Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 1 The Cold War Era is part of Political Science Class 12 Important Questions. Here we have given Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 1 The Cold War Era.
Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 1 The Cold War Era
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Which two objectives Jawaharlal Nehru wished to achieve through the strategy of Non-Alignment? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
The two objectives Jawaharlal Nehru wished to achieve through the strategy of Non-Alignment were :
- To equip India to take a firm stand on international issues.
- To enable India to balance one superpower against the other through Nans
Question 2.
Why was the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation also called Western Alliance? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) was also known as the Western Alliance because most countries of Western Europe sided with the US.
Question 3.
Why was the Warsaw Pact also called the ‘Eastern Alliance’? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
The Warsaw Pact was also called the ‘Eastern Alliance’ due to the alliance of Eastern European countries with the Soviet Union.
Question 4.
What is the full form of ‘SE/ TO’? (AH India 2015)
Answer:
The full form of ‘SEATO’ is the South East Asian Treaty Organisation.
Question 5.
What is meant by the Cold Warn (Delhi 2014)
OR
What is Cold War? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
The Cold War was the tense relationship between the US and the USSR and their allies which emerged after the Second World War. The outbreak of the Cold War was due to the different ways of thinking i.e. socialism and capitalism. This war was unlike other wars in which the two sides never clashed directly in battle.
Question 6.
Name the two superpowers responsible for the Cold War. When did the world become unipolar? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
The USA and the USSR were the two superpowers responsible for the Cold War. The world became unipolar with the disintegration of the USSR in 1991, thus, ending the bipolarity regime.
Question 7.
When and why did India sign the twenty-years ‘Treaty of Peace and Friendship’ with the Soviet Union? (All India 2012)
Answer:
India signed the twenty years ‘Treaty of Peace and Friendship’ with the Soviet Union in 1971 in order to counter the US-Pakistan, China axis. This treaty assumed India of Soviet support if the country forced any attack.
Question 8.
Why has India refused to sign the CTBT? (All Indio 2011)
Answer:
India has opposed the International treaties aimed at non-proliferation since they were selectively applicable to the non-nuclear powers and legitimized the monopoly of five nuclear powers. Thus, India has refused to sign the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT)
Question 9.
What was the main objective of the New International Order? (All India 2011)
Answer:
The main objective of the New International Order was the development of the Least Developed Countries (LDC) and to lift their people out of poverty.
Question 10.
What was the New International Order? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
New International Order was the order aimed at the economic development of the Least Developed Countries (LDC) and to lift their people out of poverty.
11. “Non-Alignment does not imply neutrality or equidistance”. What does this statement mean? (HOTS; All India 2011)
Answer:
The statement means that Non-Alignment is not a policy of ‘fleeing away’ or being neutral from the superpowers. It also means playing an active role in mediating between the two rival alliances for the cause of peace and stability.
Question 12.
Mention the impact of the end of the Cold War. (All India 2010)
Answer:
Impact of the end of the Cold War was:
- The hostility between the US and the USSR came to an end.
- The Soviet Union was disintegrated.
- The end of the Cold War meant ‘the end of Bipolarity’ in the world.
Question 13.
What is meant by unipolarity and bipolarity? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Unipolarity means the emergence of only one power i.e. the USA after the disintegration of USSR. Bipolarity means the emergence of two military alliances headed by two superpowers i.e. USSR and USA.
Question 14.
Why did India not join either NATO nor SEATO? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
India did not join either NATO or SEATO due to the development of Non-Alignment which gave it a way of staying out of the alliances. India had faith in the policy of Non-Alignment.
Question 15.
What is the balance of power? (All India 2008)
Answer:
Balance of power means when both sides have the capacity to fight against the attack and to cause so much destruction that neither an effort to initiate war.
Question 16.
Mention the name of the Eastern alliance led by the Soviet Union. (All India 2008)
Answer:
The Eastern alliance was also known as the Warsaw Pact. It was created in 1955 with principle function to counter NATO’s forces in Europe. It was led by the Soviet Union.
Question 17.
List any two characteristics of the Non-Aligned Movement. (All India 2008)
Answer:
Two characteristics of the Non-Aligned Movement were
- Dissociation from military alliances.
- Aiming for world peace.
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
In which way did the policy of Non-Alignment serve India’s interests? (All India 2017)
Answer:
Non-Alignment helped India is furthering his\national interest. It served India’s interests in two ways :
- It equipped India to take a firm stand on international issues. This way India found its place in the international political system.
- India through NAM also managed to balance one superpower against the other. It did not invite any threat from either bloc; neither alliances system could take India for granted or bully it.
Question 2.
Mention any two major military features of the Cold War. (Delhi 2016.2010.2008)
Answer:
The two major military features of the Cold War:
- Both Western and Eastern blocs competed against each other in building up their military forces as they believed that it was the key to national security.
