Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Extra Questions Science Chapter 15
Extra Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the two natural calamities?
Answer:
- Lightning and
- Earthquake.
Question 2.
Name other natural calamities except lightning and earthquake.
Answer:
Winds, storms and cyclones.
Question 3.
Name the two types of charges.
Answer:
- Positive; and
- Negative.
Question 4.
Mention the interactions of two types of charges.
Answer:
Like charges repel each other while unlike charges attract each other.
Question 5.
Name the device used to protect buildings from lightning.
Answer:
Lightning conductor.
Question 6.
In which direction does the shock waves produced by an earthquake travel?
Answer:
Both on the surface and inside the earth.
Question 7.
What happens when two clouds with unlike charges approach each other?
Answer:
Lightning strikes
Question 8.
Who discovered the static electricity or lightning in clouds and when?
Answer:
Benjamin Franklin in 1752.
Question 9.
What actually causes lightning?
Answer:
Lightning is caused by the accumulation of charges in the clouds.
Question 10.
What happens when amber is rubbed with fur?
Answer:
It develops the capacity to attract light objects.
Question 11.
What is static electricity?
Answer:
The electrical charge reproduced by rubbing two objects is called static electricity.
Question 12.
What happens when a glass rod and silk cloth are rubbed with each other?
Answer:
The glass rod gets positively charged and silk cloth negatively charged.
Question 13.
What is lightning?
Answer:
Lightning is&an electric spark on huge scale.
Question 14.
What are weak zones called?
Answer:
Seismic or fault zones.
Question 15.
How are most earthquakes caused?
Answer:
Most earthquakes are caused by the movement of earth’s plates.
Question 16.
What is a plate?
Answer:
Each fragment of the outermost layer of the earth is called plate.
Question 17.
What is the uppermost layer of the earth called?
Answer:
Crust
Question 18.
How is an earthquake caused?
Answer:
It is caused by a disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
Question 19.
What are seismic waves?
Answer:
Waves produced on the Earth’s surface because of tremors.
Question 20.
When and where a major tsunami took place in India?
Answer:
It occurred in the Indian ocean on 26th December 2004.
Question 21.
What are the natural calamities caused by earthquakes?
Answer:
Earthquakes can cause floods, landslides and tsunamis.
Question 22.
Which kind of material is used to transfer charges from one body to another?
Answer:
Metal conductor
Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is lightning? What causes lightning?
Answer:
Lightning is also an electric spark, but on a huge scale. It is caused by the accumulation of charges in the clouds.
Question 2.
What is an electric charge? What are charged objects?
Answer:
When a plastic refill is rubbed with polythene it acquires a small electric charge. Similarly when a plastic comb is rubbed with dry hair, it acquires a small charge. These objects are called charged objects.
Question 3.
What is static charge? How does it differ from electric current?
Answer:
The electric charges generated by rubbing are called static charges. The static charges do not move while charges move in electric current.
Question 4.
What do you mean by electric discharge? How does it occurs?
Answer:
When the negative and positive charges meet, streaks of bright light and sound are produced. This process is called electrical discharge. For example, electric discharge occurring between two or more clouds or between clouds and earth.
Question 5.
What is earthing? What is the application of earthing?
Answer:
The process of transfer of charges from a charged object to the earth is called earthing. It is provided in buildings to protect from electrical shocks due to any leakage of electrical current.
Question 6.
How does electric discharge occur in clouds?
Answer:
At the time of thunder negative charges are accumulated near the clouds and positive charges near the ground. When these charges meet, electric discharge takes place between the ground and clouds. In this process, a large amount of energy is released.
Question 7.
What is lightning conductor? Where is it fixed?
Answer:
Lightning conductor is a device which is used to protect buildings from the danger of lightning. It is fixed at the top of the building.
Question 8.
What is an earthquake? How is it caused?
Answer:
Sudden shaking and trembling of earth is called an earthquake. It is caused mostly due to the movement of earth’s plates inside the crust.
Question 9.
What are fault zones? Name the fault zones in India.
Answer:
Since earthquakes are caused by the movement of plates, the boundaries of the plates are weak zones where earthquakes are more likely to occur. The weak zones are also known as seismic or fault zones.
Question 10.
In India the most threatened areas or fault zones are Kashmir, Western and Central Himalayas, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, Rann of Kutch, etc.
Answer:
Tremors on the earth can also be caused when a volcano erupts, or a meteor hits the earth, or an underground nuclear explosion is carried out.
Question 11.
What are seismic waves? How are these waves recorded?
Answer:
The tremors produce waves on the surface of the earth. These are called seismic waves. These waves are recorded by an instrument called the seismograph.
Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is lightning? How does lightning strike?
Answer:
Lightning is an electric spark, but on a huge scale. It is caused by the accumulation of charges in the clouds.
When two clouds carrying opposite charges come very close to each other, the charges flow with great speed from one cloud to another through the air between them. Consequently, a very bright spark is produced. The spark caused due to the transfer of electric charge between two clouds causes lightning. It can occur when electric charges flow from one part of a cloud to another or from a cloud to the ground. Lightning is accompanied by large amounts of electric charges and very high temperatures. The huge amount of heat produced makes the air expand very suddenly what causes vibration to occur, resulting in a loud sound called thunder.
Question 2.
Explain the process of electric discharge.
Answer:
During the development of a thunderstorm, the air currents move upward while the water droplets move downward. These vigorous movements cause separation of charges. By a process, the positive charges collect near the upper edges of the clouds and the negative charges accumulate near the lower 1 edges. There is accumulation of positive near the ground also. When the magnitude of the accumulated charges becomes very large, the air which is normally a poor conductor of electricity, is no longer able to resist their flow. Finally negative and positive charges meet, producing streaks of bright light and sound called lightning and thunderstorm respectively. This process is known as electric discharge. This can occurs between two or more clouds, or between clouds and the earth.
Question 3.
What safety measures should be taken during lightning and thunderstorm?
Answer:
The following safety measures are advisable to be adopted to protect from lightning and thunderstorm:
- No open place is safe. A house or a building is a safe place. If travelling by car or by bus, it is safe to stay inside with windows and doors of the vehicle shut.
- If we are outside, the following things are important to be kept in mind:
- Open vehicles, like motorbikes, tractors, construction machinery, fields, tall trees, shelters in parks, elevated places do not protect us from lightning strikes.
- Carrying an umbrella is not at all a good idea during thunderstorms.
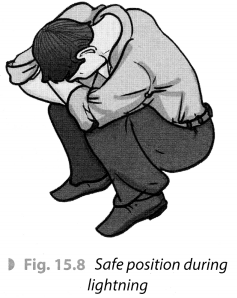
- If no shelter is available and we are in an open field, we should keep away from all trees. We should stay away from poles or other metal objects. We should not lie on the ground. Sitting in a pose as given in the Fig. 15.8 is advisable.
- If we are inside the house, we should take care as advised further:
Lightning can strike telephone cords, electrical wires and metal pipes. During a thunderstorm, contact with these should be avoided.
It is safer to use mobile phones and cordless phones. However, it is not wise to call up a person with a wired phone. Bathing should be avoided. Electrical appliances should be unplugged.
Question 4.
What is a lightning conductor? How does it work?
Answer:

Lightning conductor is a device used to protect buildings from the effect of lightning. A metallic rod, taller than the building, is installed in the walls of the buildings during its construction. One end of the rod is kept out in the air and the other is buried deep in the ground as shown in the figure. The rod provides easy route in the transfer of electric charge to the ground.
The metal columns used during construction, electrical wires and water pipes in the buildings also protect us to an extent. But we should not touch them during thunderstorm.
Question 5.
What is an earthquake? What causes an earthquake?
Explain.
Answer:
An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the earth. It lasts for a very short time. It is caused by a disturbance deep inside the earth’s crust.
We know that tremors are caused by the disturbance deep down inside the uppermost layer of the earth called crust (Fig. 15.10). The outermost layer of the earth is fragmented. Each fragment is called a plate (Fig. 15.11). These plates are in continual motion. When they brush one another, or a plate goes under another due to collision (Fig. 15.12), they cause disturbance in the earth’s crust. It is this disturbance that shows up as an earthquake on the surface of the earth.

Question 6.
What are the measures we should adopt to protect against an earthquake?
Answer:
We know that earthquakes cannot be predicted. It is, therefore, important that we should take necessary precautions to protect ourselves all the time as given below:
- In seismic zones it is advisable to make the structure of the buildings simple so that it is ‘Quake Safe’. Modern building technology can make it possible.
- In highly seismic areas, the use of mud or timber is better than using heavy construction materials.
- Since some buildings may catch fire, it is necessary that all buildings, especially tall buildings, have fire fighting equipment in working order.
- If we are at home, we should take shelter under a table and stay there till the shaking stops. We should stay away from tall and heavy objects that may fall on us. If we are in bed, we should protect our head with a pillow.
- If we are at outdoors, we should find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees and overhead power lines and drop to the ground. If travelling in a car or a bus, do not come out and drive slowly to a clear spot.
Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Extra Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
If aluminium strips of an electroscope are replaced by plastic strips and a charged body is brought in contact with the metal clip. What will happen?
