Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 Extra Questions Science Chapter 18
Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is cause for starting of melting of Gangotri glacier?
Answer:
Global warming
Question 2.
Which health problem arises by air pollution?
Answer:
Respiratory problems like asthma, breathlessness, bronchitis, etc.
Question 3.
What is global warming?
Answer:
Increasing temperature in atmosphere.
Question 4.
Which gas is responsible for depletion of ozone layer?
Answer:
Chloroflurocarbons (CFC’s).
Question 5.
What does SPM stand for?
Answer:
Solid particulate matter.
Question 6.
What is the role of activated charcoal in purification of water?
Answer:
It removes finest particles suspended in water.
Question 7.
Name a greenhouse gas.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, methane, water vapour (any one)
Question 8.
What is the formula of ozone?
Answer:
O3
Question 9.
Name the agents that pollute air and water.
Answer:
Pollutants
Question 10.
Name the main air polluting gases.
Answer:
Sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides.
Question 11.
Which radiations are absorbed by CO2?
Answer:
Infrared radiations
Question 12.
Define eutrophication.
Answer:
Enrichment of water bodies with nutrients like nitrates and phosphates is known as eutrophication.
Question 13.
Name one major source of water pollution.
Answer:
Untreated sewage
Question 14.
What is the function of ozone layer?
Answer:
Ozone layer protects us from ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Question 15.
Name diseases spread through drinking of contaminated water.
Answer:
Diarrhoea, typhoid, etc.
Question 16.
When was the Ganga action plan launched?
Answer:
In 1985
Question 17.
What is smog?
Answer:
The combination of smoke and fog is basically known as smog.
Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by water pollution?
Answer:
When water get contaminated by unwanted substances which have a harmful effect on both living and non-living things is referred to as water pollution.
Question 2.
What is greenhouse effect?
Answer:
The reflected sun rays are trapped by the earth’s atmosphere. The trapped radiation warms the earth.
This process by which the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere rises is called greenhouse effect.
Question 3.
What are the main causes of air pollution?
Answer:
Following are the main causes of air pollution:
- Poisonous gases which are expelled by various industries.
- Gases emitted by vehicles.
- Smoke and dust which are arising day by day due to human activities.
- Smoke emitted by forest fire.
Question 4.
What do you mean by air pollution?
Answer:
When air is contaminated by unwanted substances which have a harmful effect on both living and nonliving things then it is referred as air pollution.
Question 5.
What are the factors that are responsible for water pollution?
Answer:
Water gets polluted when unwanted and harmful substances are added to the water. Discharging of untreated sewage into the river, leaching of chemicals from agricultural practices and industries, oil spills, etc., causes water pollution.
Question 6.
What are the harmful effects of global warming?
Answer:
Following are the harmful effects of global warming:
- It will increase the earth’s temperature.
- Increase in earth’s temperature may lead to rise in sea level due to melting of glaciers.
- Rise in sea level will flood the coastal and low-lying areas.
- Global warming may lead to extreme weather other than cold or heat extremes.
- It may also affect many flora and fauna which are sensitive to temperature and their extinction.
Question 7.
Which factors decides quality of potable water?
Answer:
Potable water is clear, tasteless, odourless, have no contaminants and right pH. It has no harmful minerals or their level is too low to affect human health.
Question 8.
What’is global warming?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is increasing day by day and it is a warm gas, which increases the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere. It is called global warming.
Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by acid rain? How does it affect both living and non-living things?
Answer:
Due to fossil fuel and industrial combustions that mostly emits nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere. Water vapour present in atmosphere reacts with these gases to form nitric acid and sulphuric acid. Normal rain water is slightly acidic with a pH range of 5.3-6.0, because carbon dioxide and water present in the air react together to form carbonic acid, which is a weak acid. When the pH level of rain water falls below this range due to combining with these acids in atmosphere, it becomes acid rain.
Acid rain has significant effects on the world environment and public health.
- Effect on aquatic environment: Acid rain lowers pH level below 5, most fish eggs cannot hatch. Lowering in pH can also kill adult fish.
- Effect on forests: It makes trees vulnerable to disease, extreme weather, and insects by destroying their leaves, damaging the bark and arresting their growth.
- Effect on soil: Acid rain highly impacts soil microbes and biological activity as well as soil chemical compositions. Thus affecting crop production.