- The two blocs devoted much of the national capital and human resources in developing nuclear weapons as it was regarded that possession of a large number of nuclear weapons would bring national security.
Question 3.
Which two ideologies were involved in a conflict during the Cold War era and why? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Two ideologies involved in a conflict during the Cold War era were :
- The ideology of liberal democracy and capitalism (USA).
- The ideology of socialism and communism (Soviet Union).
These two ideologies were involved in a conflict during the Cold War era because both the superpowers (USA and USSR) were keen on expanding their ideological spheres of influence in different parts of the world.
Question 4.
What was the Cuban Missile Crisis? Delhi 2016.2015,2014; (All India 2012,2011)
OR
What was the Cuban Missile Crisis? Name the two world leaders who played a crucial role in it. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Cuban Missile Crisis Cuban Missile Crisis is a term that denotes the confrontation/clash between the two superpowers i.e., the USA and the USSR.
The Soviet Union led by the Nikita Khrushchev installed nuclear missiles in Cuba in the hope of converting Cuba into a Russian base. This installation of nuclear missiles threatened a number of cities in the American mainland. As a result, the US President, John F. Kennedy, and his advisors ordered the American warships to intercept any Soviet ships heading to Cuba so as to avoid a full-scale nuclear war. This series of tensions and confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union is known as the ‘Cuban Missile Crisis’ which later came to be known as ‘Cold War’.
Two world leaders who played a crucial role in the Cuban Mission Crisis were Nikita Khrushchev and John F Kennedy.
Question 5.
What constrained the superpowers to go for a full-fledged war in spite of having nuclear weapons? (AH India 2016)
Answer:
The reason behind constraining the superpowers to go for war is the ‘logic of deterrence’. According to the ‘logic of deterrence’ when both the sides have a capacity to respond against each other and each side has the capacity to ruin the other to such an extent that no country can initiate a war.
Question 6.
Mention any two of the agreements signed between the two superpowers starting in the 1960s. (All India 2016)
OR
Name any two significant agreements signed by the two superpowers in the 1960s. (AH India 2010)
Answer:
The two agreements signed between the two superpowers starting in the 1960s were :
- Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) It was signed by the US, UK, and USSR in Moscow on 5th August 1963.
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) It was signed in Washington, London, and Moscow on 1st July 1968.
Question 7.
Name any four founders of NAM and the countries they belonged to respectively, (AH India 2016)
OR
Name any two foreign leaders, along with the countries they belonged to, who are recognized as the founders of the Non-Aligned Movement. All India 2014
OR
Match the following founders of NAM to the country they belonged. (Delhi 2008)
| a. Kwame Nkrumah | 1. Yugoslavia |
| b. Gamal Abdel Nasser | 2. Indonesia |
| c. Josip Broz Tito | 3. Egypt |
| d. Sukarno | 4. Ghana |
Answer:
Four founders of NAM and their respective countries are :
| Jawaharlal Nehru | India |
| Josip Broz Tito | Yugoslavia |
| Gamal Abdel Nasser | Egypt |
| Sukarno | Indonesia |
| Kwame Nkrumah | Ghana |
Question 8.
What is meant by Non-Alignment? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
India’s Policy of Non-alignment India’s policy of non-alignment was neither negative nor passive. India’s policy can be highlighted in the following two ways :
- Firstly, non-alignment allowed India to take international decisions and steps that served its interests rather than the interest of the superpowers and their allies.
- Secondly, India was often able to balance one superpower against the other.
Question 9.
Which organization came into existence in April 1949? (All India 2014)
Answer:
The North Atlantic Treaty (NATO) came into existence in April 1949. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them in Europe or North America would be regarded as an attack on all of them. Each of these states would be obliged to help the other.
Question 10.
What is meant by ‘Arenas of Cold War’? (All India 2014)
OR
What do we refer to as Arenas of Cold War? Give any one example. (Delhi 2006)
Answer:
Arenas were the areas where the Cold War-driven crisis took place. The Cold War led to several shooting wars and conflicts. Huge military build-ups combined with failed diplomacy between the superpowers made the situation worse. The USA and the USSR came in direct confrontations in Korea (1950-53), Berlin (1958-62), the Congo (the early 1960s) and in other places.
Question 11.
Why did India not join either of two camps during the Cold War? (Delhi 2012)
OR
Why did India not join either of the two superpower camps during the Cold War era? (All indie 2010)
Answer:
India did not join any alliance because it was against the bipolarity caused by the superpowers. India was in favor of preserving its sovereignty which could have been diluted by entering into an alliance.
Question 12.
Mention the duration of the First and the Second World War. (All India 2012, 2010)
Answer:
Duration of the First and Second World war is given below The duration of the First World War—1914 to 1918 The duration of the Second World War-1939 to 1945
Question 13.
