NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life.
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following can be made into crystal?
(a) A bacterium
(b) An Amoeba
(c) A virus
(d) A sperm
Solution:
(c) Viruses can be made into crystals i.e., they can be crystallised. Crystallisation is the process of transformation of viral components into organised solid particles. Crystallisation is used to study structural characteristics of biomolecules through X-rays, laser beams etc.
Question 2.
A cell will swell up if
(a) the concentration of water molecules in the cell is higher than the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium
(b) the concentration of water molecules in surrounding medium is higher than water molecules concentration in the cell
(c) the concentration of water molecules is same in the cell and in the surrounding medium
(d) concentration of water molecules does not matter.
Solution:
(b) If a cell is placed in a solution containing higher concentration of water molecules than the concentration of water molecules in the cell (hypotonic solution), the cell will gain water by the process of osmosis (endosmosis). Although water molecules freely cross the cell membrane in both the directions but more water enters into the cell than leave and thus the cell swells up.
Question 3.
Chromosomes are made up of
(a) DNA
(b) protein
(c) DNA and protein
(d) RNA.
Solution:
(c) Chromosomes are thin, thread like structures present in the nucleus and visible during all division. Each chromosome is made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and proteins. DNA stores all the information necessary for cell to function, to grow and to reproduce.
Question 4.
Which of these options are not functions of ribosomes?
(i) It helps in manufacture of protein molecules.
(ii) It helps in manufacture of enzymes.
(iii) It helps in manufacture of hormones.
(iv) It helps in manufacture of starch molecules.
(a) (i)and(ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) and (i)
Solution:
(None) : Ribosomes are the ribonucleoprotein (ribonucleic £cid i.e., RNA + protein) particles which are not bounded by any membrane and present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis. The proteins synthesised by ribosomes may be used in the formation of new cell membranes (membrane biogenesis) or may function as enzymes and hormones. Among the given functions, only (iv) i.e. help in manufacture of starch molecules is not a function of ribosomes. Besides, some hormones are non-proteinaceous which are formed without the help of ribosomes.
Question 5.
Which of these is not related to endoplasmic reticulum?
(a) It behaves as transport channel for proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm.
(b) It transports materials between various regions in cytoplasm.
(c) It can be the site of energy generation.
(d) It can be the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
Solution:
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membranous network enclosing a fluid-filled lumen which almost fills up the intracelluar cavity. ER serves as channel for the transport of materials (especially proteins) between various regions of the cytoplasm or between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. ER also functions as a cytoplasmic framework providing the site for some biochemical activities of the cell.
Mitochondrion is the site of energy generation.
Question 6.
Following are a few definitions of osmosis. Read carefully and select the correct definition.
(a) Movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi- permeable membrane.
(b) Movement of solvent molecules from its higher concentration to lower concentration.
(c) Movement of solvent molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration of solution through a permeable membrane.
(d) Movement of solute molecules from lower concentration to higher concentration of solution through a semi-permeable membrane.
Solution:
(a) The process of osmosis is defined as the movement of water molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration through semi-permeable membrane.
Question 7.
Plasmolysis in a plant cell is defined as
(a) breakdown (lysis) of plasma membrane in hypotonic medium
(b) shrinkage of cytoplasm in hypertonic medium
(c) shrinkage of nucleoplasm
(d) none of them
Solution:
(b) When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution i.e., a solution in which concentration of water molecules outside the cell is lesser than the concentration of water molecules inside the cell, the cell will loss water by the process of osmosis (exosmosis). Although water crosses the cell membrane in both directions, but more water leaves the cell than enters resulting in the shrinkage of cell cytoplasm. This phenomenon of shrinkage of cell cytoplasm when put in a hypertonic solution is called plasmolysis.
Question 8.
Which of the following are covered by a single membrane?
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Vacuole
(c) Lysosome
(d) Plastid
Solution:
(Both (b) and (c)) Both vacuole and lysosome are single membrane bound cell organelles. Mitochondria and plastids are double membrane bound cell organelles.
Question 9.
Find out the false sentences.
(a) Golgi apparatus is involved with the formation of lysosomes.
(b) Nucleus, mitochondria and plastid have DNA; hence they are able to make their own structural proteins.
(c) Mitochondria is said to be the power house of the cell as ATP is generated in them.
(d) Cytoplasm is called as protoplasm.