- Effect on architecture and buildings: Acid rain on buildings, especially those constructed with limestone, react with the minerals and corrode them away. This leaves the building weak and susceptible to decay. Irreplaceable damage can be caused to the old heritage buildings.
- Effect on public health: When in atmosphere, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide gases, degrades visibility and can cause accidents, leading to injuries and deaths. Intensified levels of acid depositions in dry form in the air can cause lung and heart problems such as bronchitis and asthma.
- Other effects: Acid rain leads to weathering of buildings, corrosion of metals, and peeling of paints on surfaces. Acid rain also corrodes metals like steel, bronze, copper and iron.
Question 2.
What is eutrophication? How does it affect aquatic organisms?
Answer:
Enrichment of an ecosystem with nutrients, typically compounds containing nitrogen, phosphorous or both, is known as eutrophication. Eutrophication in lakes, ponds or rivers encourages the growth of algae and other aquatic plants. These algae grow rapidly in the water system and forms algal bloom. They compete for sunlight, oxygen and space. This badly affect the aquatic life and deteriorates water quality. This is also responsible for the large scale death of aquatic plants and animals.
Question 3.
Write a short note on water pollution.
Answer:
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies (e.g., lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers and groundwater). This form of environmental degradation occurs when pollutants are directly or indirectly discharged into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds.
Water is available both on surface and under the ground. The major pollutants of surface water are toxic and poisonous wastes from households, industries, nuclear wastes, oil spills, agricultural waste, accumulation of heavy metals, chemicals from chemical factories, microorganisms from human faeces, etc.
Groundwater is mainly contaminated by leaching of harmful chemicals into the soil. Seepage of sewer near groundwater aquifer contaminates with disease causing microorganisms. Accumulation of heavy metals in soil may also lead to groundwater pollution.
Water pollution affects the entire biosphere—plants and organisms living in these bodies of water. In almost all cases the effect is damaging not only to individual species and population, but also to the natural biological communities.
Question 4.
How can you prevent water pollution?
Answer:
- Be careful about what you throw down your sink or toilet. Don’t throw paints, oils or other forms of litter down the drain.
- Use enyironment-friendly household products, such as washing powder, household cleaning agents and toiletries.
- Take great care not to overuse pesticides and fertilisers. This will prevent runoffs of the material into nearby water sources.
- By having more plants in your garden you are preventing fertiliser, pesticides and contaminated water from running off into nearby water sources.
- Don’t throw litter into rivers, lakes or oceans. Help to clean up any litter you see on beaches or in rivers and lakes, make sure it is safe to collect the litter and put it in a nearby dustbin.
Question 5.
How can you prevent air pollution?
Answer:
- Conserve energy-remember to turn off lights, computers, and electric appliances when not in use.
- Use energy efficient light bulbs and appliances.
- Limit driving by carpooling, using public transportation, biking and walking.
- Combine errands for fewer trips.
- Keep your automobile well-tuned and maintained. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on routine maintenance, such as changing the oil and filters, and checking tyre pressure and wheel alignment.
- Choose environment-friendly appliances.
- Petrol can be substituted with CNG.
- Make fertilisers of biodegradable wastes instead of burning them.
- Plant more and more trees.
- Scrubbers need to be used in the smokestacks to reduce the amount of sulphur dioxide emission in air.
Question 6.
Name various techniques used for purification of water.
Answer:
Water which looks clean may still have disease-carrying microorganisms and dissolved impurities. So, it is essential to purify water before drinking.
Municipal bodies uses various physical and chemical processes before supplying water into households.
- Boiling: It is a very common practice use for obtaining safe drinking water. Boiling kills the germs present in the water.
- Filtration: This is a physical method of removing impurities and in some cases germs also. A popular household filter is a candle type filter.
- Chlorination is a commonly used chemical method for purifying water. It is done by adding chlorine tablets or bleaching powder to the water.
- Now-a-days filter with reverse osmosis (RO) which causes desalination of water along with activated charcoal (to filter impurities) and ultraviolet lamp (to kill microorganisms) are also used for purification of water.
Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 Extra Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
Name any two sources which cause air pollution due to suspended particulate matter.
Answer:
Combustion of fuels and industrial activities.
Question 2.
Name three alternative sources of energy which do not cause any pollution.
Answer:
Wind energy, solar energy and hydropower.
Question 3.
The quality of air at various locations is monitored regularly by government and other agencies. In what way can you use these data?
