NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship Chapter-6 Resource Mobilization
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
SECTION-A: FINANCE
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What do you understand by finance?
Answer. ‘Finance’ refers to funds or monetary resources needed by individuals, business houses and the government.
2.Give the significance of finance in an enterprise.
Answer. The significance of finance in enterprise is elucidated like a lubricant to the process of production.
3.Name the most important prerequisite to start an enterprise.
Answer. Finance is the most important prerequisite to start an enterprise.
4.State the most important factors for the survival of any business enterprise.
Answer. Financing, ‘production’, ‘marketing’ are deemed to be the most important factors for any business survival. Financing is considered to be the first because nothing can be done without money.
5.State how sources can broadly be classified into two major categories.
Answer. We know that these sources could broadly be classified into two major categories:
- Internal sources
- External sources
6. What do you understand by internal sources of finance?
Answer.Internal sources of finance is referred to as owner’s own money. It is also known as owner’s equity. Particularly in the case of small entrepreneurs the owner’s money is very small.
7.How will you differentiate between financial market with other market? Give one difference.
Answer. Financial market is a market in which people and entities can trade financial securities (stocks and bonds), commodities (including precious metals or agricultural goods), and others like crude oil etc. at prices that reflect supply and demand. Market refers to the aggregate of possible buyers and sellers of a certain good or service and the transactions between them.
8.‘Production’, ‘Marketing’, and Financing’ – deemed as the most important factors for any business’s survival rates. Among these name the most critical element and why?
Answer.Production, marketing, and financing, deemed to be the most important factors for any business survival. ‘ Financing’ is considered to be the first because no entrepreneur can start and run the business without money. Among this the most critical element for success in business is ‘Finance’. Before doing anything, an entrepreneur should clearly answer the following three questions:
- How much money is required?
- Where will money come from?
- When does the money need to be available?
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Which sources provide the supply for long-term funds?
Answer. Capital market consists of lenders and borrowers:
Lenders supply the funds.
Investors demand funds.
The supply of long-term funds comes from the following sources:
- Household savings
- Foreign capital
- Institutional investors
- Corporate savings
- The government
2.Name the sources of demand for capital comes from.
Answer. Capital market consists of lenders and borrowers:
- Lenders supply the funds
- Investors demand the funds The demand for capital comes from:
- Industrial Sector – It comes from the private sector into manufacturing or other economic activities.
- Government
3.Entrepreneur can use the capital raised for a variety of purposes, what are they?
Answer. Entrepreneur can use the capital raised for a variety of purposes including:
- Growth and expansion
- Retiring existing debt
- Corporate marketing and development
- Acquisition capital.
4.How can an entrepreneur, raises funds by selling the issue mainly to the institutional investors?
Answer. Private Placement: Any entrepreneur can directly sale of its securities of a company to a limited number of sophisticated investors. Entrepreneurs can raise funds by selling the securities mainly to the institutional investors like:
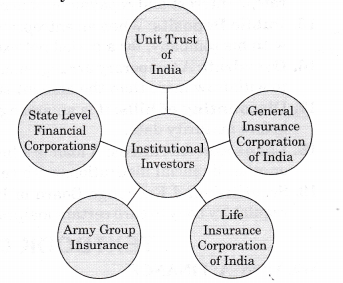
Entrepreneurs both from public limited and private limited sectors, banks heavily upon raising funds through the issues of varied financial instruments under this segment as at times they do not wish to disclose information to the open market.
5.How stock options lead to enable employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company?
Answer. Stock options or offering shares to the employees has gained much popularity in many countries of the world. This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company leading to:

C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
1.Explain some important sources of raising finance in business.
Answer. A. Methods of flotation of new issues: An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market by the following methods:
- Public issue
- Rights issue
- Private placement
- Offer to the employees
- Public issue: Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. An enterprise organizing itself as a public limited company can raise the required funds commonly by preparing a prospectus.
When an entrepreneur offers shares to the public for subscription he/she is required to comply with all the restrictions and formalities pertaining to the initial issues, prospectus drafting and launch.
One of the most difficult problems in the new venture creation process is obtaining finance when an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company. - Rights issue: Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
Normally, through a circular, rights issues are proposed to the existing shareholders and in case they are not willing to subscribe, they can renounce the same in favour of another person. This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc. - Private placement: Private placement means the direct sale by a company of its securities to a limited number of sophisticated investors. Entrepreneurs, herein, raise funds by selling the issues mainly to the institutional investors like:
• Unit Trust of India
• Life Insurance Corporation of India
• General Insurance Corporation of India
• Army Group Insurance
• State Level Financial Corporations, etc.
Entrepreneurs both from public limited and private limited sectors bank heavily upon raising funds through the issue of varied financial instruments under this segment as at times they do not wish to disclose information to the open market. - Offer to employees: Stock options or offering shares to the employees has gained much popularity in many countries of the world. This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company leading to:
• Higher efficiency
• Low labour turnover
• Better industrial locations
• Low floatation cost
• Wider/higher generation of funds.
B. Angle investors: Business angle or informal investor or an angle investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity. Venture capital is a type of private equity capital provided as seed funding to early-stage, high potential, high risk, grown up companies/entrepreneurs who lack the necessary experience and funds to give shape to their ideas.
- It is basically equity finance in relatively new companies.
- It is long-term investment in growth- oriented small or medium firms.
- Venture capitalists not only provide capital but also business skills to investee firms.
- It involves high risk-return spectrum. Funding: Obtaining venture capital is substantially different
from raising debt or a loan from a lender. Lenders have a legal right to interest on a loan and repayment of the capital, irrespective of the success or failure of a business.
SFIs were established to meet the long-term financial requirement of such enterprises on economic and social ground. These Specialized Financial Institutions in India are not only committed to financial services but are also devoted towards playing a role of a promotional “mentor” and technical advisor to a wide range of the upcoming and existing entrepreneurs. Thus, these Specialized Financial Institutions (SFIs) make an important source of medium and long¬term financing amongst all the financial institutions in India, to the industry.
A. At national level/All India development banks
- Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
- Small Industries Development-Bank of India (SIDBI)
- Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
- Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI)
B. At state level
- State Financial Corporation (SFCs)
- Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI)
- State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC)
SECTION-B: FINANCIAL MARKETS
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Define capital market.
Answer. A capital market may be defined as an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital or financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs.
2.Name the two players in the capital market.
Answer.

3.Identify the reward IPO investors seek as an appreciation of their investment.
Answer. The only reward the IPO investors seek is an appreciation of their investment and possibly dividends.
4.Identify the method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
Answer. Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
5.What do you understand by pro-rata allotment of securities?
Answer. It is used to describe a proportionate allocation. It is a method of assigning shareholders a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
6.What is Right Issue?
Answer.Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
7.When the right issue are proposed to the existing shareholders and if they are not ready to subscribe what is the next step taken by an entrepreneur?
Answer.When rights issues are proposed to the existing shareholders and in case they are not willing to subscribe, they can renounce the same in favour of another person.
8.Why right issue method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive?
Answer.The right issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as no intermediaries are required like any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.
9.What do you understand by private placement?
Answer.Private placement means the direct sale by a company of its securities to a limited number of sophisticated investors.
10.What is meant by stock options or offering shares to the employees?
Answer. A stock option is granted to specified employees of a company. ESOs carry the right, but not the obligation, to buy a certain amount of shares in the company at a predetermined price.
11.Name the method which enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company.
Answer.Stock options or offering shares to the employees is the method that enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company.
12.What is a secondary market?
Answer. It refers to the market for the purchase and some of existing securities i.e. the market securities issued earlier are sold by existing investors in this market.
13.What is the need of secondary market?
Answer. The secondary capital market, which is also known as old securities market or stock exchange deals with buying and selling of old securities i.e. the market securities issued earlier are sold by existing investors in this market, thus paving way for the entrepreneurs that if they offer high returns to market, investors will remain inclined to invest therein. The secondary market enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
14.In what forms company can raise capital through primary market?
Answer. An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market by the following methods:

B.SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.For what purpose is finance required right from the very beginning i.e. conceiving an idea?
Answer.

2.What is the need of finance?
Answer.
- Finance is one of the important prerequisites to start an enterprise.
- It helps an entrepreneur to arrange all other required resources together like, personnel, machines, materials, methods, land, etc. to start up the business systematically.
- It helps an entrepreneur to start and run his business activities smoothly and convert a dream into reality.
3.An entrepreneur is a person who bears the risks, unites various factors of production and carries out a creative innovation, and for doing all these, what is the basic requirement to be reached to this extent.
Answer. Finance.
4.State some mushrooming sources of raising finance in the business.
Answer. A company may raise funds for different purposes depending on the time periods ranging from very short to fairly long duration. The total amount of financial needs of a company depends on the nature and size of the business. The scope of raising funds depends on the sources from which funds may be available. Here, we shall discuss some mushrooming sources available to an entrepreneur to raise finance; Long-Term and Medium- Term Capital, they have the following options:
- Capital markets:
• Issue of Shares
Equity shares: The rate of dividend on these shares depends on the profits available and the discretion of directors. Hence, there is no fixed burden on the company. Each share carries one vote.
• Preference shares: Dividend is payable on these shares at a fixed rate and is payable only if there are profits. Hence, there is no compulsory burden on the company’s finances. Such shares do not give voting rights.
• Issue of Debentures. - Angle investors: Business angle or an angle investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high- return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
- Venture capital: Venture capital is an equity based investment in a growth-oriented small to medium business to enable the investors to accomplish objectives, in return for minority shareholding in the business. It is a way in which investors support entrepreneurial talent with finance and business skills to exploit market opportunities and obtain long-term capital gains.
- Specialized financial institutions Specialized Financial Institutions (SFIs) make an important source of medium and long term financing amongst all the financial institutions in India, to the industry.
A. At national level/All India development banks
- Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
B. At state level
- State Financial Corporation (SFC)
- Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI)
- State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC).
C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.State the nature of money market. Who are the major participants in the money market?
Answer.Money market refers to transactions involving lending and borrowing of money for short periods like a day a week a month or 3 to 6 months. It meets the short term requirements.
The major participants in the market are:
- Reserve Bank of India
- Commercial Banks, Cooperative Banks
- Non-Banking Finance Companies
- State Government
- Large Corporate Houses and Mutual Funds
- LIC, GIC, UTI, etc.
2.Explain how capital markets are the most important source of raising finance for an entrepreneur.
Answer. Capital markets are the most important source of raising finance for the entrepreneurs. This market:
- Mobilises the financial resources on a nation-wide scale.
- Secures the much required foreign capital and know-how to promote economic growth at a faster rate.
- Ensures the most effective allocation of the mobilized financial resources by directing the same either to such projects which are capable of the highest yield or to the under developed priority areas where there is an urgent need to promote balanced and diversified industrialization. The needs of entrepreneurs who actually use the savings for productive purposes are varied. The capital market satisfies the tastes of savers and the needs of investors through its financial instruments and institutions.
3. What do you understand by capital market? How can the capital market in India be broadly classified into different categories?
Answer.A capital market may be defined as an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital or financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs. The capital market in India may be broadly classified into:

4.Write down the sectors of organized and unorganized market.
Answer. The capital market in India may be broadly classified into:
A. Organized Markets: This segment comprises of
- Corporate enterprises
- Government and semi-government institutions requiring funds for various development activities
- Individual investors
- Corporate and institutional investors, as LIC, Banks, Finance Corporations, International financing agencies, etc.
B. Unorganized Sector:
The unorganized sector consists of
- The indigenous bankers in urban areas.
- The money lenders in rural areas.
5.What is meant by primary market? Briefly explain the concept of ‘Right Issue for existing companies’.
Answer. Primary market is basically meant to facilitate transfer of resources from the savers to the entrepreneurs seeking funds for:
- Setting new enterprises,
- Expanding,
- Diversifying.
- Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
- It is proposed through a circular to all the existing shareholders only.
- It is not mandatory to purchase these shares if any shareholders are not willing to subscribe, they can reject or disclaim and others can subscribe for it.
D. VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.“An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market.” Explain the various methods of raising the funds in the primary market by an entrepreneur.
Answer. Yes, an entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market. The various methods of raising the funds in the primary market by an entrepreneur are as follows :
- Public Issue
- Rights Issue
- Private Placement
- Offer to the employees
- Public Issue/Going Public: Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. An entrepreneur organizing itself as public limited company can raise the required funds commonly by adopting prospectus.
- Right Issues: It is an offer of new securities by a listed company to its existing shareholders only. The right issues are done always on the pro-rata basis (giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.)
• The companies send the letter of offer (circular) to all those existing shareholders whose names are recorded in the books on a particular date to issue rights.
• The time given to accept the right offer should not be less than 15 days.
• The circular/notice issued to the shareholder must state the right of the shareholder to renounce the offer in favour of others.
• After the expiry of the time mentioned in the notice, the Board of Directors has the right to dispose the unsubscribed shares in any manner as per the benefit of the company.
The existing shareholders whose names are there in the list has four options:
• They can exercise the rights.
• They can renounce the rights and sell them the same in the open market in favour of another person.
• They can renounce part of the rights and exercise the other part.
• Doing nothing.
This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc. - Private Placement: It refers to the direct sale of newly issued securities by the company to a small number of institutional investors through merchant bankers. They are generally selected clients.
• Unit Trust of India
• Life Insurance Corporation of India
• General Insurance Corporation of India
• Army Group Insurance
• State Level Financial Corporations
Advantages:
• Less time taken to issue these shares.
• Comparatively less amount of cost of capital is req*fired.
• These issues are tailor-made to suit the requirement of both the parties.
• Less formalities are required. - Offer to employees: Stock options to the employees refers to the offer given by the company to the employees to become shareholders. This method facilitates the employees to become shareholder and can earn a part of the share of profits.
2.When an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company, he/ she tends to be in advantageous position and get many benefits out of it. Explain the benefits.
Answer.