Solution:
(d) Protoplasm is considered as the physical basis of life. The protoplasm of a cell consists of nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm. Thus, cytoplasm is a part of protoplasm of the cell. The protoplasm is bound by plasma membrane whereas cytoplasm is that part of protoplasm which surrounds the nucleus.
Question 10.
Find out the correct sentence.
(a) Enzymes packed in lysosomes are made through RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum).
(b) Rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum produce lipid and protein respectively.
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum is related with the destruction of plasma membrane.
(d) Nucleoid is present inside the nucleoplasm of eukaryotic nucleus.
Solution:
(a) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) produce protein and lipid respectively. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is related with the formation of plasma membrane along with some other organelles (membrane biogenesis).
Nucleoid refers to the undefined nuclear material of prokaryotes e.g., bacteria which is devoid of a nuclear membrane.
Question 11.
Which cell organelle plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell?
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) Lysosomes
(c) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Vacuoles
Solution:
(c) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs in a cell by metabolising the toxic substances such as aspirin, insecticides, petroleum products, pollutants etc.
Question 12.
The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are manufactured by
(a) rough endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) plasma membrane
(d) mitochondria.
Solution:
(None) : The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are respectively manufactured by rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The lipid molecules for cell membrane are formed and inserted into membrane of smooth ER by smooth ER itself. The protein molecules of cell membrane are mostly synthesised and inserted into membrane at the level of rough ER.
Question 13.
The undefined nuclear region of prokaryotes are also known as
(a) nucleus
(b) nucleolus
(c) nucleic acid
(d) nucleoid.
Solution:
(d) Refer to answer 10.
Question 14.
The cell organelle involved in forming complex sugars from simple sugars are
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) ribosomes
(c) plastids
(d) Golgi apparatus.
Solution:
(d)
Question 15.
Which out of the following is not a function of vacuole?
(a) Storage
(b) Providing turgidity and rigidity to the cell
(c) Waste excretion
(d) Locomotion
Solution:
(d) Vacuoles are single membrane bound, fluid filled sacs present in the cytoplasm. Vacuoles are meant for the storage of food, water and other substances. In plant cells, vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity and rigidity to the cell. In single- celled organisms like Amoeba, the food vacuole contains the food items that the Amoeba has consumed. In some unicellular organisms, specialised vacuoles also play important roles in expelling excess water and some wastes from the cell (osmoregulation).
Question 16.
Amoeba acquires its food through a process, termed
(a) exocytosis
(b) endocytosis
(c) plasmolysis
(d) exocytosis and endocytosis both.
Solution:
(b) Endocytosis is the ingestion of food materials by the cells through the plasma membrane.
Depending upon the type of food material, endocytosis may be (i) phagocytosis (in take of solid material) or (ii) pinocytosis (intake of liquid material). Phagocytosis is a common method of feeding in some protozoans e.g., Amoeba. In this method, a part of plasma membrane invaginates in the region of solid food particle and engulfs it. The membrane enclosed vesicle called phagosome containing the food particle detaches from the plasma membrane into the cytoplasm, where its contents are digested by lysosomal enzymes.
Question 17.
Cell wall of which one of these is not made up of cellulose?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Hydrilla
(c) Mango tree
(d) Cactus
Solution:
(a) Cell wall of plants is made up of cellulose whereas cell wall of bacteria is mainly made up of peptidoglycan.
Question 18.
Silver nitrate solution is used to study
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) nucleus
(d) mitochondria.
Solution:
(b) Camillo Golgi (1898) discovered a method of staining individual nerve cells and other cell structures by using a weak solution of silver nitrate. This method is known as black reaction. Camillo Golgi discovered Golgi apparatus while he was examining the nerve cells of bam owl. Silver nitrate solution has been used since then to stain Golgi apparatus.
Question 19.
Organelle other than nucleus, containing DNA is
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) mitochondria
(d) lysosome.
Solution:
(c) Nucleus, mitochondria and plastids are the cell organelles present in eukaryotic cells that contain their own DNA.
Question 20.
Kitchen of the cell is
(a) mitochondria
(b) endoplasmic reticulum
(c) chloroplast
(d) Golgi apparatus.
Solution:
(c) Chloroplastsarethegreencoloured plastids that contain the pigment chlorophyll There are double membrane bound cell organelles that contain their own DNA and ribosomes. Chlorophyll pigment of the chloroplast traps the solar energy which is used to synthesise food by the process of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are thus the sites of photosynthesis and are commonly called ‘kitchen of the cells’.
Question 21.