Why did the two superpowers try to control the smaller nations during the Cold War? (All India 2009)
Answer:
The two superpowers tried to control the smaller nations during the Cold War because of the following reasons:
- They wanted to expand their area of influence.
- They wanted to establish their military bases in smaller countries.
Question 14.
What is the relevance of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) after the end of the bipolar world? (All India 2009)
Answer:
The role of NAM became more pronounced after the disintegration of the US SR in 1991. The USA came out as the single superpower and thus, the world became unipolar. With the downfall of the socialist camp, the Cold War rivalry lessened.
To some extent, NAM proved to be effective in the later period. It has not lost its relevance and the emphasis has shifted from political issues to economic issues such as poverty alleviation, equity injustice, promotion of industrialization, etc.
Question 15.
Mention any two examples of international issues where India took an independent stand, (AH India; Delhi 2008)
Answer:
Two examples where India took an independent stand are :
- India led the world protest against Britain when the latter attacked Egypt over Suez canal issue in 1956.
- The daring act of India of refusing to sign the NPT in 1968.
Question 16.
Give any two reasons why the smaller states in alliances in the Cold War era, used the link to the superpowers. All Indio 2008
Answer:
The smaller states in alliances in the Cold War era used the link to the superpowers because they were promised with protection, weapons and economic aid against their local rivals, mostly regional neighbors with ‘whom they had rivalries’.
Question 17.
Mention any two reforms in the UN after the Cold War. (Delhi to 2008)
Answer:
Two reforms in the UN after the Cold War were:
- Reform of the organization’s structure and processes.
- Review of the issues that fall within the jurisdiction of the organization.
Question 18.
Mention the full forms of All Indio (C) 2008
(i) CENTO
(ii) NATO
(iii) LDC
(iv) SEATO
Answer:
Full forms of the given words are :
(i) CENTO—Central Treaty Organisation
(ii) NATO—North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
(iii) LDC—Least Developed Countries
(iv) SEATO—South East Asian Treaty Organisation
Question 19.
Name one pact of Eastern alliances and three pacts of Western alliances during the Cold War. (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
One pact of Eastern alliances was the Warsaw Pact between USSR and its allies.
Three pacts of Western alliances were :
- NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
- SEATO South East Asian Treaty Organisation
- CENTO Central Treaty Organisation
Question 20.
Mention any two superpowers confrontation during the Cold War which took place in (AH India 2008)
(i) 1950-53
(ii) 1962
Answer:
- 1950-53 During this period, the Korean war took place in which North Korea invaded South Korea. United Nation and the USA sided with South Korea and China and USSR with North Korea.
- 1962 In 1962 Cuban crisis occurred. In communist-ruled Cuba, both superpowers USA and USSR confronted over the deployment of missiles. USSR stopped deployment of missiles over the objection and interception of their ships by the US.
Question 21.
How did NPT (Non-Proliferation Treaty) not seek to abolish nuclear weapons and was discriminatory? (Delhi 2008)
Answer:
NPT’s main concern was to curb the proliferation of nuclear weapons not the abolition of that. It allowed only nuclear weapon states to possess nuclear weapons and stopped others from acquiring it. Hence, it was discriminatory between nuclear weapon states and other countries of the world.
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Why did India distance itself from the two camps led by the US and the Soviet Union? Explain. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
After the Second World War, there were two camps led by the US and the Soviet Union who became the superpowers. These two superpowers were keen on expanding their spheres of influence in different parts of the world. Many countries decided to join either the US or the USSR. But a country like India distanced itself from the two camps. The reason behind this was the policy of Non-Alignment which it followed.
India adopted the policy of non-alignment because it gave India the power to take international decisions and Steps that served its interest rather than the interests of the superpowers and their allies and also the power to balance one superpower against the other.
Non-Alignment helped India in furthering its national interest.
Question 2.
Why did the superpowers need smaller states as their allies? Explain any four reasons. (All India 2014)
OR
State four reasons as to why superpowers should have military alliances with small countries. (All Indio 2012)
OR
Why did the superpowers have military alliances with the small countries? State any four reasons for it. (Delhi 2013, 2010)
Answer:
The USA and the USSR were the superpowers of the world. They exercised tremendous political, economic and military powers at their disposal.
The reasons due to which superpowers should have military alliances with small countries were :
- They entered into military alliances with smaller countries to spread their ideas and to propagate their ideologies to checkmate the other.
- The small countries were economically retarded, they easily got accommodated into their military plan.
- Also having a large number of smaller countries in one’s camp boosted the balance of power towards a particular bloc.
- To gain access to their vital resources such as oil and minerals.
Question 3.