3.While there are benefits to going public, at the same time additional obligations and reporting requirements on the companies and its directors means disadvantages too. What are they? Explain.
Answer.While there are benefits to going public, it also means additional obligations and reporting requirements such as:
- Increasing accountability to public shareholders
- Need to maintain dividend and profit growth trends
- Becoming more vulnerable to an unwelcome takeover
- Need to observe and adhere strictly to the rules and regulations by governing bodies
- Increasing costs in complying with higher level of reporting requirements
- Relinquishing some control of the company following the public offering
- Suffering a loss of privacy as a result of media interest
Discussions with lawyers, independent accountants and other professional advisors will also provide better considerations.
Overall, going public is a complex decision that requires careful consideration and planning.
Entrepreneurs should examine their current and future capital needs, and be aware of how an IPO will affect the availability of future financing.
E. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
1. Why primary market is also known as new issue market? Give one reason.
Answer. When an entrepreneur decides to issues securities like shares, debentures to the public for the first time for the purpose of obtaining capital funds such issues of securities are even referred as “new money issues”. Primary market is known as new issue market.
SECTION-C: STOCK EXCHANGE
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What are the responsibilities of governing body?
Answer. The governing body is responsible for policy formulation and proper functioning of the exchange, having wide range of powers:
- Elect the office bearers and set up committees
- Interpret rules, regulations and by-laws
- Admit and expel members
- Adjudicate disputes
- Manage the properties and finance of the exchange
- Conduct the affairs of the exchange.
2.Name the stock exchanges where most of the stock trading in India is done.
Answer. Most of the stock trading in India is done on NSE and BSE.
The BSE is the Bombay Stock Exchange and the NSE is the National Stock Exchange.
The BSE is situated at Bombay and the NSE is situated at Delhi.
These are the major stock exchanges in the country.
3.What is a secondary capital market?
Answer. Any transaction in shares or debentures subsequent to its primary offering is called “Secondary Transaction”. Thus, the secondary capital market, which is also known as old securities market or stock exchange deals- with buying and selling of old securities i.e. the market securities issued earlier are sold by existing investors in this market.
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
1.What is the alternate name of stock used by different people?
Answer. The word “stock” is called by different names with different people like shares, equity, scrip and so on but all these words have same meaning.
C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Explain the importance of Stock Exchange from the companies point of view.
Answer. From the companies point of view:
- Widespread market
- High share value
2.Explain the importance of Stock Exchange from the viewpoint of investors.
Answer. From the investor’s point of view:
- Dissemination of useful Information: It publishes useful information regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals.
- Ready Market: It will be easy way platform for all those for buying and selling shares and convert it into cash through a member of stock exchange.
- Investors’ Interests Protected: Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not exploit the investors.
- Genuine guidance about the securities listed.
- Barriers of distance removed.
- Knowledge of profit or loss on investments and ensures a measure of safety and fair dealings to the investors.
3.Explain the importance of Stock Exchange from the viewpoint of society.
Answer. From the societies point of view:
- Rapid Capital Formation
- Economic Development
- National Projects
4.Rahil (Finance) and Anushk (HR) are doing MBA (IIM Indore). While reading the newspaper Anushk saw the heading Sensex goes up. But last week the heading was different that Sensex goes down now some confusion was going on her mind, immediately she asked her Friend Rahil the same? Now according to you how Rahil will clear the confusion of Anushk? Explain and give some value points.
Answer. Rahil explains him in this way: The Sensex is an “index”.
An index is basically an indicator. It gives you a general idea about whether most of the stocks have gone up or most of the stocks have gone down.
The Sensex is an indicator of all the major listed companies of the BSE.
The BSE, is the Bombay Stock Exchange and the NSE is the National Stock Exchange. The BSE is situated at Bombay and the NSE is situated at Delhi. These are the major stock exchanges in the country.
If the Sensex goes up, it indicates that the prices of the stocks (shares) of most of the major companies on the BSE have gone up.
If the Sensex goes down, this tells you that the stock price of most of the major stocks on the BSE have gone down.
In this way Rahil cleared the confusion
of Anushk.
Value Points:
- Quest for knowledge
- Helpfulness
- Consideration for others
- Awareness of responsibility
- Readiness to cooperate
- Friendship.
D. VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Write down the features of stock exchanges.
Answer.
- Association of persons: A stock exchange is an association of persons or body of individuals which may be registered or unregistered.
- Recognition from central government: Stock exchange is an organized market. It requires recognition from the Central Government.
- Market for securities: Stock exchange is a market, where securities of corporate bodies, government and semi-government bodies are bought and sold.
- Deals in second hand securities: It deals with shares, debentures, bonds and such securities already issued by the companies. In short, it deals with existing or second hand securities and hence it is called secondary market.
- Regulates trade in securities: Stock exchange does not buy or sell any securities on its own account. It merely provides the necessary infrastructure and facilities to its members and brokers who trade in securities. It regulates the trade activities so as to ensure free and fair trade.
- Allow dealings only in listed securities: In fact, stock exchanges maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on its floor. Securities which do not figure in the official list of stock exchange are called unlisted securities. Such unlisted securities cannot be traded in the stock exchange.
- Transactions effected only through members: All the transactions in securities at the stock exchange are effected only through its authorized brokers and members. Outsiders or direct investors are not allowed to enter in the trading circles of the stock exchange. Investors have to buy or sell the securities at the stock exchange through the authorized brokers only.
- Working as per rules: Buying and selling transactions in securities at the stock exchange are governed by the rules and regulations of stock exchange as well as SEBI Guidelines. No deviation from the rules and guidelines is allowed in any case.
- Specific location: Stock exchange is a particular market place where authorized brokers come together daily (i.e. on working days) on the floor of market called trading circles and conduct trading activities. The price of different securities traded are shown on electronic boards. After the working hours market is closed. All the working of stock exchange is conducted and controlled through computers and electronic system.
- Financial barometers: Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country. Industrial growth and stability is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
2.Explain the functions of stock exchange.
Answer.Stock exchange performs a number of functions in respect of marketability of different types of securities for investors and borrowing companies. It’s important functions are:
- Continuous and ready market for securities:
• Stock exchange provides a central market for purchase and sale of securities.
• It provides ready and continuous outlet for buying and selling of securities.
• It facilitates and helps all buyers to buy and sell securities as and when they want. - Facilitates evaluation of securities:
• It is useful for the correct evaluation of industrial securities.
• It publishes price quotation of the shares of the companies that have been listed with them after thorough analysis of demand and supply position.
• This enables investors to know the true worth of their holdings at any time. - Checks on brokers: It checks and controls the activities of brokers and protect the investors from being deceived.
While dealing,’if any broker is found indulging in malpractices as overcharging or giving wrong information, his/her licence may be cancelled. - Provides safety and security in dealings:
• All activities of the stock exchange are controlled by the provisions of the Securities Control (Regulation) Act and this creates confidence in the mind of investors.
• Each and every dealings and transactions are conducted as per well defined rules and regulations, fraudulent practices stands checked effectively ensuring safety, security and justice in dealings. - Regulates company management: All listed companies in the stock exchange, compulsorily have to follow with rules and regulations of concerned stock exchange and work under the vigilance of their authorities.
E. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
1.Stock exchange performs a number of functions in respect of marketability of different types of securities for investors and borrowing companies. Explain the important functions of stock exchanges.
Answer.
- Continuous and ready market for securities: Stock exchange provides a central market for purchase and sale of securities. It provides ready and continuous outlet for buying and selling of securities. Buyers and sellers strongly believe that they would be able to buy and sell securities as and when they want.
- Facilitates evaluation of securities: Stock exchange is useful for the evaluation of industrial securities. It publishes price quotation of the shares of the companies that have been listed with them after thorough analysis of demand and supply position. This enables investors to know the true worth of their holdings at any time.
- Checks on brokers: Stock exchanges control the activities of brokers and protect the investors from being deceived. Now, if any broker is found indulging in malpractices as overcharging or giving wrong information, his/her licence may be cancelled.
- Provides safety and security in dealings: Activities of the stock exchange are controlled by the provisions of the Securities Control (Regulation) Act and all this creates confidence in the minds of investors. As transactions are conducted as per well defined rules and regulations, fraudulent practices stands checked effectively ensuring safety, security and justice in dealings.
- Regulates company management: Listed companies have to comply with rules and regulations of concerned stock exchange and work under the vigilance of stock exchange authorities.
- Intensifying capital formation: Stock exchange accelerates the process of capital formation through creating the habit of saving, investing and risk taking among the investing class by converting their savings into profitable, safe investments.
- Facilitates raising of new capital:Because of stock exchange, for either development, organisation or expansion, the need for more capital by the existing companies is easily met out.
- Facilitates public borrowing:Stock exchange serves as a platform for marketing government securities. It enables government to raise public debt easily and quickly.
- Facilitates healthy speculation: Healthy speculation keeps the exchange active. Normal speculation is not dangerous but provides more business to the exchange. However, excessive speculation is undesirable as it is dangerous to investors and the growth of corporate sector.
- Serves as economic barometer: Stock exchange indicates the state of health of companies and the national economy. It acts as a barometer of the economic situation/conditions and is thus referred to as ‘pulse of economy’ or ‘economic mirror’.
- Facilitates bank lending: Banks easily know the prices of quoted securities. They offer loans to customers against corporate securities. This gives convenience to the owners of securities.
SECTION-D: SEBI AND OTHERS
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What do you mean by stock exchange?
Answer.A stock exchange means anybody of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealing in securities,
2.What is SEBI?
Answer. The Securities and Exchange Board of India or SEBI is the regulator for the securities market in India. It was established on 12 April, 1992 through the SEBI Act, 1992.
3.State three functions of SEBI rolled into one body.
Answer. SEBI has three functions rolled into one body: quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial and quasi-executive.
4.“Humorously, they were once given the acronym FFF for Angel Investors”. What does FFF stand for?
Answer. Friends, Family and Fools.
5.What do you understand by angel investors?
Answer. Business angel or informal investor or an angel investor, is an individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What is SEBI and what is its role?
Answer. The Securities and Exchange Board of India or SEBI is the regulator for the securities market in India.
Role of SEBI:
- It is a supervising and regulatory body to check certain malpractices and works for promoting the securities markets in India.
- It has three functions rolled into one body: quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial and quasiexecutive.
- It drafts regulations in its legislative capacity, it conducts investigation and enforcement action in its executive function and it passes rulings and orders.
2.Who manages SEBI?
Answer. SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of following:
- Chairman who is nominated by Union Government of India.
- Two members, i.e. Officers from Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from Reserve Bank of India.
- The remaining 5 members are nominated by Union Government of India, out of them at least 3 shall be whole-time members.
3.Explain briefly the three functions of SEBI rolled into one body.
Answer. SEBI has quasi-legislative capacity as it makes rules and regulations. It has rule-making authority related to the matters of securities in India.
SEBI is a quasi-judicial body as it has an entity such as an arbitrator or tribunal board, and has powers and procedures resembling those of a court. SEBI is quasi-executive as it functions like an executive but that is not really an executive.
4.What do you understand by venture capital?
Answer.
- Venture capital is a type of private equity capital provided as seed funding to early-stage.
- The investors provide funds to give shape to their ideas.
- It aims at avoiding death of an enterprise even before they could be tried.
- This investment enables the investors to accomplish objectives, in return for minority shareholding in the business or the irrevocable right to acquire.
- It is more accurate to view venture capital broadly as a professionally managed pool of equity capital.
- It is a way by which investors support entrepreneurial talent with finance and business skills for obtaining long-term capital gains.
5.Enlist several categories of financing possibilities in which smaller ventures sometimes rely on.
Answer. Following are several categories of financing possibilities in which smaller ventures sometimes rely on:
- Venture capital
- Seed Capital Finance
- Start up finance
- Loan from various financial institutions like, IDBI, SIDBI, IFCI, ICICI, NABARD, IIBI, SFCs, TFCI, AND SIDC.
6.Why are venture capitalists typically very selective in deciding while doing the investment?
Answer.
- Venture capital involves high risk as its is done for entrepreneurs who lack the necessary experience and funds to give shape to their ideas.
- The proposal of a new venture involves new or untried technology put forward by professionally or technically qualified persons involving high risk factors. This may fail to attract investments from public, which may result in their death even before they could be tried.
- Also the investments of venture capitalists are illiquid and require the time period to give returns. Venture capitalists thus have to carry out detailed due diligence prior to investment.
C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Explain the powers SEBI has been vested with for discharging of its functions efficiently.
Answer. SEBI has been vested with the following powers:
- To make and approve by-laws of stock exchanges.
- To enquire the stock exchange to amend their by-laws.
- Inspect the books of accounts and call for periodical returns from recognized stock exchanges.
- Inspect the books of accounts of financial intermediaries.
- Compel certain companies to list their shares in one or more stock exchanges.
- Levy fees and other charges on the intermediaries for performing its functions.
- Grant license to any person for the purpose of dealing in certain areas.
- Delegate powers exercisable by it.
- Prosecute and judge directly the violation of certain provisions of the Companies Act.
- Power to impose monetary penalties.
2.What are the features of venture capital finance?
Answer. Venture capital finance has the following features:
- Equity: It is equity finance in relatively new ventures and new companies.
- Long term: It is long-term investment in growth-oriented small or medium firms.
- Skills: Venture capitalist also business skills to investee firms. This raises the chances of success of the emerging firm.
- Risk: It involves high risk-return spectrum.
- Private equity: It is a subset of private equity.
- Involvement: The venture capital institutions make a continuous involvement in the business.
3.When can an entrepreneur seek venture capital financing?
Answer. An entrepreneur seeks venture capital financing under following circumstances:
- High risk: Ventures which involve high risk due to various reasons like technological, creativity and innovation, etc. are subjected to high risk related to returns. Here the venture capitalist comes forward.
- Seed funding: Seed money, is a form of securities offering in which an venture investor purchases part of a business. Interest of the venture capitalist for purchase of security is also a reason.
- Expansion: If the entrepreneur wants to expand then he goes for venture capital.
- Business skills: Lack of business skills also forces the entrepreneur to go for venture capital.
D. VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
1.Explain the characteristics of angle investors.
Answer. Following are the characteristics of angle investors:
- High net worth: Most angle investors are current or retired executives, business owners, etc. They have the knowledge, expertise, and funds to help start-ups.
- High risk: Angle investors bear extremely high risk. They expect a very high return on investment which they are making.
- Guidance: Most angle investors provide proactive advice, guidance, or mentoring services for the start-ups in its early days of the enterprises.
- High returns: Angle investors also have objective to create successful companies by providing value creation, and guiding investors realize a high return on investments.
- Experience: Angle investors have a sharp inclination to keep themselves updated to current developments in a particular business area and then mentor another group of entrepreneurs by making use of their precious experience.
- Type of Investments: Most angles invest in small, start-up businesses with fewer employees. The arrangements are informal.
- An individual investor: Angle investors are usually individuals.
E. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Question 2.Why it is said that “A venture capitalists investments are illiquid”. Give reason.
Answer. Illiquid describes an asset or security that cannot be sold quickly. Uncertainly the asset value is associated with the investment. This can be due to economic instability or issues relating to the asset. If the asset value declines, it becomes an illiquid asset due to the unclear value. It can be hard to locate a market for these products. This may lead to loss of the money.
SECTION-E: SPECIALISED FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
A. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.What is the role of Specialized Financial Institutions in India?
Answer.
- The role of Specialized Financial Institutions (SFIs) also called development banks make an important source of medium and long-term financing amongst all the financial institutions in India.
- They generally provide finances to the business and they help in promotion of new industries/new entrepreneur.
2.Enumerate the types of Specialised Financial Institutions from where entrepreneur can access capital according to their need and requirements.
Answer.A. At national level/All India development banks
- Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
- Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI)
B. At state level
- State Financial Corporation (SFCs)
- Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI)
- State Industrial Development ,Corporations (SIDC)
3.When was SIDBI established?
Answer. SIDBI was established in April 1990, as a wholly owned subsidiary of IDBI, under the Small Industries Development Bank of India Act, 1990.
B. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Explain the need and importance of Specialized Financial Institutions in India.
Answer. As SFIs provide developmental finance, that is, finance for investment in fixed assets, they are also known as ‘development banks’ or ‘development financial institutions’. Establishing of SFIs facilitated:
- Provision of sufficient long-term funds in the desired sectors in accordance with planned priorities to the industrial units and entrepreneurs.
- New and small entrepreneurs in setting up industry.
- Development of: (i) Small scale industry, and (ii) Projects in backward areas.
- Provision of technical and managerial advice to the entrepreneurs, facilitating thus, in identification, evaluation and execution of new investment enterprises.
- Underwriting of and direct subscription to the issue of shares and debentures in the capital market of the upcoming ventures.
- Establishment of enterprises which require extraordinarily large amount of finance for their projects with a long-gestation period.
2.Explain the objectives and functions of SIDC.
Answer.
- SIDCs: The State Industrial Development Corporations (In-corporated under the Companies Act, 1956) were set up in different states as state government as companies wholly owned by them, the main objectives of SIDCs was promoting industrial development in all states of the countries.
- At present, 22 such SIDCs are functioning in India.