Lipid molecules in the cell are sythesised by
(a) smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(b) rough endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Golgi apparatus
(d) plastids.
Solution:
(a) Refer to answer 12.
Question 22.
Cell arises from pre-existing cell was stated by
(a) Haeckel
(b) Virchow
(c) Hooke
(d) Schleiden.
Solution:
(b) Rudolf Virchow (1855) proposed that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. His actual aphorism was ‘Omnis cellula e cellula’.
Question 23.
Cell theory was given by
(a) Schleiden and Schwann
(b) Virchow
(c) Hooke
(d) Haeckel.
Solution:
(a) The cell theory, that all the plants and animals are composed of cells and that the cell is the basic unit of life, was presented by two biologists, M.J. Schleiden (1838) and Theodore Schwann (1839).
Question 24.
The only cell organelle seen in prokaryotic cell is
(a) mitochondria
(b) ribosomes
(c) plastids
(d) lysosomes.
Solution:
(b) A prokaryotic cell is the cell that lacks all the membrane bound cell organelles such as a well developed nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, ER, Golgi apparatus etc. However ribosomes are not surrounded by membrane therefore they are present in prokaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells are characteristic of prokaryotes e.g., bacteria, cyanobacteria, etc.
Question 25.
0rganelie without a cell membrane is
(a) ribosome
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) chloroplast
(d) nucleus.
Solution:
(a) Ribosomes are ribonucleoprotein particles which are not surrounded by any membrane. Golgi apparatus, chloroplast and nucleus are all double membrane bound cell organelles.
Question 26.
1 µm is
(a)10-6m
(b) 10-9m
(c) 10-10m
(d) 10-3m
Solution:
(a)
Question 27.
Lysosome arises from
(a) endoplasmic reticulum ,
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) nucleus
(d) mitochondria.
Solution:
(b) Golgi apparatus is involved in the formation of lysosomes. Endoplasmic reticulum provides the precursors of enzymes to Golgi apparatus required for the formation of lysosomes.
Question 28.
Living cells were discovered by
(a) Robert Hooke
(b) Purkinje
(c) Leeuwenhoek
(d) Robert Brown.
Solution:
(c) Cells were first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He observed the cells in a cork slice (dead cells) with the help of a primitive microscope. Leeuwenhoek (1674), with the improved microscope, discovered the free-living cells in pond water for the first time. Robert Brown (in 1831) discovered the nucleus in the cell. Purkinje (in 1839)coined
Question 29.
Select the odd one out.
(a) The movement of water across a semi- permeable membrane is affected by the amount of substances dissolved in it.
(b) Membranes are made of organic molecules like proteins and lipids.
(c) Molecules soluble in organic solvents can easily pass through the membrane.
(d) Plasma membranes contain chitin sugar in plants.
Solution:
(d) Plasma membrane is a living, thin, elastic, selectively permeable membrane which chemically consists of lipids (20-79%), proteins (20-70%), carbohydrates (1-5%) and water (20%). Chitin sugar is not present in the plasma membrane of plants.
Question 30.
Why are lysosomes known as’suicide-bags’of a cell?
Solution:
Mane Lysosomes are known as ‘suicide bags’ of the cell because they contain digestive enzymes capable to digest the whole cell when the situation demands. When the cell gets damaged during some disturbance in cellular metabolism, lysosomes may burst and digestive enzymes thus released digest r their own cell. This is a mechanism of self-defence by the cell.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 31.
Do you agree that “a cell is a building unit of an organism”. If yes, explain why?
Solution:
Yes, a cell is a building unit of an organism. The body of an organism is made up of various organ systems like digestive system, reproductive system etc. The organ systems are made up of various organs which in turn are made up of tissues. A tissue is a group of cells performing the same function. Hence, a cell is the basic building unit (or structural unit) of an organism. It can be represented as:
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ → Organism System
Question 32.
Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time?
Solution:
Soap solution is a hypertonic solution i.e., it is more concentrated than the cells of our skin. As we know when a cell is immersed in a hypertonic solution, water leaves the cell by the process of exosmosis resulting in shrinkage of the cell. In the same way, while washing clothes for a long time, exosmosis occurs in the skin cells resulting in the shrinkage of skin cells of our fingers.
Question 33.
Why is endocytosis found in animals only?