Why is the policy of Non-Alignment of India criticized? Explain any two reasons. (All India 2013)
OR
India’s policy of Non-Alignment has been criticized for being ‘inconsistent’ and ‘unprincipled’. Do you agree? Why? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
India’s policy of Non-Alignment has been criticized for being ‘inconsistent’ and unprincipled due to following reasons:
- Firstly, Non-Alignment was seen as unprincipled because India was unable to communicate its ideas clearly to the world. On many occasions, India did not rise above to take a solid stand on world issues.
- Secondly, India took contradictory postures which were highly inconsistent with its foreign policy. For instance, India’s Treaty of Friendship with the USSR in August 1971 for 20 years was considered as the violation of the principles of the Nans
Question 4.
Name any two founders of Nans The first NAM summit was the culmination of which three factors? (Delhi 2012)
OR
Mention the names of any two founders of NAM (Non-Aligned Movement). The first NAM summit was the culmination of which three factors? (All India 2008)
Answer:
The founders of the Non-Aligned Movement were:
- Jawaharlal Nehru of India
- Josip Broz Tito of Yugoslavia
The first NAM summit was held in Belgrade in 1961. Following factors were responsible for this summit
- NAM countries were cooperating on various world agendas.
- Cold War had already worsened the world order which heightened rivalry between the superpowers and increased the tension worldwide.
- Many newly independent and decolonized countries of Asia and Africa region came into the International Arena and took membership of the UN.
Question 5.
Explain any four objectives of the Non-Alignment Movement. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The four objectives of the Non-Aligned Movement were :
- To mediate between the two rival alliances for the cause of peace and stability and refraining member countries from joining military blocs.
- To take measures for the economic development of the third world countries i.e. newly decolonized countries.
- To enable newly decolonized countries to pursue independent policies.
- To draft a policy aiming at the strengthening of independence, ending of colonialism and promoting world peace.
Question 6.
What is the rationale of the Non-Aligned Movement after the end of the Cold War? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The rationale of the Non-Aligned Movement after the end of the Cold War was based on a recognition that decolonized states shared a historical affiliation. They can become a powerful force if they come together.
This meant that very small and poor countries need not become followers of any big power, instead, they could also adopt an independent foreign policy.
Another important rationale behind the movement was based on a resolve to democratize the international system to redress existing inequalities also.
Question 7.
How is Non-Alignment different from ‘neutrality’ or ‘equidistance’? (Delhi 2011)
OR
How was Non-Alignment neither isolation nor neutrality towards international affairs? (All India 2008)
Answer:
NAM provided a third option or an alternative to bipolarity. It was different from ‘neutrality’ and equidistance in the following way:
- Newly independent countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America used NAM as a platform to raise their voice.
- NAM as a policy of Non-Alliances should not be equated with isolationism. NAM sought active involvement in world affairs.
- India with the Non-aligned countries participated in the mediating process of resolving the crisis between the rival alliances. Their positive attributes were the unity they forged amongst themselves and they resolve to maintain distance from superpowers despite the attempt by the two superpowers to bring them into their alliance.
Question 8.
Explain any four important events of the Cuban Missile Crisis, (All India 2010)
Answer:
The four important events that took place during the Cuban Missile Crisis were :
- In 1962, the USSR installed its missiles in Cuba. It intended to convert Cuba into Russian missile base.
- America became aware of the intentions of Russia. As a warning, it ordered American warships to intercept Soviet ships moving to Cuba.
- The US was feared of developing nuclear weapons on part of the USSR to challenge the supremacy of the US.
- The World was divided into two power blocs to expand their own spheres of influence in the world.
Question 9.
What was India’s response to the Cold War? Explain. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
In response to the Cold War, India adopted a two-pronged strategy to combat it. These were :
- Firstly, it stayed away from the power blocs and their influence.
- Secondly, it criticized those countries which were newly independent and subsequently becoming allies of the two power blocs.
India was actively pursuing the task of slowing down of the Cold War rivalries through the instrument of Nans India chose those regions which were neglected by both superpowers to seek an end to Cold War rivalry. Those regions later became a part of what Nehru envisaged was a ‘commonwealth of the cooperating nations’.
Question 10.
Why were most of the Non-Aligned countries categorized as an LDCs (Least Developed Countries)? (Delhi 2010,2008)
Answer:
The term Least Developed Countries (LDCs) was created during the Cold War era. The Non-Aligned countries were those which were not aligned with any superpower blocs. These were the newly decolonized countries and were very poor. After achieving independence, they looked upon the developed countries for initiating the process of economic development.
These countries were far behind the countries of the first and ’second world in terms of economic growth and development.
The countries, which come under the LDC category are the countries of Asia, Africa and Latin America. Strikingly, these were the countries which were under foreign rule for decades. They rose to the center stage in the wake of NAM becoming influential.
Question 11.
Mention any four realities that have changed world politics after the Cold War. (All Indio 2008)
Answer:
The world was restructured after the Cold War. Following were the four realities that changed world politics after the Cold War
- The Cold War ended with the disintegration of the USSR in 1991 which led to the emergence of 12 independent republics carved out of the then USSR which eventually made the Common Wealth of the Independent States (CIS).