Answer:
These data can be used to generate awareness about air pollution among people and to take immediate action to control it causes.
Question 4.
What is the best way to dispose off dry leaves? Why?
Answer:
Dry leaves can be converted into compost which is good for maintaining soil nutrients. Secondly, it does not cause pollution.
Question 5.
We should plant trees and nurture the ones already present in the neighbourhood. Why?
Answer:
Plants absorb carbon dioxide gas and releases oxygen. Thus, they play important role in purifying the earth’s atmosphere. By absorbing CO2 they also reduces the chance of global warming. Trees provide habitat to many birds and animals. They maintain water cycle in the nature and also prevent soil erosion.
Question 6.
Why is it advised that industries should switch over to cleaner fuels such as CNG and LPG in the Taj Mahal Zone in Agra?
Answer:
With mushrooming industries and oil refineries suspended particulate matter is increasing in the air. These suspended particulate matter, dust and dirt get settle on the marble giving the Taj Mahal a yellowish appearance. This is reducing the aesthetic value of one of the seven wonders of the world.
Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 Extra Questions Value-Based Questions
Question 1.
If we look at our daily routine, it will be observed that we use many chemicals which pollutes water bodies. But all these chemicals have become inseparable part of our daily life like detergents, toothpastes, soaps, shampoos, dish wash liquids and bars, disinfectants, etc. If this sewage from our house is discharged in water bodies untreated causes havoc.
- What is water pollution?
- What are the major pollutants of sewage from houses?
- Do you think we can do something in our end to reduce pollution from household?
- What values do we acquire from this?
Answer:
- Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies by directly or indirectly discharging pollutants without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds.
- Grey water (from sinks, tubs, washing machines, etc.), soap, detergents, toilet paper, disinfectants, etc.
- Yes, we can minimise the use of many chemicals. We can use natural soaps, shampoos, toothpastes and detergents which are easy to decompose.
- Awareness that how day-to-day activities is also degrading the nature.
Activities and Projects
Question 1.
In some cities, a pollution check has been made compulsory for vehicles. Visit a petrol pump in order to learn about the process of conducting a pollution check. You may systematically record your findings in the following areas:
- Average number of vehicles checked per month.
- Time taken to check each vehicle.
- Pollutants checked for.
- The process of testing.
- Permissible levels of emission of various gases.
- Measures taken if the emitted gases are above the permissible limits.
- How frequently is a pollution check required?
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 2.
Conduct a survey in your school to investigate various environment related activities that have been undertaken. The class can divide itself into two groups, with each group looking at a different area. For example, one group can find out whether there is an environment club in the school. What are its objectives? What is its calendar of events? How can you become a member?
If your school does not have such a club, you even think of starting one along with a few of your friends.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 3.
Organise a field visit to a river in or around your town with the help of your teachers. Observations followed by discussion could focus on
- the history of the river.
- cultural traditions.
- role of the river in meeting the town’s water needs.
- pollution concerns.
- sources of pollution.
- effects of pollution on the people living by the riverside as well as those living far away.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 4.
Find out with the help of your teachers and the internet (if possible), whether there are any international agreements to control global warming. Which are the gases covered under these agreements?
Answer:
Do it yourself.
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
Which of the following is a major source of water pollution?
(a) Sulphur dioxide
(b) Nitrogen oxide
(c) DDT
(d) Hydrogen oxide
Question 2.
The phenomenon of marble cancer is due to
(a) soil particles
(b) fog
(c) CFCs
(d) acid rain
Question 3.
Which gas is the major pollutant of air?
(a) Carbon monoxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Oxygen
(d) Propane
Question 4.
The solid or liquid particles dispersed in the air are called
(a) oxides
(b) acids
(c) hydrocarbons
(d) aerosols
Question 5.
Water containing high salt concentration can be purified by
(a) boiling
(b) UV radiation
(c) filtration
(d) reverse osmosis
Question 6.
The Taj Mahal is being affected due to
(a) noise pollution
(b) air pollution
(c) water pollution
(d) soil pollution
Question 7.
Greenhouse gas is
(a) nitrogen
(b) methane
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) both (b) and (c)
Question 8.
Pollution of water is due to
(a) oil refineries
(b) paper factories
(c) sugar mills
(d) all of these
Question 9.
The percentage of nitrogen is
(a) 21%
(b) 78%
(c) 12%
(d) 87%
Question 10.