Solution:
Endocytosis is the ingestion of material by the cells through the plasma membrane. It is more difficult to occur in plants than in animals because of the presence and absence of cell wall in plants and animals respectively. The plasma membrane of a plant cell is usually pressed against the rigid cell wall by turgor pressure, which hinders the plasma membrane from invaginating into the cytoplasm. Turgor pressure is a positive pressure which develops in a plant cell due to the entry of water into it.
Question 34.
A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after some time, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain.
Solution:
The phenomenon responsible for such situation is exosmosis. Concentrated solution of salt is hypertonic to the cells of our body i.e., concentration of water molecules in it is lesser than the concentration of water molecules in the cells of our 6ody. When a person drinks concentrated salt solution, water comes out of the cells of the alimentary canal (stomach, intestine etc.) by the process of exosmosis causing a loss of water in the cells. This results in dehydration, diarrhoea and vomiting.
Question 35.
Name any cell organelle which is non membranous.
Solution:
Ribosomes are the non membranous cell organelles.
Question 36.
We eat food composed of all the nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. After digestion, these are absorbed in the form of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol etc. What mechanisms are involved in absorption of digested food and water?
Solution:
Absorption is the process by which nutrients pass from the alimentary canal (mainly small intestine) into the blood and lymph. The mechanisms involved in the absorption of digested food (nutrients other than water) are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and active transport. Glucose is absorbed by active transport, some amino acids are absorbed by active transport and some by facilitated diffusion, fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed by simple diffusion. Mechanism /involved in the absorption of water is osmosis.
Question 37.
If you are provided with some vegetables to cook. You generally add salt into the vegetables during cooking process. After adding salt, vegetables release water. What mechanism is responsible for this?
Solution:
The mechanism responsible for this process is exosmosis. Addition of salt during cooking makes the surrounding medium hypertonic i.e., the surrounding medium has lower water concentration than the cells of vegetables. As we know when a cell is immersed in a hypertonic solution, water leaves the cell by the process of exosmosis resulting in its shrinkage. Therefore, vegetables release water after adding salt during cooking process.
Question 38.
If cells of onion peel and RBC are separately kept in hypotonic solution, what among the following will take place? Explain the reason for your answer.
(a) Both the cells will swell.
(b) RBC will burst easily while cells of onion peel will resist the bursting to some extent.
(c) a and b both are correct.
(d) RBC and onion peel cells will behave similarly.
Solution:
(c) Cells of onion peel are surrounded by a cell wall whereas the RBCs (red blood cells) do not have cell wall. When the cells of onion peel and RBCs are separately kept in hypotonic solution, RBCs will first swell up and then burst due to endosmosis. However, cell wall in the cells of onion peel exerts a counter wall pressure when the cells become fully turgid. This stops further entry of water into the cells and thus the cells do not burst.
Question 39.
Bacteria do not have chloroplast but some bacteria are photoautotrophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of bacterial cell performs this?
Solution:
In most photosynthetic bacteria, pigments and enzymes involved in photosynthesis are found in infoldings of plasma membrane that extend into the cytoplasm.
Question 40.
Match the following A and B.
| A | B | ||
| (a) | Smooth endoplasmic reticulum | (i) | Amoeba |
| (b) | Lysosome | (ii) | Nucleus |
| (c) | Nucleoid | (iii) | Bacteria |
| (d) | Food vacuoles | (iv) | Detoxification |
| (e) | Chromatin material and nucleolus | (v) | Suicidal bag |
Solution:
(a) (iv)
(b) (v)
(c) (iii)
(d) (i)
(e) (ii)
Question 41.
Write the name of different plant parts in which chromoplast, chloroplast and leucoplast are present.
Solution:
Chromoplasts are present in flowers, fruits and other colourful parts of the plant. Chloroplasts are present in green coloured parts e.g., leaves of the plant. Leucoplasts are present in non-photosynthetic and storage organs of the plant e.g., seeds, fruits, tubers, roots etc. ”
Question 42.
Name the organelles which show the analogy written as under
(a) Transporting channels of the cell _______
(b) Power house of the cell _______
(c) Packaging and dispatching unit of the cell _______
(d) Digestive bag of the cell _______
(e) Storage sacs of the cell _______
(f) Kitchen of the cell _______
(g) Control room of the cell _______
Solution:
(a) Endoplasmic reticulum
(b) Mitochondria
(c) Golgi apparatus
(d) Lysosome
(e) Vacuoles
(f) Chloroplast
(g) Nucleus
Question 43.
How is a bacterial cell different from an onion peel cell?
Solution:
A bacterial cell is a prokaryotic cell which contains a poorly defined region called nucleoid. All the membrane-bound cell organelles are absent in a bacterial cell.