- The Cold War had divided the Berlin in the very beginning, however, with the end of the Cold War, the Berlin wall collapsed, which unified Germany and Berlin became the capital of United Germany.
- The significant reality in the post-Cold War era, which the world witnessed was the ending of bipolarity and emergence of the USA as the sole superpower which eventually demanded an end to an arms race.
- The US made the capitalist economy as the new dominant model of an economic system which led to the near death of communism.
Question 12.
What is the New International Economic Order (NIEO)? What role was played by it in changing NAM into an economic pressure group? (Delhi (C) 2008)
Answer:
NIEO was a set of proposals put forward during the 1970s by some developing countries through the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) to promote their interests by improving their conditions in international trade.
The need for the NIEO lies in the fact that the developing countries had to go for sustained development to remove the tag of Least Developed Countries (LDCs) on them.
Gradually, the concern of the Non-Alignment Movement changed to give greater importance to economic issues. In 1961, at the first summit of NAM at Belgrade, economic issues had not been very important. By the mid-1970s, they had become the most important issues. As a result, NAM became an economic pressure group.
Question 13.
What is meant by the Arenas of the Cold War? Highlight the role played by the Cold War in avoiding another World War? (Delhi (C) 2008)
Answer:
Arenas of the Cold War were the areas where the Cold War-driven crisis took place. The Cold War led to several shooting wars and confrontations. Huge military build-ups combined with failed diplomacy between the superpowers worsened the situation.
The USA and the USSR came in direct confrontations in Korea (1950-53), Berlin (1958-62), the Congo (the early 1960s) and in other places.
Cold War played an important role in avoiding another World War. The reason behind the Cold War avoided World War like the situation is the logic of deterrence. It means when both the sides have a capacity to retaliate against each other and each side has the capacity to ruin the other to such an extent that no country can initiate a war.
6 Marks Questions
Question 1.
How far is it correct to say the international alliances during the Cold War era were determined by the requirements of the superpowers and the calculations of the smaller states? Explain. (HOTS; Delhi 2016)
Answer:
To a large extent, it is correct to say that the International alliance during the Cold War era were determined by the requirements of the superpower. It is justified from the following points :
1. The smaller states decided to an alliance with the two superpowers because they were promised protection, weapons and economic aid against their local rivals. Hence, this led to a division of the world into two camps.
2. The countries which sided with the US came to know as a Western alliance and those who backed USSR were known as Eastern alliance. The Western alliance countries organized themselves into an organization known as the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO). It came into existence in April 1949. It was an association of twelve states which declared that armed attack on any one of them in Europe or North America would be regarded as an attack on all of them.
The Eastern Alliance, on the other hand, known as the Warsaw Pact, was led by the Soviet Union. It was created in 1955 and its principal function was to counter NATO’s forces in Europe.
3. Europe became the bone of contention between the superpowers. They also used their military power to bring countries into their respective alliances. For example, the Soviet Union used its influence in Eastern Europe just to ensure that the Eastern half of Europe remained within its sphere of influence.
4. The United State built an alliance system called the South East Asian Treaty Organisation (SEATO) and the Central Treaty Organisation (CENTO) in East and South East Asia and in West Asia (Middle East). To counter this, the Soviet Union and communist China responded by having close relations with regional countries such as North Vietnam, North Korea, and Iraq.
Question 2.
Why was the end of the Second World War considered to be the beginning of the Cold War? Explain. (All India 2016)
Answer:
The end of the Second World War was considered to be the beginning of the Cold War because it led to the rise of two major centers of power. It paved the way for the Cold War Era. The Second World War came to an end with the dropping of nuclear bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki (the two Japanese cities). It led to the withdrawal of Japan from the war. The dropping of the bomb by the US was criticized as well as support.
According to the critics of this decision, the USA was aware of the surrender of Japan hence dropping the bomb was not necessary. They argue that the US action was intended to stop the Soviet Union from making military and political gains in Asia and elsewhere and to show Moscow that the United States was supreme. The supporters of the decision claim that the dropping of the bomb was a necessary step to end the war quickly and to stop further loss of American and allied lives.
The consequence of this was the rise of two new powers on the global stage. With the defeat of Germany and Japan, the devastation of Europe and in many other parts of the world, the United States and the Soviet Union became the greatest powers in the world.
Question 3.
Describe any three reasons for the superpowers to have military alliances with smaller countries during the Cold War period. (Delhi 2015)
OR
What is Cold War? Why did the superpower depend on a military alliance with smaller countries? (Delhi 2012)
OR
What was the Cold War? Why did the superpowers need any allies during the Cold War? (Delhi (C) 2008)
Answer:
The Cold War was the tense relationship between the US and the USSR and their allies which emerged after the Second World War. The outbreak of the Cold War was due to the different ways of thinking i.e. Socialism and Capitalism. This war was unlike other wars in which the two sides never clashed directly in battle. The fear that a relationship would end in the nuclear war did not materialize.