Answer:
The plastic strips will show repulsion. Charges from the charge body will be transfer from the metal rod to the plastic strips. As a result, similar charges will develop on the plastic strips and repulsion will occur.
Question 2.
If a charged plastic straw is brought near another uncharged plastic straw, what will happen?
Answer:
They will attract each other due to presence of unlike charges on them.
Question 3.
During construction of a building, the lightning conductor was a little shorter and cannot be buried in the ground. Would the lightning conductor be still effective? Explain.
Answer:
No, it will not be effective. Since lightning conductor was not connected properly to the earth, therefore, the charge will not pass through to the earth.
Question 4.
If air and cloud were good conductors of electricity, do you think lightning could occur? Explain.
Answer:
If air and cloud were good conductors of electricity then charge separation will not take place and hence lightning will not occur.
Question 5.
The strips of an electroscope diverge when a charged body is brought in contact with the metal clip.
What will happen to the strips if we gently touch the metal clip with hands?
Answer:
The strips will collapse due to discharging of the charges through our hand.
Question 6.
On a dry day why do you get a slight shock on touching the screen of a television or computer monitor (with picture tube)?
Answer:
Electric charges accumulated on the screen of television or computer monitor get discharge through our body. Thus, we get a slight shock.
Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 Extra Questions Value-Based Questions
Question 1.
Ms Neena, Science teacher of class VIII, taught children how to protect themselves and what to do during an earthquake. She even performed an earthquake drill in school for better understanding in children. Children enjoyed this drill and learned a lot from this.
(a) What to do during an earthquake if you are stuck indoor?
(b) What causes earthquakes?
(c) How you must keep yourself ready for an earthquake?
(d) What values of Ms Neena is shown here?
Answer:
(a) The following must be done if someone had stuck indoor:
- Stay away from glass, windows, outside doors and walls.
- Stay away from anything that could fall such as lightning fixtures or furnitures.
- Get under a sturdy table/desk, hold it firmly and cover your head.
- Stay calm and do not panic. Stay inside until shaking stops and it is safe to go outside.
(b) Earthquakes are usually caused when rock underground suddenly breaks along a fault. This sudden release of energy causes the seismic waves that make the ground shake.
(c) We must keep ourself ready for an earthquake by:
- Having proper knowledge about do’s and don’ts during an earthquake.
- Keeping a disaster kit ready in the time of need.
- Helping needy and injured person after an earthquake.
(d) Ms Neena has future vision, scientific temperament, intelligent, compassionate, caring, dedicated, etc.
Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Open a water tap. Adjust the flow so that it forms a thin stream. Charge a refill. Bring it near the water stream. Observe what happens. Write a short report on the activity.
Answer:
We observe that water stream is attracted towards the charged refill. It is just like as pieces of papers are attracted by the charged comb. It so happens because water stream and the charged refill have dissimilar charges.
Question 2.
Make your own charge detector. Take a paper strip roughly 10 cm x 3 cm. Give it a shape as shown in Fig. 15.7. Balance it on a needle. Bring a charged body near it. Observe what happens. Write a brief report, explaining its working.

Answer:
When we touch one side of the paper with a charged body, paper strips will open. This is due to the two sides of paper strips get the same type of charge from the charged body and they repel each other.
Question 3.
This activity should be performed at night. Go to a room where there is a fluorescent tube light. Charge a balloon. Switch off the tube light so that the room is completely dark. Bring the charged balloon near the tube light. You should see a faint glow. Move the balloon along the length of the tube and observe how the glow changes.
Caution: do not touch the metal parts of the tube or the wires connecting the tube with the mains.
Answer:
Do it yourself at home.
Question 4.
Find out if there is an organisation in your area which provides relief to those suffering from natural disaster. Enquire about the type of help they render to the victims of earthquakes. Prepare a brief report on the problems of the earthquake victims.
For more information on these topics, visit:
- science.howstuffworks.com/lightning.htm
- science.howstuffworks.com/earthquake.htm
Answer:
Do it yourself.
I. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
Like charges
(a) attract each other
(b) repel each other
(c) no interaction takes place
(d) none of these
Question 2.
Earthquake of which magnitude of the following cause the maximum damage?
(a) 3.0
(b) 8.0
(c) 5.0
(d) 4.0
Question 3.
Lightning occurs due to
(a) wind
(b) rain
(c) electric discharge
(d) earthquake
Question 4.
The shaking and trembling of earth is called
(a) tsunami
(b) volcano
(c) earthquake
(d) none of these
Question 5.
The magnitude of an earthquake is measured ii
(a) Kelvin scale
(b) Celsius scale
(c) Decibel scale
(d) Richter scale
Question 6.