An onion peel cell is a eukaryotic plant cell which contains a well defined nucleus and all the membrane-bound cell organelles such as
mitochondria, ER, etc.
Question 44.
How do substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) move in and out of the cell?
Solution:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) move in and out of the cell by the processes diffusion and osmosis. The process of movement of molecules of a substance from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration is called diffusion. CO2is a cellular waste which gets accumulated in high concentration inside the cell.
In the cell’s external environment, the concentration of CO2 is low as compared to that inside the cell. As soon as there is a difference of concentration of CO2 inside and outside a cell, CO2 moves out of the cell from a region of high concentration, to a region of low concentration outside the cell by the process of diffusion.
Water moves into and out of the cell from the region of its higher contentration to the region of its lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane by the process of osmosis.
Question 45.
How does Amoeba obtains its food?
Solution:
Amoeba obtains its food by the process of endocytosis. Endocytosis refers to the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to engulf the food particle and ultimately forming an intracellular membrane-bound vesicle.
Depending upon the type of food material, endocytosis may be (i) phagocytosis (intake of solid material) or (ii) pinocytosis (intake of liquid material).
Phagocytosis is a common method of feeding in some protozoans e.g., Amoeba. In this method, a part of plasma membrane invaginates in the region of solid food particle and engulfs it. The membrane enclosed vesicle called phagosome containing the food particle detaches from the plasma membrane into the cytoplasm, where its contents are digested by lysosomal enzymes.
Question 46.
Name the two organelles in a plant cell that contain their own genetic material and ribosomes.
Solution:
Mitochondria and plastids are the two cell organelles in a plant cell that contain their own genetic material (i.e., DNA) and ribosomes.
Question 47.
Why are lysosomes also known as “scavengers of the cells”?
Solution:
Lysosomes are known as “scavengers of the cells” because they are a kind of waste disposal system of the cell. This is due to the presence of powerful digestive enzymes which are capable of breaking down all organic material. Lysosomes help to keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material (such as bacteria, food particles etc.) as well as worn-out cell organelles.
Question 48.
Which cell organelle controls most of the activities of the cell?
Solution:
Nucleus controls most of the activities of the cell (such as cellular metabolism, reproduction etc.) due to the presence of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which contains all the information required by the cell. DNA directs the synthesis of RNA, which in turn directs the synthesis of proteins and enzymes required for various cellular activities.
Question 49.
Which kind of plastid is more common in
(a) roots of the plant
(b) leaves of the plant
(c) flowers and fruits.
Solution:
(a) Leucoplasts are more common in non-photosynthetic organs such as roots of the plant.
(b) Chloroplasts are more common in green photosynthetic parts such as leaves of the plant.
(c) Chromoplasts are more common in colourful parts such as flowers and fruits of the plant.
Question 50.
Why do plant cells possess large sized vacuole?
Solution: In mature plant cells, a large central vacuole occupying most of the cell space is present. It is because in the plant cells, vacuole does not only store food material and waste products, rather it also contains cell sap. The cell sap helps to keep the cell turgid and provides rigidity and support to it. Vacuole also helps in maintaining water balance of the cell. Thus plant cells possess large sized vacuole.
Question 51.
How are’ chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other?
Solution:
Chromatin occurs as diffuse network of fine filaments in non-dividing nucleus. At the time of cell division, chromatin material becomes condensed into rod-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome has a centromere and two arms called chromatids.
Question 52.
What are the consequences of the following conditions?
(a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium.
(b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium.
(c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium.
Solution:
(a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium will lose water due to exosomosis. The cell will ultimately shrink.
(b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium will gain water due to endosmosis and the cell will ultimately swell up.
(c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium will remain in its original state as there is no net movement of water into or out of the cell.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 53.
Draw a plant cell and label the parts which
(a) determines the function and development of the cell
(b) packages materials coming from the endoplasmic reticulum
(c) provides resistance to microbes to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting
(d) is site for many biochemical reactions necessary to sustain life.
(e) is a fluid contained inside the nucleus.
Solution:
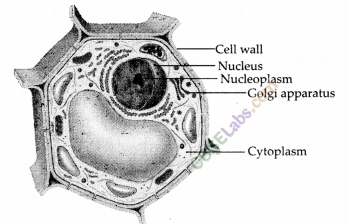
(a) Nucleus
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Cell wall
(d) Cytoplasm
(e) Nucleoplasm
Question 54.
lllustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. How is it different from animal cell?