The USA and the USSR were the superpowers of the world. They exercised tremendous political, economic and military powers at their disposal.
The reasons due to which superpowers should have military alliances with small countries were :
- They entered into military alliances with smaller countries to spread their ideas and to propagate their ideologies to checkmate the other.
- The small countries were economically retarded, they easily got accommodated into their military plan.
- Also having a large number of smaller countries in one’s camp boosted the balance of power towards a particular bloc.
- To gain access to their vital resources such as oil and minerals.
Question 4.
Suppose there had been no Cold War, how would that situation have affected India’s foreign policy? (All India 2015)
Answer:
The situation must have created the differences :
1. The spirit of Panchsheel (Peaceful coexistence) would have been endangered due to India’s unsafe condition after the Second World War, her existence could have been divided into many units. In addition, there were issues of shortage of food grain supply, industrial supply for the development of industries. In this case, India must have gone either into isolation or would have joined any superpower camp. India would have been a member of NATO or Warsaw Pact.
2. India must have added some better strategies to its foreign policy. If the situation had not been as it was, UNO and other institutions would not have been created. New strategies would have been framed for the existence of India.
3. Self-sufficiency has been achieved by India. If Non-Alignment was followed strictly, India has been self-sufficient.
Question 5.
How did the ‘New International Economic Order’ come into being? Which reforms were proposed by UNCTAD in its report in 1972? Delhi 2015,2012; (All Indio 2008)
OR
Evaluate the New International Economic Order of the 1970s, (AH India 2009)
Answer:
The idea of a New International Economic Order (NIEO) was in direct response to the poor economic development in third world countries.
They were stereotyped as the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) by the advanced countries because of their state of being under-developed. Achieving economic independence was the goal of these countries and this was precisely the reason for the establishment of the NIEO.
Recognizing the right of the LDCs to develop their economies, the United Nations Conference to Trade and Development (UNCTAD) in its report titled ‘Towards a New Trade Policy for Development in 1972/ proposed a reform of the global trading system.
The reforms were :
- To give autonomy to LDCs so that they can have control over their natural resources.
- To provide LDCs access to Western markets so that the LDCs could sell their products and hence trade could become profitable for them.
- Western countries should reduce the cost of technology imported to LDCs.
- LDCs should be given a greater role in international economic institutions.
Gradually, the nature of Non-Alignment changed to give greater importance to economic issues. In 1961 at the first summit, economic issues were not very important. By the mid-1970s, they had become the most important issues. Thus, NAM became an economic pressure group.
Although, these reforms sent alarm-bells in the ears of the developed countries, however, they could not sustain the pressure of economic development from the LDCs. This led to the fading of NIEO in the 1980s. It should be noted that the Nop-Aligned countries maintained unity in the initial phase of the Nans
Question 6.
Describe the role played by India in keeping the Non-Aligned Movement alive and relevant. (Delhi 2015)
OR
Assess India’s role in Non-aligned movement, (AH India 2009)
Answer:
The Non-aligned Movement aimed at establishing a new and equitable international economic, social and political order. Non-aligned countries played a role in reducing Cold War conflicts and averting some serious crisis. For example, Jawaharlal Nehru, one of the key leaders of the NAM played a crucial role in mediating between the two Koreas thereby resolving the arousal of conflicts.
Furthermore, India adopted the policy of NAM/Instead of joining one of the superpower blocs, it acted as a mediator between two rival alliances. India did so for the cause of peace and stability. India raised the voice against the newly decolonized countries of becoming part of these alliances.
Some examples where India exercise the policy of NAM by taking an independent decision are as follows:
- India led the world protest against Britain when Britain attacked Egypt over the Suez Canal issue in 1956 and
- The bold decision of India refusing to sign the NPT (Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty) in 1968.
India also helps in taking measures for the economic development of the third world, non-aligned, newly decolonized countries to enable them to pursue independent policies.
Thus, India played an active role in keeping the Non-aligned Movement alive and relevant.
Question 7.
‘Non-Aligned Movement has become irrelevant today’. Do you agree with the statement? Support your answer with any three suitable agreements. (HOTS; All Indio 2014)
OR
What is the relevance of the Non-Aligned Movement after the end of the Cold War? Explain, (AH India 2012)
OR
Analyze the relevance of the Non- Aligned Movement (NAM) in the unipolar world. Explain. (All Indio 2010)
Answer:
NAM which emerged as the alternative to the partisan politics of the first and second world was based on the idea of mutual understanding and mutual cooperation among member countries.
The main objective with which NAM was created was to safeguard the identity of the third world countries who were used as pawns by the superpowers in the power game which was the product of the Cold War and its cumulative effects.