3.Write the full form of and when it was established.
(a)SIDC
(b) TFCI
(c) SFC’s
(d) NABARD
(e) IFCI
(f) IDBI
(g) ICICI
Answer.

C. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Apoorva wants to start a new business near to her locality, for which she requires capital. State different types of national level and state level financial institutions from where Apoorva can access capital according to her needs and requirements.
Answer. Types of Specialised Financial Institutions: Entrepreneurs have access to any of the following SFIs to choose from, according to their needs and requirements:

2.Write down the objectives of IDBI.
Answer. The main objectives of IDBI:

3.Write an explanatory note on the financing schemes of state level financial institutions and their importance in promotion of an entrepreneur in India.
Answer.At State Level State Financial Corporation (SFCs):
To meet the financial needs of small and medium enterprises, the government
of India passed the State Financial Corporation Act in 1951, empowering the state governments to establish development banks for their respective I regions. There are 18 SFCs at present.
Objectives: The objectives of State Financial Corporations are as under:
- Provide financial assistance to small and medium industrial concerns.
These may be from corporate or co-operative sectors as in case of IFCI or may be partnership, individual or Joint Hindu family business,
engaged not only in the manufacture, preservation or processing of goods. - Provide long and medium-term loan repayment ordinarily within a period not exceeding 20 years.
- Grant financial assistance to any
single industrial concern under corporate or co-operative sector with an aggregate upper limit of r rupees Sixty lakhs. In any other case(partnership, sole proprietorship or Joint Hindu family) the upper limit is rupees thirty lakhs. - Provide financial assistance generally to those industrial concerns whose paid up share capital and free reserves do not exceed Rs 3 crore.
- To lay special emphasis on the development of backward areas and small scale industries.
Functions:
- Grant of loans and advances to or subscribe to debentures of, industrial concerns repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
- Guaranteeing deferred payments due from an industrial concern for purchase of capital goods in India.
- Underwriting of the issue of stock, bonds or debentures by industrial concerns.
- Subscribing to, or purchasing of, the stock, shares, bonds or debentures of an industrial concern subject to a maximum of 30 per cent of the subscribed capital, or 30 per cent of paid up share capital and free reserve, whichever is less.
- Act as agent of the Central government, State government, IDBI, IFCI or any other financial institution in the matter of grant of loan or business of IDBI, IFCI or financial institution. Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI): The Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI) was born as a result of the Government of India’s decision, in 1987, to promote a separate all- India financial institution for providing financial assistance to tourism-related activities/projects.
Functions:
- TFCI provides financial assistance to enterprises for setting up or the development of tourism-related projects, facilities and services such as hotels, restaurants, holiday resorts, amusement parks, entertainment centres, education and sports, rope ways, cultural centres, convention halls, transport, travel and tour operating agencies, air services, tourism emporia and sports facilities.
- It also provides advisory and merchant banking services in this field.
- The projects with a capital cost of Rs 1 crore or above are generally eligible for assistance from TFCI. Smaller projects would also be considered.
State Industrial Development Corporation (SIDCs): Incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 SIDCs were set up in different states as wholly owned companies for promoting industrial development in their respective states. The main functions of SIDCs are as follows:
- Providing term finance to all small, medium, and large industrial enterprises set up in the state.
- Underwriting and directly subscribing to shares, and debentures of industrial enterprises being set up in the state.
- Preparing feasibility studies, conducting market surveys and motivating private entrepreneurs to set up their industrial ventures in the state.
- Collaborating with private entrepreneurs to set up industrial ventures in joint and assisted sectors.
- Implementing IDBI’s scheme of seed capital in the state.
Finance can be procured, just like any other resource, against a cost. Procurement of finance involves risk and formalities to comply with. Entrepreneurs need a careful attitude, to sensibly make a choice of sources to generate funds. No one source can be deemed to be the best source. Thus, it is always advisable to select a combination of sources so that both cost and risk can be kept at lowest.
- Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI)
- State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC)
4.Write a short note on IIBI.
Answer. Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI): The Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was formed by transforming the Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI). It was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies. IRBI was incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 and renamed as the Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. in March 1997.
Functions: IIBI offers a wide range of products and services such as:
- Term-loan assistance for project finance
- Short duration non-project asset – backed financing working capital/ other short term loans to companies
- Equity Subscription Asset Credit
- Equipment finance
- Investments in Capital Market and Money market instruments.
5.Describe the form of assistance provided by SIDBI to the industrial concern.
Answer. The financial assistance of SIDBI to the small scale sector is channelised through the following two routes:
- Indirect Assistance: Under its indirect schemes, SIDBI extends refinance of loans to small scale sector by Primary Lending Institutions (PLIs) viz. SFCs, SIDCs and Banks. At present, such refinance assistance is extended to 892 PLIs and these PLIs extend credit through a net work of more than 65,000 branches all over the country. All the Schemes of SIDBI both direct and indirect assistance are in operation in all the States of the country through 39 regional/branch offices of SIDBI.
- Direct Assistance: SIDBI directly assists SSIs under:
• Project Finance Scheme
• Equipment Finance Scheme
• Marketing Scheme
• Vendor Development Scheme
• Infrastructural Development Scheme
• ISO-9000
• Technology Development & Modernisation Fund.
D. VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.Explain the main objectives and functions of ICICI.
Answer. The ICICI has been established to achieve the following objectives:
- To assist in the formation, expansion and modernization of industrial units in the private sector.
- To stimulate and promote the participation of private capital (both Indian and foreign) in such industrial units.
- To furnish technical and managerial aid so as to increase production and expand employment opportunities.
2.Explain in detail objectives and three important Primary functions ofNABARD.
Answer. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD): On 15th December, 1981, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) Bill was passed in the Parliament, which started functioning on 1st July, 1982. NABARD was established according to the Preamble to the Act, for providing credit for the promotion of:
- Agriculture
- Small-scale Industries
- Cottage and Village Industries
- Handicrafts and other rural crafts
- Other economic activities in rural areas with a view for promoting IRDP.
Objectives:
- The bank will serve as a financing institution for institutional credit such as long-term, short-term, and for the promotion of activities in rural areas.
- To provide direct lending to any institution as may be approved by the central government.
Functions: The primary functions of NABARD can be classified under three heads:
- Credit Functions: NABARD provides different types of refinance to eligible institutions. They assist entrepreneurs through:Short-term credit to State Cooperative Banks, Regional Rural Banks and Other financial institutions approved by RBI.
- Developmental Functions:
• NABARD coordinates the operations of rural credit institutions.
• It develops expertise to deal with agricultural and rural problems so as to assist in rural development efforts. - Regulatory Functions:
• NABARD is empowered to undertake inspection of RRBs and Cooperative Banks, other than the Primary Cooperative Banks.
• Toopenanew branch, arecommendation ofNABARD is imperative by RRBs or Cooperative Banks to seek permission from RBI.
E.HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
1.“TFCI is playing vital role in the development of entrepreneurship in modern economy”. Comment.
Answer.The Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI) was born as a result of the Government of India’s decision, in 1987, to promote a separate all- India financial institution for providing financial assistance to tourism-related activities/projects.
It was incorporated as a public limited company under the Companies Act, 1956 on 27 January, 1989. It became operational with effect from 1 February, 1989.It is a specialized all-India development financial institution to cater to the needs of the tourism industry.
Functions:
- It provides financial assistance to enterprises for setting up or the development of tourism- related projects, facilities and services such as hotels, restaurants, holiday resorts, amusement parks, entertainment centres, education and sports, rope ways, cultural centres, convention halls, transport, travel and tour operating agencies, air services, tourism emporia and sports facilities.
- It provides advisory and merchant banking services in this field.
- The projects with a capital cost of Rs 1 crore or above are generally eligible for assistance from TFCI. Smaller projects would also be considered.
(d) TFCI has sanctioned assistance to 2003 projects aggregating to Rs 5.2 billion during the last five years, resulting in more than 12,217 hotel rooms and direct employment to 22,938 people.
Values:
- Universal and equality
- Resourcefulness
- Services to others
- Readiness to cooperate
- National awareness
- Employment opportunities
- Fulfilling the needs of the people
- Helpfulness and contributing to entrepreneur for the growth of the country.
3. Hari is an entrepreneur who wants to start an amusement park in Indore. He knows that she needs a huge amount of initial capital. According to you, which of the financial institution will be more suitable to him? Suggest and Explain why?
Answer. Accordingly Hari should approach to Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI), the financial institution.
TFCI is playing vital role in the development of entrepreneurship in modern economy. The Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI) was born as a result of the Government of India’s decision, in 1987, to promote a separate all-India financial institution for providing financial assistance to tourism-related activities/projects.It was incorporated as a public limited company under the Companies Act, 1956 on 27 January, 1989.It became operational with effect from 1 February, 1989. It is a specialized all- India development financial institution to cater to the needs of the tourism industry.
The various functions:
- It provides financial assistance to enterprises for setting up or the development of tourism- related projects, facilities and services such as hotels, restaurants, holiday resorts, amusement parks, entertainment centres, education and sports, rope ways, cultural centres, convention halls, transport, travel and tour operating agencies, air services, tourism emporia and sports facilities.
- It provides advisory and merchant banking services in this field.
- The projects with a capital cost of? 1 crore or above are generally eligible for assistance from TFCI. Smaller projects would also be considered.
Values:
- Providing employment opportunities
- Cater to the financial needs of the tourism industry.
- To protect national property.
- Awareness of responsibility of citizenship
- Initiative
- Proper utilization of time and resources.
3.Assuming that you wish to start a small scale industry for manufacturing and selling detergent powder, discuss how would you seek support of financial institutions.
Answer. Yes, to start with a small scale industries for manufacturing and selling is really a tough job in this competitive world where already many other detergent manufacturing units are there. Detergents are also known as synthetic detergents. They are different from oil-based soap though both soaps and detergents are surfactants. There are a number of varieties of detergents varying in percentages of active matter present in them and also different colours. Manufacturing process is very simple and only mixing is involved. Hence, this product is best suited for manufacturing in small-scale sector.
An entrepreneur can seek support from various financial institutions and others.
- Angle Investors:
• Business angle or an angle investor is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies having a high- risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
• Apart from investing funds, most angles provide proactive advice, guidance, industry connections and mentoring start-ups in its early days. - Venture Capitalist:
• Venture capital is an equity based investment in a growth-oriented small to medium business to enable the investors to accomplish objectives, in return for minority shareholding in the business or the irrevocable right to acquire.
• The private equity capital provided as funding to early-stage, high potential, high risk, growth up companies/entrepreneurs who lack the necessary experience and funds to give shape to their ideas.
• Accordingly, it is more accurate to view and go for venture capital broadly as a professionally managed pool of equity capital.
• Venture capital is a way in which investors support entrepreneurial talent with finance and business skills to exploit market opportunities and obtain long-term capital gains.
State Financial Corporations (SFCs):
- It will be to meet the financial needs of small and medium enterprises, established as development banks for their respective regions. Under the Act, SFCs have been established by state governments to meet the financial requirements of medium and small sized enterprises. There are 18 SFCs at present. According to the location I can easily approach the same.
- Grant of loans and advances to or subscribe to debentures of, industrial concerns repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
- Guaranteeing loans raised by industrial concerns which are repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
- Guaranteeing deferred payments due from an industrial concern for purchase of capital goods in India.
4.Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of financial institutions for an entrepreneur.
Ans.Advantages of financial institutions for an entrepreneur
- Borrowing money from the bank is one of the simplest ways to get needed funds to start or grow your business.
- To grant loans and advances.
- To underwrite or to subscribe to shares or debentures of industrial concerns.
- To guarantee loans raised by industrial concerns in the market.
- To provide consultancy and merchant banking services in or outside India.
- To provide technical, legal, marketing and administrative assistance to any industrial concern or person for promotion, management or expansion of any industry.
- Co-ordination, regulation and supervision of the working of other financial institutions such as IFCI, ICICI.
- To act as trustee for the holders of debentures or other securities.
- To provide long and medium-term credit to industrial concerns engaged in manufacturing, mining, shipping and electricity generation and distribution.
- The bank will serve as a financing institution for institutional credit such as long-term, short-term, and for the promotion of activities in rural areas.
- Provides financial assistance to enterprises for setting up or the development of tourism-related projects.
Disadvantages: Procurement of finance involves risk and formalities to comply:
- State Financial Corporations only provide long and medium-term loan repayment ordinarily within a period not exceeding 20 years.
- Some financial institutions provide financial assistance generally to those industrial concerns whose paid up share capital and free reserves do not exceed Rs 3 crore.
- Rate of interest is too high sometimes not able to pay the debt amount and its interest.
5.Distinguish between ICICI and SIDBI.
Answer.

6.How NABARD is different from TFCI?
Answer.


7.Company A goes for public issue of 10,000 shares @ Rs 10 each. Application were received for only 5,000 shares. Can the company proceed with the process of issuing shares?
Answer. In the case of Company A
Issued shares to public — 10,000 Shares @ 10 each.
Applied share public by — 5,000 Shares @ 10 each.
Company receives only 50% of the subscription within 120 days from the date of the issue, then it is called as Minimum subscription.
As per the SEBI guidelines, if the company does not receive 90% of the issue amount from the public subscription including development from underwriters within 120 days from the date of the issue, the amount of subscription received is required to be refunded to the applications. In case of disputed development also, subscription is required to be refunded if 90% of the issued amount plus accepted. Development from underwriters if any is not received within 120 days of the issue of prospectus, all the money received from the applicants for shares is required to be repaid forthwith without interest and if any such money is not so repaid in the next 10 days (after the expiry of 120 days), the directors of the company are jointly and severally liable to repay that money, with interest from the expiry of the 130 days.
The company should refund the amount within 10 weeks of the closing of the subscription list and pay interest, if refunds are delayed by more than 8 days after this period.
VALUE BASED QUESTIONS
Question 1. Harish is working as the chief accountant in ABC infrastructure Ltd. He came to It also provides advisory and merchant banking services in this field.know that the company is planning to announce an interim dividend. He purchased 2000 shares of the Co. at the market price of ? 215 with the expectation of an appreciation in the market price. When the price increased to ^ 537 he sold his holdings & made a handsome profit. Name the related concept which social values have been affected here?
Answer. Before deciding right or wrong conduct of a chief accountant let us understand what is interim dividend, role of a chief accountant, his conduct for his benefit and affected social values.
- Interim dividends are dividend payments made before a company’s Annual General Meeting (AGM) and final financial statements. This declared dividend usually accompanies the company’s interim financial statements.
- As a chief accountant of a company he should not disclose confidential information which might be acquired in course of his work during the meeting time and he should not even use such information for his personal gain or gain for others.
- The above case study is concerned with unethical behaviour done by the chief accountant.
- Affected social values are trust, honesty, duty, loyalty and truthfulness.
Question 2. By offering shares to its employers what values are promoted by a company.
Ans. Offering shares for sale to its employers means firstly new securities are offered to an intermediary at a fixed price then it is further resold to general public at a higher price.
Following values are promoted by a company:
- Self existent.
- Intermediaries can earn high amount of profits in future.
- Readiness to cooperate.
- Free from the tedious work of making public issue.
- Encouraging them for saving.
- Building a trust.
- It helps easily and directly in capital formation of the company.
- It is an easy method raising funds.
- Helpfulness.
- Faithfulness for utilization of their money.
Question 3.Mr. B the financial Manager of ABC Company purchases 100 shares of the Company just before the rights issue was announced. Is the behaviour of the manager ethical? What would you do as a legal advisor of the company?
Answer.
- Yes, the behaviour of the manager is unethical because rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on prorate basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
- As a legal advisor of the company, I advice that he should not be given that right of extra shares.
- As a manager his responsibility is to develop and analyse information
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question 1. What do you mean by “Financial Intermediation”?
Answer. The role of transferring financial resources from the surplus units to the deficit units is referred to as “Financial Intermediation”.
Question 2. Who plays a very vital role in a financial intermediatary.
Answer.Capital markets play a very vital role in a financial intermediatary.
Question 3. Identify the logo given below.

Answer. IDBI Bank.
Question 4. Name one of the financial institutions guaranteeing loans raised by Industrial concerns which are repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
Answer. State Financial Corporations (SFCs) guaranteeing loans raised by industrial concerns which are repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
Question 5. List any four participants in capital market.
Answer.