Chlorofluorocarbon is used in
(a) refrigerators
(b) air conditioners
(c) aerosol sprays
(d) all of these
Question 11.
Which of the following is not a way to conserve water?
(a) Replace
(b) Reuse
(c) Reduce
(d) Recycle
Question 12.
Water suitable for drinking is known as
(a) impure water
(b) pure water
(c) potable water
(d) safe water
Question 13.
The contamination of natural environment is known as
(a) pollution
(b) greenhouse effect
(c) global warming
(d) CFCs
Question 14.
Agents that pollute water, soil and air is known as
(a) pollutants
(b) waste
(c) effluent
(d) garbage
Question 15.
The amount of oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere is
(a) 78%
(b) 21%
(c) 0.01%
(d) 3%
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Methane
(c) Water vapour
(d) Carbon dioxide
Question 17.
The occasion of planting lakhs of trees in the month of July every year is known as
(a) Forest conservation day
(b) Plantation month
(c) Van mahotsav
(d) Wildlife week
Question 18.
Which of the following procedures will give you water free from all impurities?
(a) Chlorine tablets
(b) Boiling
(c) Distillation
(d) Filtration
Answer:
1. (c)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (d)
5. (d)
6. (b)
7. (d)
8. (d)
9. (b)
10. (d)
11. (a)
12. (c)
13. (a)
14. (a)
15. (b)
16. (a)
17. (c)
18. (c)
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s.
1. Water which is suitable for drinking is called _________ water.
2. _________ is one of the most famous rivers of India.
3. _________ % of the world’s population is without safe drinking water.
4. _________ % of nitrogen is present in earth’s atmosphere.
5. _________ are those kind of pollutants which are used in air conditioners and refrigerators.
6. The _________ present in the faeces of mammals are indicators of the quality of water.
7. An odd combination of smoke and fog is called _________.
8. The solid or liquid particles dispersed in air are called _________.
9. Most of the atmospheric air is contained in the atmospheric layer called _________.
10. Water is a _________ natural resources.
11. Cholera is a _________ borne disease.
12. _________ is produced from incomplete burning of fuel.
13. _________ kills the germs present in water.
14. Increasing levels of _________ gases are leading to global warming.
15. _________ corrodes the marble of monuments.
Answer:
1. potable
2. Ganga
3. 25
4. 78
5. CFC’s
6. bacteria
7. smog
8. aerosols
9. troposphere
10. precious
11. water
12. Carbon monoxide
13. Boiling
14. greenhouse
15. Acid rain
III. Match the following
Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.
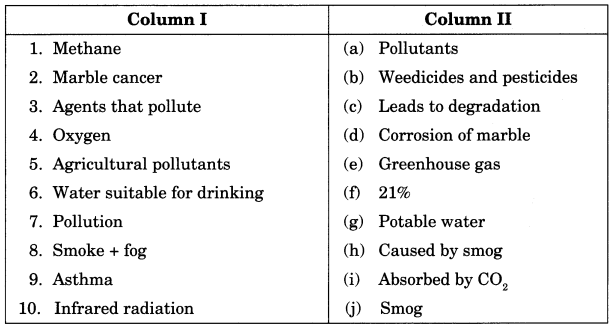
Answer:
1. (e)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (f)
5. (b)
6. (g)
7. (c)
8. (j)
9. (h)
10. (i)
IV. True or False
State whether the given statements are true or false.
1. CFC’s are not used in refrigerators.
2. 78% of oxygen is present in earth’s atmosphere.
3. Rapid growth of algae on the surface of water is known as algal bloom.
4. SO2, CO2 and nitrogen oxides are polluting gases.
5. Infrared radiations are absorbed by oxygen.
6. Acid rain does not affect the soil and plants.
7. Substances which contaminate the air are called water pollutants.
8. Smog causes breathing difficulties.
9. CFC’s damage the ozone layer of the atmosphere.
10. Water which looks clean still has dissolved impurities and disease causing microorganisms.
11. Corrosion of marble is known as marble cancer.
12. Global warming is a serious threat for life on earth.
13. Potable water is translucent.
14. We can use any amount of chlorine to purify water.
15. Water is a precious natural resource.
Answer:
1. False
2. False
3. True
4. True
5. False
6. False
7. False
8. True
9. True
10. True
11. True
12. True
13. False
14. False
15. True