The superpowers looked at NAM with disgust, but for the third world countries, it was an important platform protecting the integrity of the third world countries. NAM during the Cold War era softened the Cold War rivalries and contained the further worsening of the Cold War situation.
The role of NAM became more pronounced after the disintegration of the USSR in 1991-USA came out as the single superpower and thus, the world became unipolar. With the downfall of the socialist camp, the Cold War rivalry lessened.
No, I do not agree that the Non-Aligned movement has become irrelevant today. It has not become outdated. It is due to the following reasons:
- Its members are still bound by the common history and common objectives like economic development of the least developed countries.
- NAM members seek economic aid from the developed countries so that the undeveloped countries can use it into economic prosperity.
- The members of NAM are anti-colonialist and anti-communist. Their main motives were to emphasis on the rights of nations and materialization of peace and security through participation in resolving international issues.
Question 8.
Explain the Eastern and Western alliances during the Cold War period. Name any two European countries from amongst the following which was not members of these alliances France, Poland, Sweden, Spain, Austria, Romania (All Indio 2012)
Answer:
The two superpowers i.e. the USA and the USSR were keen to expand their spheres of influence in different parts of the world. Hence, the world was sharply divided between the two alliance systems.
These were the Eastern Alliance and the Western alliance. The countries which were part of these two alliances were smaller states who got the promise of protection, weapons, and economic aid against their local rivals. Therefore, these alliance systems threatened to divide the entire world into two camps. Most countries of Western Europe sided with the US and those of Eastern Europe joined the Soviet camp.
Description of these two alliance is given below :
- The Eastern alliance or the Warsaw Pact was led by the Soviet Union. It was created in 1955 and its principal function was to counter NATO’s forces in Europe.
- The Western alliance was formed into an organization, the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO). The alliance sided with the US. It came into existence in April 1949 and was an association of twelve states. It declared that armed attack on any one of them in Europe or North America would be regarded as an attack on all of them.
The two countries which were not members of these alliances were Sweden and Austria.
Question 9.
Explain any six factors which helped the Soviet Union in becoming a superpower after the Second World War. (Delhi 2012)
OR
Analyze any six factors which helped the Soviet Union in becoming a superpower after the Second World War. (All India 2010)
Answer:
The six factors which helped the Soviet Union in becoming a superpower after the Second World War era are :
- East European countries came under the control of USSR.
- Their political and economic systems were modeled after USSR.
- USSR emerged as a leader of socialist bloc countries.
- The Soviet Union has complex communication networking, vast energy resources-oil, iron, and steel machinery.
- Production and improvement of the transport sector.
- USSR’s domestic consumer industry produced everything from Pins to Cars.
- Ensured a minimum standard of living for all citizens.
- Government subsidized basic necessities including health, education, children and other welfare schemes.
- No unemployment.
- State ownership over land and productive assets.
Question 10.
What led to the emergence of a bipolar world? What were the areas of Cold War between the two blocks? (Delhi 2011; All Indio 2011)
Answer:
The reasons for the emergence of a bipolar world were :
- Both the superpowers i.e. the US and USSR were keen to expand their spheres of influence in different parts of the world.
- The smaller countries decided to join either of the alliances in order to get protection, weapons and economic aid against their local rivals.
- The enhanced system threatened to divide the entire world into two camps.
Arenas were the areas where the Cold War-driven crisis took place. The Cold War led to several shooting wars and confrontations. The USA and the USSR came in direct confrontations in Korea (1950-53), Berlin (1958-62), the Congo (the early 1960s) and in other places. It was against this background that the Non-Aligned Movement played a crucial role.
Question 11.
What is meant by isolationism, neutrality, and Non-Alignment? Examine the growth of Non-Aligned Movement. (All indin 2010)
Answer:
Isolationism It is the policy or doctrine of isolating one’s country from the affairs of other nations by declining to enter into alliances, foreign economic commitments, international agreements, etc; seeking to devote the entire efforts of one’s country to its own development.
Neutrality It is the policy or status of a nation that does not participate in a war between other nations. It is a concept opposed to a state of war.
Non-Alignment is a concept aiming at an independent and peaceful co-existence. It believes in non-involvement in tensions and possible conflicts between power blocs.
Non-Alignment It grew into a popular international movement. Various countries of the world having different interests joined it. In spite of the heterogeneous character of NAM, it has made an important contribution to development. A vast majority of NAM members had suffered untold humiliation and suffering under the imperialist domination. But as they were free nations now, they wanted to assert themselves and to charter their own cause of action. Non-Aligned Movement gave recognition to the smaller countries to have their foreign policy instead of following big powers.
Passage-Based Questions
Question 1.