Question 6.Name one financial institution which was formed by transforming The Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India.
Answer. The Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was formed by transforming The Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI).
Question 7. Name one financial institution which was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies.
Answer. Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies.
Question 8. Name one financial institution which can sanction amount to a single concern i.e. minimum amount Rs. 5 lakhs and it does not go beyond the maximum limit of Rupees one crore.
Answer.Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI).
Question 9. Name one financial institution which extends seed capital/loan assistance under the National Equity Fund, Mahila Udyan Nidhi and Mahila Vikas Nidhi.
Answer. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI).
Question 10. Name one of the financial institutions guaranteeing loans raised by industrial concerns which are repayable within a period not exceeding 25 years.
Answer. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
Question 11. Why stock exchange is called as the ‘financial barometers’ and development indicators of national economy?
Answer. Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country. Industrial growth and stability is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
Question 12. By which act the organisation, management, membership and functioning of stock exchanges in India are governed?
Answer.The organisation, management, membership and functioning of stock exchanges in India are governed by the provisions of The Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956.
Question 13. Name the market which enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
Answer. The secondary market enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
Question 14. Who are in need of the help of capital markets?
Answer. The help of capital market is for:
- Industry
- Trade
- Finance
- Government.
Question 15. For what purpose the productive capital is raised?
Answer. Productive capital is raised and made available for industrial purposes.
Question 16. Mention two major instruments of capital market.
Answer.
- Equity Shares
- Debentures
Question 17. What is the other name of primary market?
Answer. New Issue Market (NIM).
Question 18. Name two methods of flotation of primary market.
Answer.
- Private Placement
- e-IPOs.
Question 19. Name the most popular method of raising funds by companies in the primary market.
Answer. Offering shares through prospects.
Question 20. Name two segments of capital market.
Answer.
- Primary market
- Secondary market.
Question 21. What do you mean by lease rent?
Answer. When assets are owned by ICICI but allowed to be used by industrial concerns for a consideration is called lease rent.
Question 22. Name two Indian stock market index.
Answer. SENSEX and NIFTY.
Question 23. Name two National Stock Exchanges.
Answer. NSE (National Stock Exchange of India) and OTCEI (Over the Counter Exchange of India)
Question 24. Name two regional stock exchanges.
Answer.
- Bombay Stock Exchange and
- Calcutta Stock Exchange.
Question 25. “ Internal sources are referred to as owner’s own money”. Give one alternate name for owner’s own fund.
Answer. Alternate name for owner’s own fund is also known as ‘equity’.
Question 26. Define Stock Exchange.
Answer. A stock exchange means anybody of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealing in securities. Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956.
Question 27. Name the institution which owned.an asset but allowed to be used by industrial concerns for a consideration called lease rent.
Answer. ICICI.
Question 28. Why is NSEI called a ringless stock exchange?
Answer. In traditional stock exchange securities are traded only by coming into a specified place called ring.But NSEI has not kept a particular place for trading/dealings in the transactions. All the transactions take place electronically or e-issues.
Question 29. What do you understand by listed securities?
Answer.When companies securities that are registered and traded in stock exchange are known as “Listed Securities”.
Question 30. Bhavin, Abhishek and Mohit are the directors of a newly established company at Indore. The paid-up capital equity share capital of a company is 4 crore, they are interested to trade its shares at all India level stock exchange. You are a finance manager of a company, suggest the name of the stock exchange for the purpose of trade.
Answer.National Stock Exchange of India (NSEI).
Question 31. What do you mean by capital market?
Answer. A capital market may be defined as an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital or financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs.
Question 32. What do you mean by primary market?
Answer. Primary market refers to the market where issue of securities (shares, debentures and bonds) being issued for the first time by new companies or new issue of securities by existing companies to investors. It is basically to facilitate transfer of resources from the savers to entrepreneur for seeking more funds.
Question 33. “SEBI is managed by its members”. How many members are there in SEBI and who nominate them?
Answer. SEBI is managed by its members
- Chairman who is nominated by Union Government of India.
- Two members, i.e. Officers from Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from The Reserve Bank of India.
- The remaining five members are nominated by Union Government of India, out of them at least three shall be whole-time members.
Question 34. Rahul wants to start an amusement park near Vishakhapatanam. This will require an investment of Rs 50 lakhs. Name the financial institution which Rahul should approach for financing this venture. [CBSE Delhi 2015]
Answer. Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI).
Question 35. Geeta Ram, an orange grower from Nagpur, wants to start a small juice producing factory using the oranges grown by him as well as by his fellow villagers. Name the financial institutions he should contact for obtaining loan for starting his factory. [All India 2015]
Answer. Geeta Ram should contact National Bank for Agricultural and Rural development (NABARD) for starting his factory.
II.SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question 1. What is meant by ‘Capital Structure’?
Answer. It is the composition or mix of different types of long-term capital whether owned or borrowed. It includes all the long term funds consisting of share capital, debentures, bonds, loans and reserves.
Question 2. How does capital market satisfy firstly savers and at the same time investors ?
Answer. Capital market is a place where savers as well as investors get maximum satisfaction. The capital market satisfies the tastes of savers and the needs of investors through its various financial instruments and institutions. As per entrepreneurs requirement they enter either of the following markets available under capital market.
Question 3. What does the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 permit?
Answer. This Act permits only recognized stock exchanges to function under the rules, regulations and by-laws approved by the ‘ Central Government.
The organisation, management, membership and functioning of stock exchanges in India are governed by the provisions of The Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956.
Question 4. How do primary and secondary markets promote capital formation?
Answer. In the primary market the flow of funds is from savers to investors, that directly promotes capital formation. At the same time secondary market enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments. It indirectly promotes capital formation.
Question 5. For all entrepreneurs/all enterprises at all times, how different sources are differently related?
Answer. We are even aware that not all of them are equally appropriate to all enterprises at all times as these different sources carry very different:
- Obligations
- Responsibilities
- Opportunities.
Question 6. “ Stock market imparts liquidity to investment.” Comment.
Answer.
- “Stock market imparts liquidity to investment.’’The important function of stock market is to provide a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities.
- It also gives an investor to reinvest and disinvest.
- This market imparts liquidity to the long-term securities held by them by providing an auction market for these securities.
- It enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
Question 7. Why capital markets are the most important source of raising finance for the entrepreneurs?
Answer. Capital markets are considered as the most important source of raising finance for the entrepreneurs as this market can:
- Mobilize the financial resources on a nation-wide scale.
- Secure the required foreign capital and know-how to promote economic growth at a faster rate.
- Ensure the most effective allocation of the mobilized financial resources by directing the same either to such projects which are capable of the highest yield or to the underdeveloped priority areas where there is an urgent need to promote balanced and diversified industrialization.
The needs of entrepreneurs who actually use the savings for productive purposes are varied.
Question 8. Explain the regulatory functions of NABARD.
Answer.
- NABARD is empowered to undertake inspection of RRBs and Cooperative Banks, other than the Primary Cooperative Banks.
- To open a new branch, a recommendation of NABARD is imperative by RRBs or Cooperative Banks to seek permission from RBI.
- RRBs and Cooperative Banks, along with RBI, are required to file returns and documents with NABARD.
Question 9. What is pro-rata allotment and how to calculate the amount of it? Give one example.
Answer.Pro-rata allotment of shares is opted by the Company when there is an over-subscription. The excess application money is adjusted towards the sum due on allotment.
We calculate the amount of Pro-rata in the following way:
Suppose X Ltd invited applications for 1,00,000 shares and received applications for 1,50,000 shares. In this case the pro-rata is calculated as 1,50,000/1,00,000 = 3:2. Hence the Pro-rata is 3:2.
Question 10. Name some Institutional investors to whom entrepreneurs can raise funds by selling the issues.
Answer. Entrepreneurs, herein, raise funds by selling the issues mainly to the institutional investors like:
- Unit Trust of India
- Life Insurance Corporation of India
- General Insurance Corporation of India
- Army Group Insurance
- State Level Financial Corporations, etc.
Question 11. Mohit Pipes and Tube Co. Ltd. goes for public issue of 10,000 shares @ Rs 10 each. Applications were received for 15,000 shares. How did the company proceed with the process of issuing shares?
Answer. In the case of Mohit Pipes and Tube Co. Ltd
Issued shares to public — 10,000 Shares @ 10 each.
Applied share public by — 55,000 Shares @ 10 each.
Company receives only 150% of the subscription within 120 days from the date of the issue, it is called as Over-subscription.
Company will proceed with the issued shares i.e. 10,000 shares and excess shares will be refunded according to SEBI guidelines.
The over-subscribed amount after the finalisation of allotment, should be refunded to the applicants within 10 weeks of the closure of subscription list. If the money is not so refunded, the company is liable to refund the money with interest as specified from the expiry of the 8 days after 10 weeks of the closure of subscription list.
Question 12. How venture capital can best be characterized as a long-term investment discipline?
Answer. Venture capital can best be characterized as a long-term investment discipline, usually occurring over a five-year period that helps in the creation of
- early-stage companies,
- the expansion and revitalization of existing businesses, and
- the financing of leveraged buyouts of existing divisions of major or privately owned enterprises.
Question 13. Why stock exchange is also known as secondary market?
Answer.Stock exchange or Secondary market is an institution or place which provide a platform for buying and selling of existing securities only and prices are decided by demand and supply of securities. It is located at a specified place. It indirectly promotes capital formation or easy way of encashability of securities through buying and selling.
Question 14. “Stock exchange is a market where it sell all types of securities. Do you agree?
Answer.No, I do not agree. Stock exchanges maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on its floor. Securities which do not figure in the official list of stock exchange are called unlisted securities. Such unlisted securities cannot be traded in the stock exchange.
Question 15. For what type of ventures SIDBI provide Venture Capital assistance to the entrepreneurs.”
Answer. SIDBI provide venture capital assistance to the entrepreneurs for their innovative ventures if they have a sound management team, long term competitive advantage.
Question 16. Name the specialised institutions which provides leasing and factoring to small- scale units.
Answer. Leasing and factoring to small-scale units are provided for by SIDBI.
Question 17. “Stock exchanges control the activities of brokers and protect the investors from being deceived. But, if any broker is found indulging in malpractices as overcharging or giving wrong information, then what action will be taken against him?
Answer. If: any broker is found indulging in malpractices as overcharging or giving wrong information, then his/her licence may be cancelled.
Question 18. “Stock Exchange provides safety and security in dealings”. How?
Answer. Activities of the stock exchange are controlled by the provisions of the Securities Control (Regulation) Act and all this creates confidence in the minds of investors. As transactions are conducted as per well defined rules and regulations, fraudulent practices stands checked effectively ensuring safety, security and justice in dealings.
Question 19. How the prices of different securities traded are shown in the stock market?
Answer. The price of different securities traded are shown on electronic boards.
III. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question 1. How stock options method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits?
Answer. Stock options or offering shares to the employees has gained much popularity in many countries of the world.
This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company leading to:
- Higher efficiency
- Low labour turnover
- Better industrial locations
- Low floatation cost
- Wider/higher generation of funds.
Question 2. What is seed capital? Give example.
Answer.
- Capita] needed to set up a new business or enterprise. It can be obtained from owners or his/her relatives or from outside sources.
- It is that money used for the initial investment in a project or start up company provided to an entrepreneur to prove the feasibility of the project and quality of start up capital.
- To avail this sources of finance he may concern and contact various agencies, financial institutions. Example: Narayan Murthy started Infosys in 1981, he had no capital and his wife Sudha Murthy gave him Rs 10,000 which can be considered as seed capital.
Question 3. Explain the features of Venture capital.
Answer.Venture capital finance has the following features:
- It is basically equity finance in relatively new companies.
- It is long-term investment in growth- oriented small or medium firms.
- Venture capitalists not only provide capital but also business skills to investee firms.
- It involves high risk-return spectrum.
- It is a subset of private equity.
- The venture capital institutions have a continuous involvement in the business after making the investment.
- Such institutions disinvest the holdings either to the promoters or in the market.
Question 4. “Primary market basically to facilitate transfer of resources from the savers to the entrepreneurs seeking funds.” How?
Answer.Primary market refers to a place where issue of securities (shares, debentures and bonds) being issued for the first time by new companies or new issue Of securities by existing companies to investors. In these market all the entrepreneurs raise funds for:
- Setting new enterprises
- Expanding
- Diversifying
Therefore, it is also called as “New Issue Market”.
The ‘new issues’ may be issued by:
- New companies – also called initial issues.
- Old companies – also called further issues.
Question 5. What do you understand by Public Issue/ Going Public/Offers Through Prospectus/ Initial Public Offers (IPOs)?
Answer. Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus.
- It involves all public limited company can raise the required funds commonly by preparing a prospectus.
- Prospectus helps a company to raise funds through public.
- When an entrepreneur offers shares to the public for subscription he/she is required to comply with all the restrictions and formalities according to the provision of companies Act and SEBI Guidelines of pertaining to the initial issues, prospectus drafting and launch.
- The issues must be listed on at least one stock exchange.
Question 6. What do you understand by Private placement of shares?
Answer. Private placement means the direct sale by a company of its securities to a limited number of sophisticated investors. Entrepreneurs, herein, raise funds by selling the issues mainly to the institutional investors like:
- Unit Trust of India
- Life Insurance Corporation of India
- General Insurance Corporation of India
- Army Group Insurance
- State Level Financial Corporations, etc.
Entrepreneurs both from public limited and private limited sector, bank heavily upon raising funds through the issue of varied financial instruments under this segment as at times they do not wish to disclose information to the open market.
Question 7. How many venture capital institutions are there in India?
Answer. On present, many Venture Capital Companies/funds have been set up in India, in both the public and the private sectors, for example,
- Industrial Development Bank of India’s Venture Capital Fund
- Technology Development and Information Company of India Ltd. (TDICI)
- Risk Capital and Technology Finance Corporation Ltd.
- Gujarat Venture Finance Ltd. (GVFL)
- Andhra Pradesh Industrial Development Corporation (APIDC) Venture Capital Fund.
- National Venture Fund for Software and IT Industry.
- The Can bank Venture Capital Fund
- The Credit Capital Venture Fund Ltd. etc.
Question 8. Explain the functions of Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd (IIBI).
Answer.
- The Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was formed by transforming the Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI).
- It was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies.
- IRBI was incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 and renamed as the Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. in March 1997.
Functions: IIBI offers a wide range of products and services such as:
- Term-loan assistance for project finance.
- Short duration non-project asset – backed financing working capital/ other short term loans to companies.
- Equity Subscription Asset Credit.
- Equipment finance.
- Investments in Capital Market and Money market instruments.
Question 9. “Working in stock exchange means any one can enter for trading and no specific rules are to be followed.” Justify.
Answer.
- Stock exchange is a place where all the transactions in securities are effected only through its authorized * brokers and members means no outsiders or direct investors are allowed to enter in the trading circles of the stock exchange.
- Buying and selling transactions in securities at the stock exchange are governed by the rules and regulations of stock exchange as well as SEBI Guidelines. No deviation from the rules and guidelines is allowed in any case.
Question 10. “ Stock exchanges are the financial barometers of an economy”. How?
Answer.
- Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country.
- It help businesses to raise capital and give investors opportunities to back new and established enterprises.
- It also help business and entrepreneurs to come together to buy and sell trade shares for the purpose to raise more capital.
- Continuous growth of industries is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
- Rising stock market, through rising prices, more investors can create a sense of confidence and gives positive direction in the growth of an economy.
Question 11. Explain the organisation and management, membership and functioning of stock exchange in India.
Answer. The organisation, management, membership and functioning of stock exchanges in India are governed by the provisions of The Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956. This Act permits only recognized stock exchanges to function under the rules, regulations and by-laws approved by the Central Government.At present there are 24 stock exchange in India.
The stock exchanges of India have the following organisational form:
- Voluntary non-profit making associations
- Public limited company
- Company limited by guarantee
The governing body is responsible for policy formulation and proper functioning of the exchange, having wide range of powers viz.
- Elect the office bearers and set up committees
- Admit and expel members
- Manage the properties and finance of the exchange
- Interpret rules, regulations and by-laws
- Adjudicate disputes
- Conduct the affairs of the exchange
Question 12. ‘For the smooth and orderly functioning of corporate sector in a free market economy, stock exchanges are indispensable because of different roles played by them for different groups.’ Explain the importance of stock exchange to investors in the light of this statement.[CBSE Delhi 2015]
Answer.Importance of stock exchange to investors:
- Dissemination of useful Information: Stock exchange publish useful information regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals. The interested persons buy and sell their securities on the basis of information provided by the stock exchanges.
- Ready Market: Persons desirous of converting their shares into cash may easily do so through a member of stock exchange.
- Investors’ Interests Protected: Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not , exploit the investors.
Question 13. Naveen after completing his M. Tech in Nano Technology wanted to start his own business. He thought to manufacture sophisticated instruments used in surgery. He knew that his knowledge of Nano Technology will help him in manufacturing these instruments. According to him such instruments will help the surgeons to operate upon the patients with accuracy, with minimum blood loss and quick post operation recovery. Such types of instruments are used in advanced countries only and there was a risk in marketing the same. The cost price of machinery required, for manufacturing such instruments was very high and more research was required in this field of Nano Technology. For seed funding, Naveen approached. ‘Himani Capital Ltd.’ who finance such types of projects. ‘Himani Capital Ltd.’ after analysing the proposal agreed to provide seed capital to Naveen. Explain the different stages of ‘Early Stage Financing’ to seek venture capital finance after the one discussed above.[CBSE Delhi 2015]
Answer.
- Pre-start up and start up finance: A business plan is presented by the entrepreneur to the VC firm. A management team is being formed to run the venture. If the company has a board of directors, a person from the VC firms wall take seats at the board of directors. The VC firm monitors the feasibility of the product and the capability of the management-team from the board of directors.
- Second round financing: This is the first encounter with the rest of the market. The entrepreneur, at this stage, needs assistance from the Venture Capitalist for expansion, modernization, diversification so that the economies of scale and stability could be attained.
Question 14. ‘Angel Investors’ and ‘Venture Capital’ are the two sources of raising finance for an entrepreneur. Explain the concept of both the sources stating one distinguishing feature of each.[All India 2015]
Answer. Angel Investor is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start¬ups and early stage companies using a high-risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
Venture Capital is a type of a private equity capital provided as seed funding to early stage, high potential, high risk, growth up companies/entrepreneurs. Distinguishing Feature: Angel investors participate in the management of the business but venture capitalists do not take part in the management of the business.
Question 15. Ganga Dhar was working as the production manager in a German company. The company was producing remote operated high-end kitchen equipments. He resigned from his job and returned to Patna, his hometown. In Patna he met Aditya, his old friend, who had been managing his factory producing steel utensils with old technology. Ganga Dhar encouraged Aditya for the production of high-end kitchen equipments. He also promised to help Aditya by providing funds and his expertise so that the production unit run by Aditya can develop into a big production house and its investors may get high return on investments. Identify the kind of‘source of capital’ provided by Ganga Dhar to Aditya and explain the same. [All India 2015]
Answer. Angel Investors:
Following are the features of Angle Investors:
- They are current or retired executives, business owners or high net worth individuals who have the knowledge, experience, and funds.
- They bear extremely high risk and expect a very high return.
- They provide proactive advice, ‘ guidance industry connections and mentoring start-ups in its early days.
- Their objective is to create great companies by providing value creation.
- They have a sharp inclination to keep abreast of current.
Question 16. Ram was very thrilled with his new job. He was placed in a small factory manufacturing door knobs as a stock keeper. After a few days, while taking stock he understood that nuts and various small parts constituted majority of the cost of production. After some time, the firm went into a loss and the owner decided to look into the various factors that could have constituted the loss. Ram expressed his concern that inventory was not properly maintained and that there are various techniques which are involved and if followed properly the company will not be in a loss. The owner agreed to the suggestion. He also decided to take help from some specialized government institution initiate steps for technological up gradation, and modernization of existing units. [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
- What technique was suggested by Ram? Explain it.
- Which specialized financial institution is the owner thinking of approaching and state any one of its objectives?
Answer. ABC Analysis
- The inventory control technique known as ABC analysis builds on Pareto’s Principle.
In ABC analysis, a company reviews its inventory and sorts all SKUs into three categories, called ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ items.
The typical breakdown might look like this: ‘A’ inventory: 20 per cent of SKUs, 80 per cent of value. ‘B’ inventory: 30 per cent of SKUs, 15 per cent of value. ‘C’ inventory: 50 per cent of SKUs, 5 per cent of value.
A particular company’s numbers may be different, hut the pattern would be similar we should be able to discern a similar kind of pattern. - SIDBI (Small Industries Development Bank of India)
Objectives of SIDBI are:Initiate steps for technological up gradation, and/or modernization of existing units.
Question 17. Why is stock exchange important for an investor? [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Answer. Importance of stock exchange from the viewpoint of investors:
- Dissemination of useful information: Stock exchange publishes useful information regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals.
The interested persons buy and sell their securities on the basis of information provided by the stock exchanges. - Ready market: Persons desirous of converting their shares into cash may easily do so through a member of stock exchange.
- Investors’ interests protected:Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not exploit the investors.
- Genuine guidance about the securities listed: The investors can safely depend upon the information provided by the stock exchanges.
- Barriers of distance removed: Stock exchange removes the barriers of distance with regard to securities listed there. Without stock exchange the securities of a Delhi company may have a limited market in Delhi only.
- Knowledge of profit or loss on investments: The investors can estimate the profit or loss on the total amount of investments in securities, by comparing the original amount invested and the price of securities on a particular day.
IV.VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question 1. Explain the concept of IDBI (its full form, establishment year, purpose, objectives, and functions).
Answer.