Which is the sure test of charge on a body?
(a) Lightning
(b) Combination
(c) Repulsion
(d) Insulation
Question 7.
Major earthquakes are less likely to occur in
(a) North-East India
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Rann of Kutch
(d) Odisha
Question 8.
Tsunami means
(a) floods
(b) earthquake
(c) earthquake under sea
(d) volcanic eruption under sea
Question 9.
Lightning always follows
(a) rain
(b) thunder
(c) the easiest path
(d) a straight path
Question 10.
The outermost layer of the earth is called
(a) mantle
(b) outer core
(c) crust
(d) inner core
Question 11.
Lightning conductor is used
(a) to destroy the buildings
(b) to protect the buildings
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Question 12.
Types of charges gained by rubbing objects are
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 1
Question 13.
The process of transfer of charges from a charged object to the earth is called
(a) lightning
(b) oscillation
(c) earthing
(d) electron movement
Question 14.
Where is the lightning conductor located?
(a) In the bottom of the building
(c) In the middle of the building
(b) On the top of the building
(d) Anywhere can be installed
Question 15.
The point from where the shock waves of an earthquake originate is called
(a) epicentre
(b) seismic focus
(c) focal depth
(d) none of these
Question 16.
The epicentre of an earthquake is
(a) in the core of earth
(b) on the surface of earth
(c) in the middle of earth
(d) none of these
Question 17.
Which of the following is not likely to cause tsunami?
(a) Nuclear explosion under sea
(b) Earthquake
(c) Volcanic eruption
(d) Lightning
Question 18.
The process of electric discharge can occur between
(a) two or more clouds
(b) clouds and the earth
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Question 19.
During lightning air is normally
(a) a good conductor
(b) a bad conductor
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Question 20.
If two charged objects are brought close to each other then
(a) they will attract each other.
(b) they will repel each other.
(c) they may attract or repel depending on the charges they carry.
(d) there will be no effect between them.
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (b)
3. (c)
4. (c)
5. (d)
6. (c)
7. (d)
8. (c)
9. (b)
10. (c)
11. (b)
12. (b)
13. (c)
14. (b)
15. (b)
16. (b)
17. (d)
18. (c)
19. (a)
20. (c)
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s.
1. Lightning is an __________ on a huge scale.
2. The electrical charges generated by rubbing two object is__________ electricity.
3. The electrical charges can be transferred from a __________ object to another through a __________ conductor.
4. The crust and mantle is broken into pieces known as __________
5. __________ is an instrument that records seismic waves.
6. __________ is the sudden shaking and trembling of the earth.
7. Lightning is always followed by __________ .
8. __________ is an earthquake under sea.
9. Transfer of charge to the earth is __________.
10. Richter scale measure __________ of earthquake.
11. When two bodies are rubbed against each other, they acquire __________ and __________ charges.
12. __________ can be charged with static electricity.
13. There are two kinds of charges __________ and .
14. The uppermost layer of the earth is called __________.
15. All building especially tall building must be equipped with __________.
16. __________ can save buildings from destruction due to lightning.
17. When charges flow, they constitute __________
18. The outer layer of the earth is __________
19. Interaction of charges is called __________
20. Benjamin Franklin showed lightning in __________.
Answer:
1. electric spark
2. static
3. charged, metal
4. tectonic plates
5. Seismograph
6. Earthquake
7. thunder
8. Tsunami
9. earthing
10. magnitude
11. equal, unlike
12. Insulator
13. positive, negative
14. crust
15. lightning conductor
16. Lightning conductor
17. an electric current
18. fragmented
19. lightning
20. 1752
III. Match the following
Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.

Answer:
1. (i)
2. (h)
3. (g)
4. (f)
5. (d)
6. (e)
7. (c)
8. (j)
9. (b)
10. (a)
IV. True or False
State whether the given statements are true or false.
1. We can predict an earthquake.
2. Richter scale is used to measure earthquake.
3. We cannot predict cyclones.
4. The electric charges produced by rubbing are called static charges.
5. The process of transferring charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing.
6. A device used to protect tall buildings from lightning is called metal detector.
7. The plates of the outermost layer of the earth are always in continuous motion.
8. Any conductor can be used to make a lightning conductor.
9. An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the earth.
10. During earthquake, we should take shelter under a heavy table.
11. The waves are recorded by Richter scale.
12. A seismograph records waves.
13. The outermost layer of the earth is not fragmented.
14. An earthquake lasts for a long time.
15. A lightning conductor is fixed in the bottom of the building.
Answer:
1. False
2. True
3. False
4. True
5. True
6. False
7. True
8. False
9. True
10. True
11. False
12. True
13. False
14. False
15. False