Study the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow All India 2017 The smaller states in the alliances used the link to the superpowers for their own purposes. They got the promise of protection, weapons and economic aid against their local rivals, mostly regional neighbors with whom they had rivalries. The alliance systems led by the two superpowers, therefore, threatened to divide the entire world into two camps. This division happened first in Europe. Most countries of Western Europe sided with the US and those of Eastern Europe joined the Soviet camp. That is why these were also called the ‘Western’ and the ‘Eastern’ alliances.
(i) Name one organization each related to the ‘Western’ and the ‘Eastern’ alliances.
(ii) Why were the smaller states interested in joining the super alliances?
(iii) How did the ‘alliance system’ threaten to divide the world?
Answer:
(i) NATO has been related to the ‘Western’ alliance and Warsaw was related to the ‘Eastern’ alliance.
(ii) Smaller states were interested to join super alliances because they got the promise of protection, weapons, and economic aid against their local rivals.
(iii) ‘Alliance system’ threatened to divide the world by dividing the entire world into two camps Soviet and US or socialist and capitalist.
Question 2.
Read carefully the passage given below and answer the following questions (Delhi 2015)
The Cold War was not simply a matter of power rivalries, military alliances and of a balance of power. These were accompanied by a real ideological conflict as well, a difference over the best and most appropriate way of organizing political, economic, and social life all over the world.
(i) Why is a war-like situation called the Cold War?
(ii) Identify one military pact each signed by each of the two superpowers to balance the power rivalries.
(iii) Differentiate between the ideologies represented by rival blocs.
Answer:
(i) The Cold War referred to the competition, the tensions and a series of confrontations between the two power blocs i.e. the USA. and the Soviet Union.
(ii) The Western alliance also known as the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) came into existence in April 1949. It was a group of twelve states.
(iii) The ideology of the USA was liberal democracy and capitalism whereas the ideology of the Soviet Union was of socialism and communism.
Question 3.
Study the passage given below and answer the questions that follow (All India 2013)
The two superpowers were keen on expanding their spheres of influence in different parts of the world. In a world sharply divided between the two alliance systems, a state was supposed to remain tied to its protective superpower to limit the influence of the other superpower and its allies Most countries of Western Europe sided with the U.S. and those of Eastern Europe joined the Soviet camp.
(i) Name the two superpowers.
(ii) Why did the allies want to remain tied with one of the superpowers?
(iii) Why did the superpowers want to bring other countries into their camps?
Answer:
(i) The two superpowers the USA and USSR.
(ii) Allies wanted to remain with one of the superpowers to stand still in the world economy and get the benefits in case of emergency or trade purpose.
(iii) The superpowers want to bring other countries into their camps just to control them and to spread their influence.
Value Based Questions (VBQs)
Question 1.
Analyze any three points of criticism and any three core values and enduring ideas related to the Non-Aligned Movement. (Delhi 2010; All India 2010)
Answer:
India’s Policy of Non-Alignment could not escape criticism. Here are two major criticisms:
- Non-Alignment was seen as unprincipled because India was unable to communicate its ideas clearly to the world. On many occasions, India did not rise above to take a solid stand on world issues.
- India took contradictory postures which were highly inconsistent with its foreign policy. For instance, India’s Treaty of Friendship with the USSR in August 1971 for 20 years was considered as the violation of the principles of the Nans
- During the Bangladesh crisis also India developed good relations even with the US in the name of diplomatic and military support.
However, Non-Alignment contained some core values and enduring ideas. These were :
- Cooperation among member nations.
- Historical affiliation among colonized states and they too can become a powerful force if come together.
- It has also based on a resolve to democratize the international system by thinking about an alternative world order to redress existing inequalities.
Map-Based Question
Question 1.
Study the political outline map of the world given below in which six different countries have been marked as (1), (2), (3), (4), (5) and (6). Identify these countries and name them. Also classify them as First World, Second World, and Third World countries. Write your answer in the Answer-Book as per the following format (Delhi 2011)
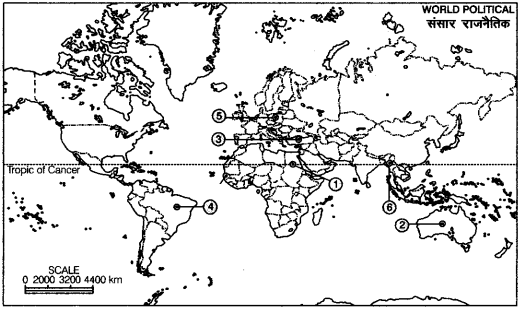
Answer:
| No. of the Country | Name of the Country | First World/Second World/Third World |
| 1. | Egypt | Third World |
| 2. | Australia | First World |
| 3. | Turkey | First World |
| 4. | Brazil | Third World |
| 5. | Poland | Second World |
| 6. | Myanmar | Third World |
We hope the Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 1 The Cold War Era help you. If you have any query regarding Political Science Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 1 The Cold War Era, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.