Question 2. What is ‘venture capital’? Explain the mode of raising funds.
Answer.The term ‘venture capital’ is defined as a equity by which an investor supports an entrepreneur talent with finance and business skills to exploit market opportunities and thus obtain a longterm market gains. These are investors and investment companies whose specialty is financing new, high potential, high- technology oriented entrepreneurial ventures.
The mode of raising funds through venture capitalists:
- They are more interested in financing ventures which are in their second or third stage of development .
- They often provide initial equity investment to start up a business such ventures can be of software, biotechnology, high-potential ventures, high-technology ventures or are venture having high potential prospects and returns expected.
- Venture capitalists look for a high rate of return. Thus, they want equity, or some share of ownership in return for their capital.
- They are willing to take the higher risk of losing their capital for a chance of profit from the business’s success.
- The venture capitalist sells his or her percentage of the business to either another investor or back to the entrepreneur after specific number of years association or when he finds returns lowering down.
- Mostly small business approach to venture capitalists when they want to start or grow a business but couldn’t persuade banks to lend money.
- These investors have a deep insight about the fields in which they make their investment, but they behave like more or less as non-working partners do not interfere in the management of the enterprise but protect them at initial stage by keeping good contact with them.
- Venture capitalists are more careful while investing in any venture as they know that investment is highly illiquid. It means it is not subject to repayment on demand.
Question 3. When is it appropriate to use financial institutions as a source of financing?
Answer.Financing, an enterprise-whether large or small is a critical element for success in business. Financing is the use and manipulation of money. Raising money for a business is one aspect of financing.
All new entrepreneurs most of the time face difficult problems to arrange start up finance.
While finance is a life blood of the business and is needed throughout the life of business, the new entrepreneur faces significant difficulties in acquiring capital at start-up.
- The entrepreneur needs to consider all possible sources of capital and select the one that will provide the needed funds at minimal.
- Different sources of funds are used at various stages in the growth and development of the venture.
- If an entrepreneur cannot personally supply the necessary amount of money, another option is ‘OTHER PEOPLE’S MONEY (OPM)’. It means before seeking outside financing; an entrepreneur should first explore all methods of internal financing and the other external financing and if it suits an entrepreneur he can go for financial institutions as a sources of financing.
- Institutional finance refers to institutional financing.
- Sources of finance to Industry, other than commercial banks. These institutions are established by the Central/State Government, aiming at:
(a) Promoting the industrial development of a country.
(b) Providing both owned capital and land capital for long and medium term requirements.
(c) Supplement the traditional financial agencies like commercial banks.
(d) To encourage setting up of industries in backward areas.
(e) To provide technical assistance to industrial units.
(f) To develop investment markets.
Question 4. On the basis of duration, classify the sources of finance.
Answer.Sources of finances can be classified on the basis of duration

