds. In a displacement reaction, only a single displacement takes place whereas in a double displacement reaction, two displacements take place between the molecules.
For example,
In the reaction,
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Mg displaces hydrogen from HCl as Mg is more reactive than H. It is therefore an example of Displacement reaction In the reaction,
BaCl2(aq) + K2SO4(oq) → 2BaSO4(s) + 2KCl(aq)
Both K and Ba displace each other from their compounds by exchanging ions. It is therefore an example of a double displacement reaction.
Oxidation and Reduction:
Those reactions in which addition of oxygen to a substance or removal of hydrogen from a substance takes place or the loss of electron from an element, are called oxidation reactions.
Those reactions in which addition of hydrogen to a substance or removal of oxygen from a substance takes place or the gain of electron in an element are called reduction reactions.
For example, in the reaction
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Hydrochloric acid is oxidized to chlorine (as hydrogen is removed from HCl) and Manganese dioxide is reduced to manganese dichloride (as oxygen is removed from MnO2).
HCl is the reducing agent and MnO2 is the oxidizing agent.

Oxidising Agent
The substance which provides oxygen for oxidation or the substance which removes hydrogen.
Reducing Agent
The substance which gives hydrogen for reduction or the substance which removes oxygen.
Important
- The substance which gets oxidised is the reducing agent.
- The substance which gets reduced is the oxidising agent.
In other words, one reactant gets oxidised white the other gets reduced during a reaction. Such reactions are coiled oxidation-reduction reactions or Redax reactions.

Example 9. Identify the substances that are oxidized and that are reduced in the following equation.
(A) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
(B) CuO(S) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
Answer:
In the equation 4Na(S) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
Na is oxidized to Na2O as there is an addition of oxygen and O2 gets reduced.
(B) In the equation,
CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(S) + H2O(l)
CuO gets reduced to Cu by losing oxygen and H2 gets oxidized to H2O by gaining oxygen.
Example 10.
Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s) + C(S) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(I) Lead is getting reduced
(II) Carbon Dioxide is getting oxidised
(III) Carbon is getting oxidised
(IV) Lead oxide is getting reduced
(a) (I) and (II)
(d) (I) and (III)
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
(e) all
Answer:
(a) (I) and (II)
Explanation: In the given reaction, PbO loses oxygen to form Pb. Therefore, PbO (lead oxide) is reduced.
Moreover, C is oxidized to CO2 by the addition of oxygen. Therefore, (III) and (IV) are correct and (I) and (II) are incorrect.