Methods of Raising Capital: A company may raise funds for different purposes depending on the time periods ranging from very short to fairly long duration. The total amount of financial needs of a company depends on the nature and size of the business. The scope of raising funds depends on the sources from which funds may be available. The business forms of sole proprietor and partnership have limited opportunities for raising funds. They can finance their business by the following means:
- Investment of own savings
- Raising loans from friends and relatives
- Arranging advances from commercial banks
- Borrowing from finance companies.
Question 5. Companies can raise finance by a number of methods. What are the methods to raise long-term and medium-term capital finance?
Answer.Issue of Shares: It is the most important method. The liability of shareholders is limited to the face value of shares, and they are also easily transferable. A private company cannot invite the general public to subscribe for its share capital and its shares are also not freely transferable. But for public limited companies there are no such restrictions. There are two types of shares:
- Equity shares: The rate of dividend on these shares depends on the profits available and the discretion of directors. Hence, there is no fixed burden on the company. Each share carries one vote.
- Preference shares: Dividend is payable on these shares at a fixed rate and is payable only if there are profits. Hence, there is no compulsory burden on the company’s finances. Such shares do not give voting rights.
Issue of Debentures: Companies generally have powers to borrow and raise loans by issuing debentures. The rate of interest payable on debentures is fixed at the time of issue and are recovered by a charge on the property or assets of the company, which provide the necessary security for payment- The company is liable to pay interest even if there are no profits. Debentures are mostly issued to finance the long-term requirements of business and do not carry any voting rights.
Loans from Financial Institutions: Long-term and medium-term loans can be secured by companies from financial institutions like the Industrial Finance Corporation of India, Industrial ; Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI), State level Industrial Development Corporations, etc. These financial institutions grant loans for a maximum period of 25 years against approved schemes or projects. Loans agreed to be sanctioned must be covered by securities by way of mortgage of the company’s property or assignment of stocks, shares, gold, etc.
Loans from Commercial Banks: Medium-term loans can be raised by companies from commercial banks against the security of properties and assets. Funds required for modernisation and renovation of assets can be borrowed from banks. This method of financing does not require any legal formality except that of creating a mortgage on the assets.
Public Deposits: Companies often raise funds by inviting their shareholders, employees and the general public to deposit their savings with the company. The Companies Act permits such deposits to be received for a period up to 3 years at a time. Public deposits can be raised by companies to meet their medium-term as well as short-term financial needs. The increasing popularity of public deposits is due to:
- The rate of interest the companies have to pay on them is lower than the interest on bank loans.
- These are easier methods of mobilising funds than banks, especially during periods of credit squeeze.
- They are unsecured.
- Unlike commercial banks,the company does not need to satisfy credit-worthiness for securing loans.
Reinvestment of Profits: Profitable companies do not generally distribute the whole amount of profits as dividend but, transfer certain proportion to reserves. This may be regarded as reinvestment of profits or ploughing back of profits. As these retained profits actually belong to the shareholders of the company, these are treated as a part of ownership capital. Retention of profits is a sort of self financing of business. The reserves built up over the years by ploughing back of profits may be utilised by the company for the following purposes:
- Expansion of the undertaking
- Replacement of obsolete assets and modernisation.
- Meeting permanent or special working capital requirement.
- Redemption of old debts.
- It enables the company to adopt a stable dividend policy.
Question 6. “Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs.” Explain its benefit and drawbacks.
Answer. Meaning of Public Issues: This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. When an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company, he/ she tends to be in advantageous position because of reaping the following benefits: Access to capital or raising funds:
- An entrepreneur stands to gain by going public in access to capital.
- Generally, the capital is paid off at the liquidation of a company or not to be repaid immediately and does not involve an interest charge.
- The only reward the IPO investors seek is an appreciation of their investment by getting dividends.
Entrepreneur can use the capital raised for a variety of purposes including:
- growth and expansion,
- retiring existing debt,
- corporate marketing and development,
- acquisition capital.
Other advantages:
- Mergers and acquisitions: Public stock of a company can be used for businesses to grow through acquisitions.
- Higher valuations: Public companies are typically valued more than private companies.
- Benchmark trading price: The trading price of a public company’s stock serves as a benchmark of the offer price of other securities.
- Capital formation: Raising capital later is typically easier because of the extra liquidity for the investors.
- Incentives: Stock options and stock incentives can be very helpful in attracting employees.
- Reduced business requirements: While an underwritten initial public offering requires significant earnings, the lack of earnings does not keep a private company from going public.
- Less dilution: There is less dilution of ownership control compared to an IPO.
- Liquidity: A public company provides liquidity for management, minority shareholders, and investors.
- Prestige: Added prestige and visibility with customers, suppliers, as well as the financial community.
Question 7. State the limitations of Public Issues.
Answer. The various limitations/obligations’ are as follows:
- Increasing accountability to public shareholders.
- Need to maintain dividend and profit growth trends.
- Becoming more vulnerable to an unwelcome takeover.
- Need to observe and adhere strictly to the rules and regulations by governing bodies.
- Increasing costs in complying with higher level of reporting requirements.
- Relinquishing some control of the company following the public offering.
- Suffering a loss of privacy as a result of media interest.
Question 8. Explain the features of Stock Exchanges.
Answer. Following are the features of stock exchange—:
- Association of persons: It is an association of persons or body of individuals which may be registered or unregistered.
- Recognition from central government: It is an organized market. It requires recognition from the Central Government.
- Market for securities: It is a market, where securities of corporate bodies, government and semi-government bodies are bought and sold.
- Deals in second hand securities: It deals with shares, debenture, bonds and such securities already issued by the companies. In short, it deals with existing or second hand securities and hence it is called secondary market.
- Regulates trade in securities: It does not buy or sell any securities on its own account. It merely provides the necessary infrastructure and facilities to its members and brokers who trade in securities. It regulates the trade activities so as to ensure free and fair trade.
- Allow dealings only in listed securities: It always maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on its floor.
- Transactions effected only through members: All the transactions in securities at the stock exchange are effected only through its authorized brokers and members. No outsiders or direct investors are allowed to enter in the trading circles of the stock exchange.
- Working as per rules: Buying and selling transactions in securities at the stock exchange are governed by the rules and regulations of stock exchange as well as SEBI Guidelines. No deviation from the rules and guidelines is allowed in any case.
- Specific location: It is a particular market place where authorized brokers come together daily (i.e. on working days) on the floor of market called trading circles and conduct trading activities. The price of different securities traded are shown on electronic boards. After the working hours market is closed. All the working of stock exchange is conducted and controlled through computers and electronic system.
- Financial barometers: Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country. Industrial growth and stability is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
Question 9. Who are called as “Angel Investors”? Explain the features of “Angel Investors”.
Answer. Business angel or informal investor or an angel investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start¬up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
Features of Angel Investors: Providing start-up finance to the needy who want to start a small own business. The main people involved to provide funds are “friends and family”, (it can be seed funding and formal venture capital). But raising of funds cannot be more than a few thousands from friends and family, even the venture capitalist are least interested to make investments. Thus, angel investments is a common second round of financing for high-growth start-ups or early stage companies.
- Most angel investors are current or retired executives, business owners or high net worth individuals who have the knowledge, expertise, and funds that help start-ups match up to industry standards.
- They bear extremely high risk and are usually subject to dilution from future investment rounds.
- They expect a very high return on investment.
- Apart from investing funds, most angels provide proactive advice, guidance, industry connections and mentoring start-ups in its early days.
- Their objective is to create great companies by providing value creation, and simultaneously helping investors realize a high return on investments.
- They have a sharp inclination to keep abreast of current developments in a particular business arena, mentoring another generation of entrepreneurs by making use of their vast experience.
Question 10. When and how to seek Venture Capital Finance?
Answer. Entrepreneurs can typically seek venture capital to assist at any of the following four stages in the company’s development:
(i) Early stage financing this stage includes:
(a) Seed capital
(b) Pre-start up and start up
(c) Second-round financing
(a) Seed capital finance:
• It refers to the capital required by an entrepreneur for conducting research at pre-commercialization stage.
• During this stage, the entrepreneur has to convince the investor (VC) why his idea/product is worthwhile.
• The investor will investigate into the technical and economical feasibility of the idea.
• In some cases, there is some.sort of prototype of the idea/product that is not fully developed or tested.
• As the risk element at this stage is very high, investor (VC) may deny to assist if he does not see any potential in the idea.
• Entrepreneur’s ability, technological skills and competencies are required to match with the market opportunities so as to successfully convince about product/idea’s feasibility to the venture capitalist.
(b) Start up finance:
• If the idea/product/process is qualified for further investigation and/or investment, the process will go to the second stage; this is also called the start-up stage.
• A business plan is presented by the entrepreneur to the VC firm. A management team is being formed to run the venture.
• If the company has a board of directors, a person from the VC firms will take seats at the board of directors.
• While the organisation is being set up, the idea/product gets its form.
• The prototype is being developed and fully tested.
• Sometimes, clients are being attracted for initial sales. The management-team stablishes a feasible production line to produce the product.
• The VC firm monitors the feasibility of the product and the capability of the management-team from the board of directors.
(c) Second-round financing:
• At this stage, the time comes the idea has been transformed into a product and is being produced and sold.
• This is the first encounter with the rest of the market, the competitors and attempt is to squeeze in the market and get some market share from the competitors.
• The entrepreneur, at this stage, needs assistance from the Venture Capitalist for expansion, modernization, diversification so that the economies of scale and stability could be attained.
(ii) Last stage financing/bridge/pre-public stage: In general, this is the last stage of the venture capital financing process. The main goal of this stage is for the venture to go public so that investors can exit the venture with a profit commensurate with the risk they have taken.
At this stage, the venture achieves a certain amount of market share. This gives the venture some opportunities for example:
• Merger with other companies.
• Keeping new competitors away from the market.
• Eliminate competitors.
• Development capital.
Question 11. When was SEBI established? What are the main aims of SEBI?
Answer.
- SEBI was officially established by The Government of India in the year 1988 and given statutory powers in 1992 with SEBI Act, 1992 being passed by the Indian Parliament.
- SEBI has it’s Headquarter at the business district of Bandra Kurla Complex in Mumbai, and has Northem, Eastern, Southern and Western Regional Offices in New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai and Ahmedabad respectively.
- Initially, SEBI was a non-statutory body without any statutory power. However, in the year of 1995, SEBI was given additional statutory powers by the Government of India through an amendment to the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992. In April, 1998 the SEBI was constituted as the regulator of capital markets in India under a resolution-of the Government of India.
SEBI’s Establishment: SEBI was established as a supervising and regulatory body to curb certain malpractices and to promote the Securities Markets in India.
V. VALUE BASED QUESTIONS
Question 1. An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market. Explain the various methods of raising the funds in the primary market by an entrepreneur. Give some value points for this method of raising funds.
Answer.Yes, an entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market. An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market by the following methods:
- Public Issue
- Rights Issue
(iii) Private Placement
(iv) Offer to the employees
(i) Public Issue/Going Public: Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. An entrepreneur organising itself as public limited company can raise the required funds commonly by adopting prospectus.
(ii) Right Issues: It is an offer of new securities by a listed company to its existing shareholders only. The right issues are done always on the pro-rata basis (giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding).
(a) The companies send the letter of offer (circular) to all those existing shareholders whose names are recorded in the books on a particular date to issue rights.
(b) The time given to accept the right offer should not be less than 15 days.
(c) The circular/notice issued to the shareholder must state the right of the shareholder to renounce the offer in favour of others.
(d) After the expiry of the time mentioned in the notice, the Board of directors has the right to dispose the unsubscribed shares in any manner as per the benefit of the company.
The existing shareholders whose names are there in the list has four options:
• They can exercise the rights.
• They can renounce the rights and sell them in the open market in favour of another person.
• They can renounce part of the rights and exercise the other part.
• Doing nothing.
This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.
(iii) Private Placements: It refers to the direct sale of newly issued securities by the company to a small number of institutional investors through merchant bankers. They are generally selected clients.
(a) Unit Trust of India
(b) Life Insurance Corporation of India
(c) General Insurance Corporation of India
(d) Army Group Insurance
(e) State Level Financial Corporations
Advantages:
(a) Less time taken to issue these shares.
(b) Comparatively less amount of cost of capital is required.
(c) These issues are tailor-made to suite the requirement of both the parties.
(d) Less formalities are required.
(iv) Offer to Employees: Stock options to the employees refers to the offer given by the company to the employees to become shareholders. This method facilitates the employees to become shareholder and can earn a part of the share of profits.
Value Points:
• Proper utilization of time.
• Understanding each other and making the issues tailor-made so that the it can suite the requirements of both the parties.
• To prevent the use of paper and save precious natural resources.
• Choice to exercise the rights.
• Truthfulness.
• Disciplined as the issues are for the existing shareholders and issues can be till prescribed date only.
• Stock options to the employees shows the company’s respect to the employees.
• Raising of funds through existing shareholder shows the awareness of responsibility of employees towards company and showing helpfulness.
• Help to protect company’s property.
• Team spirit and team work to ensure the growth of the company.
• Ownership quality by the shareholders.
• Initiative by Board of Directors and the existing shareholders to protect the company.
Question 2. Explain the functions of stock exchange. Give some value points to it.
Answer. Stock exchange performs a number of functions in respect of marketability of different types of securities for investors and borrowing companies. It’s important functions are:
- Continuous and ready market for securities:
(a) Stock exchange provides a central market for purchase and sale of securities.
(b) It provides ready and continuous outlet for buying and selling of securities.
(c) It facilitates and helps all buyers to buy and sell securities as and when they want. - Facilitates evaluation of securities:
(a) It is useful for the correct evaluation of industrial securities.
(b) It publishes price quotation of the shares of the companies that have been listed with them after thorough analysis of demand and supply position.
(c) This enables investors to know the true worth of their holdings at any time. - Checks on brokers:
(a) It checks and controls the activities of brokers and protect the investors from being received,
(a) While dealing, if any broker is found indulging in malpractices as overcharging or giving wrong information, his/her licence may be cancelled. - Provides safety and security in dealings:
(a) All activities of the stock exchange are controlled by the provisions of the Securities Control (Regulation) Act and all this creates confidence in the minds of investors.
(b) Each and every dealings and transactions are conducted as per well-defined rules and regulations, fraudulent practices stands checked effectively ensuring safety, security and justice in dealings. - Regulates company management:
(a) The companies which are listed also have to operate within the strict rules and regulations.
(b) This ensures safety of dealing through stock exchange.
(c) All of them have to work under the vigilance of stock exchange authorities. - Intensifying capital formation and promoting the habit of saving and investment:
(a) The stock market offers attractive opportunities of investment in various securities.
(b) It encourages people to save more and invest in securities of corporate sector rather than investing in unproductive assets such as gold, silver, etc.
(c) It also creates a habit of risk taking among the investing class by converting their savings into profitable and help them for safe investments. - Facilitates raising of new capital: It facilitates an entrepreneur of existing companies for the need for more capital for further development, organisation or expansion and help them to meet the need.
- Facilitates public borrowing: It serves as a platform for marketing government securities. It enables government to raise public debt easily and quickly.
- Facilitates healthy speculation:To ensure liquidity and demand of supply of securities, the stock exchange permits healthy speculation of securities and always keeps the exchange active.
- Serves as economic barometer:Stock exchange indicates the state of health of companies and the national economy. It acts as a barometer of the economic situation/conditions and is thus referred as pulse of economy or economic mirror.
- Facilitates bank lending: Banks easily know the prices of quoted securities. They offer loans to customers against corporate securities. This gives convenience to the owners of securities.
Value Points:
- Helpfulness: The stock market helps to value the securities on the basis of demand and supply factors.
- Quest for knowledge: The valuation of securities is useful for investors, government and creditors.
(a) The investors know the value of their investment.
(b) The creditors know the value of credit worthiness.
(c) Government knows to impose taxes on value of securities. - Truthfulness and equality—Only listed companies can operate in stock exchange.
- To protect national property and economic growth: In stock exchange securities of various companies are bought and sold. This process of disinvestment and reinvestment helps to invest in most productive investment proposal and this leads to capital formation and economic growth.
- Readiness to cooperate and ensures safety of dealing through stock exchange.
- Encourage and promotes the habit of savings and honest investment: It offers attractive opportunities of investment in various securities. It encourages people to save more and invest in securities of corporate sector rather than investing in unproductive assets such as gold, silver, etc.
- Better transparency, genuine settlement cycle, honest transaction, etc.
Question 3. Explain the necessity of a stock exchange in the economy.
Answer. Stock exchange indicates about the good or bad health of an economy.
For the smooth and orderly functioning of corporate sector in a free market economy, stock exchanges are indispensable, because of the different roles played by them for different groups.
- Stock exchange indicates about the good or bad health of an economy. It is an investment intermediary which facilitates economic and industrial development of a country.
- All the stock markets influence economic activities through the creation of liquidity.
- It increases the business and earnings of people and gives a positive impact to the growth of an economy.
- Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations and build a trust between the members and investors so that members may net exploit the investors, with this belief more number of investors are added into it, which is really helpful for the economic growth.
- Through easy funds mobilizing, the boosted production fetches more capital, enhancing economic development.
- It operates through the medium of stock exchanges which regulates the trading activities in this market and ensures a measure of safety and fair dealings to the investors.
- Stock exchanges play a key role in allocating capital to the corporate sector, which has significant effects on the economy as a whole.
- Stock exchanges maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on its floor. In entrepreneurial- oriented countries, the growth of listed companies contributes a wide portion of a nation’s increase in GDP.
- Stock exchange provides a central market for purchase and sale of securities. It provides ready and continuous outlet for buying and selling of securities. Buyers and sellers strongly believe that they would be able to buy and sell securities as and when they want.
Question 4. “ Stock market contributes to better allocation of capital and intensities capital formation.” Do you agree? Explain.
Answer. Yes, I agree with the statement. Stock market contributes to better allocation of capital and intensifies capital formation. The shares of profit making companies are quoted at higher prices and are actively traded so such companies can easily raise fresh capital from stock market. The general public hesitates to invest in securities of loss making companies. So stock exchange facilitates allocation of investor’s fund to profitable channels. Stock exchange intensifies the process of capital formation through creating the habit of saving, investing and risk taking among the investing class by converting their savings into profitable, safe investments.
Question 5. “ Stock exchange imparts liquidity to investment.” Comment.
Answer. Stock exchanges enhance the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
- From the investor’s point of view, this market imparts liquidity to the long-term securities held by them providing an auction market for these securities.
- Generally, in the stock market securities are held for long term and get matured after a long time period. But stock market facilitates to sold the securities easily and at any time the security holders want and convert it into cash.
- It operates through the medium of stock exchanges which regulates the trading activities in this market and ensures a measure of safety and fair dealings to the investors.
Question 6. Explain the importance of a stock exchange from the view point of entrepreneurs/companies.
Answer. The importance of a stock exchange from the view point of entrepreneurs /companies:
- Recognition: The market values of companies’ shares are published in important dailies. This enhances the reputation of good companies/ entrepreneurs.
- Wide market: The securities of some companies are listed in some stock exchanges. The market for the securities of such companies is considerably widened. Thus, larger amounts of capital may be raised from different types of investors.
- Higher share values: People have a tendency to buy shares that have some premium value. Demand of such shares increases. This leads to further increase in the price of such shares.
Value Points:
• Enhances the reputation of good companies
• Universal
• Social services
• National awareness
• Readiness to cooperate
• Helpfulness
• Consideration for others
• Friendship
Question 7. Explain the importance of a stock exchange from the viewpoint of society.
Answer. The importance of a stock exchange from the viewpoint of society:
- Rapid capital formation:
(a) Many people save their money and are ready to invest where they can get high rate of returns, when they check with the good companies with high premium amount they tempted to invest in securities.
(b) This habit leads to investment of savings in corporate and government securities.
(c) The high returns of dividend from these securities may further be invested in buying more securities.
(d) This flow of funds leads to rapid and continuous capital formation. - Economic development:
(a) It is the market in which existing securities are purchased and sold.
(b) This process is called as disinvestment and reinvestment.
(c) Through easy funds mobilisation, this leads to more capital, enhancing economic development of the country. - National projects: As stock exchange promotes, the capital formation by rating and approving the projects which brings national prosperity can be easily undertaken.
Value Points:
- National prosperity.
- This habit leads to investment of savings in corporate and government securities.
- Easy funds mobilizing.
- Enhancing economic development.
- Promoting the people to come with the projects.
- Helping and providing the people a platform to buy and sell the securities.
- Readiness to cooperate.
Question 8. Explain the importance of a stock exchange from the viewpoint of investors.
Answer.From the viewpoint of investors
- Dissemination of useful information:
(а) Stock exchange publishes useful information regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals.
(б) All the shareholders who wish to buy and sell their securities accordingly use the provided information. - Ready market: It gives a ready market for the security holders, so that all those who wish and are in need of money can easily convert their shares into cash online or through intermediaries. –
- Investors’ interests protected: Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not exploit the investors.
- Genuine guidance about the securities listed: The investors can safely depend upon the information provided by the stock exchanges.
- Barriers of distance removed:
(a) Stock exchange removes the barriers of distance with regard to securities listed there.
(b) Without listing the shares in stock exchange the securities can be sold out in a limited market only. - Knowledge of profit or loss on investments: The investors can estimate the profit or loss on the total amount of investments in securities, by comparing the original amount invested and the price of securities on a particular day.
Value points:
- Sharing the information
- Helpfulness
- Quest for knowledge
- Discipline in following rules and regulations
- Resourcefulness
- Equality for all regarding the brokerage
- Team spirit
- Universal
• Shareholders shows the spirit of enquiry.
VI. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Question 1. Identify the logo given below. Write the full form of it and when it was established.


Answer.

Question 2. Explain the concept of IFCI.
Answer.


VII. EVALUATION AND MULTI-DISCIPLINARY QUESTIONS
Question 1. Harsh has come up with an innovative idea of school bags. He believes that this can bring a new way of thought in the minds of consumers with respect to school bags. He want to start the production of bags by setting up SSI in the industrial area. He should contact which financial institute for assistance in opening his innovative venture. Write the features of this financial institution.
Answer. Harsh should contact SIDBI for financial assistance in opening his innovative venture. Features of SIDBI are:
- The financial assistance of SIDBI to the small scale sector is channelised through the following two routes:
(a) Indirect Assistance
(b) Direct Assistance - It stimulate and promote the participation of private capital (Indian) in such industrial units;
- SIDBI has taken over there sponsibility of administering following two funds which were previously administered by IDBI i.e.
(a) Small Industries Development Fund
(b) Small Industries Development Assistance Fund. - SIDBI’s financial assistance to SSS is primarily channelised through the existing credit delivery system consisting of commercial banks, co-operative banks, RRBs and SFCs.
- Refinance loans and advances extended by the primary lending institutions to small scale industrial units, along with providing them even resource support.
- Discounts and rediscounts bills arising from sale of machinery to or its manufacture by industrial units in the small-scale sector.
Question 2. Amar is running a village industry of processing of fruits. He took loan from State Bank of India. Even after this loan he is not able to meet his financial requirements. He is now looking for someone who can re-finance his industry of rural area. He should contact which financial institution for this purpose? Identify and explain any three functions of this financial institution.
Answer. He should contact NABARD for this purpose.
Functions of NABARD are:
- NABARD is empowered to undertake inspection of RRBs and Cooperative Banks, other than the Primary Cooperative Banks.
- To open a new branch, a recommendation of NABARD is imperative by RRBs or Cooperative Banks to seek permission from RBI.
- RRBs and Cooperative Banks, along with RBI, are required to file returns and documents with NABARD.
Question 3. Omar is successfully producing a spareparts of machines in his enterprise. Omar Industrial Spares Ltd. He is in need of a machine costing Rs 14 lakhs and is to be imported from Swedan. Suggest him a financial institution who can provide loan assistance for 10 years. Write the functions of this financial institution.
Answer.The State Financial Corporation (SFC) can provide him a Ion for 10 years. Functions of SFC:
- Grant of loans and advances to or subscribe to debentures of, industrial concerns repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
- Guaranteeing deferred payments due from an industrial concern for purchase of capital goods in India.
- Underwriting of the issue of stock, bonds or debentures by industrial concerns.
- Subscribing to, or purchasing of, the stock, shares, bonds or debentures of an industrial concern subject to a maximum of 30 per cent of the subscribed capital, or 30 per cent of paid up share capital and free reserve, whichever is less.
- Act as agent of the Capital government, State government, IDBI, IFCI or any other financial institution in the matter of grant of loan or business of IDBI, IFCI or financial institution.
Question 4. Success of franchises such as McDonald’s, Burger King, KFC, Boston Market, Subway, Midas, Jiffy Lube, Holiday Inn, Mail Boxes and Merry Maids is that, all these firms have established an excellent franchise system that effectively provides the necessary services to the franchisee. With respect to the above, describe the advantages of Franchising to the franchisee.
Answer.Advantages of Franchising:
- Proven idea: Business is based on a proven idea. Success of the product can be checked in the market.
- Profit from brand recognition: Franchises develop an image in the marketplace. This saves both time and money of advertising, promotion, recognition, etc. Image of the product is a favourable one and is in the minds of consumers.
- Recognized brand name and trademarks: Entrepreneur gets a recognized brand name and trademarks. Benefit from any advertising or promotion by the parent company automatically benefits the franchise.
- Support from parent company: The franchisor gives support in the form of training, help setting up the business, a manual telling how to run the business and ongoing advice.
- Exclusive rights of the territory: The franchisor can’t sell any other franchises in the same territory which leads to the creation of monopoly power in the territory.
- Easier Financing: Financing the business becomes easier due to the associated brand name. Banks are more likely to lend money to buy a franchise with a good reputation.
NCERT SolutionsHistoryPolitical ScienceSociologyPsychologyHumanities