Solution:

Differences between a plant cell and an animal cells are given as follows :
| Plant cell | Animal cell |
| 1. Cell wall is present. | Cell wall is absent. |
| 2. A large central vacuole is present. | Many small vacuoles are present. |
| 3. Nucleus is peripheral in position. | Nucleus is centrally placed. |
| 4. Golgi apparatus is present in the form of freely distributed units called dictyosomes. | Single Golgi apparatus is present generally near the nuclear envelope. |
| 5. Centrioles are absent. | Centrioles are present. |
| 6. Plastids are present. | Plastids are absent. |
| 7. Mitochondria are comparatively fewer in number. | Mitochondria are numerous. |
| 8. Lysosomes are rarely present. | Typical lysosomes are present. |
| 9. Reserve food material is mainly starch. | Reserve food material is mainly glycogen. |
Question 55.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of an animal cell.
Solution:

Question 56.
Draw a well labelled diagram of an eukaryotic nucleus. How is it different from nucleoid?
Solution:

Differenrence between nucleus and nucleoid are:
| Nucleus | Nucleoid |
| 1. It is larger in size. | 1. It is smaller in size. |
| 2. It is bounded by double membrane. | 2. It is not bounded by any membrane. |
| 3. It contains nucleolus. | 3. It does not contain nucleolus. |
| 4. It contains DNA associated with histone proteins. | 4. It contains naked DNA i.e., DNA is not associated withb histone proteins. |
| 5. It is present in eukaryotic cells. | 5. It is present in prokaryotic cells. |
| 6. Plastids are present. | 6. Plastids are absent. |
Question 57.
Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biogenesis?
Solution:
Differences between rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) are as follows :
| RER | SER |
| 1. RER has ribosomes attached to its surface. | 1. SER does not have ribosomes attached to its surface. |
| 2. RER takes part in protein synthesis. | 2. SER takes part in synthesis of lipids and fats. |
Membrane biogenesis (i.e., formation of plasma membrane) is carried out by the joint activity of some cell organelles.
The proteins and lipids, essential for building the cell membrane, are respectively manufactured by rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The lipid molecules for cell membrane are formed and inserted into membrane of smooth ER by smooth ER itself. The protein molecules of cell membrane are mostly synthesised and inserted into membrane at the level of rough ER. In the process of glycosylation, short chains of sugars, called oligosaccharides, are added to molecules of proteins and lipids at the level of Golgi apparatus. In this way, the formation of plasma membrane (membrane biogenesis ) involves thd following organelles, all forming the so-called endomembrane system :
Rough ER → Smooth ER → Golgi apparatus → Secretory vesicle → Plasma membrane.
Question 58.
In brief state what happens when
(a) dry apricots are left for sometime in pure water and later transferred to sugar solution?
(b) a red blood cell is kept in concentrated saline solution?
(c) the plasma membrane of a cell breaks down?
(d) rheo leaves are boiled in water first and then a drop of sugar syrup is put on it?
(e) Golgi apparatus is removed from the cell?
Solution:
(a) When dry apricots are left in pure water, they swell up due to endosmosis and when they are kept in sugar solution, they shrink due to exosmosis.
(b) When a red blood cell is kept in concentrated saline solution, it loses water due to exosmosis and1 shrinks. It gives shrivelled appearance (cernation).
(c) If plasma membrane of a cell breaks down, all the protoplasmic materials including cells organelles will come out of the cell resulting in their non-functioning and hence death of the cell. Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane which regulates transport of certain specific substances into and out of cell maintaining the identity of the cell. If plasma membrane of a cell breaks down, there may occur loss of some essential components of the cell and the substances which are not required by the cell may enter into it. This would ultimately lead to death of the cell.
(d) Cells of the rheo leaves will get killed on boiling, hence no plasmolysis will occur. Therefore there will be no effect of putting sugar syrup over the leaves.
(e) If Golgi apparatus is removed from the cell, modification, sorting and packaging of materials coming from ER or synthesised in the Golgi apparatus itself, will not take place. Other functions carried out by the Golgi apparatus such as synthesis of complex sugars, formation of lysosomes, membrane biognesis etc. will also not take place, resulting in non-functioning and hence death of the cell.
Question 59.
Draw a neat diagram of plant cell.
Solution:

NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings
- Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
- Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Chapter 6 Tissues
- Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
- Chapter 8 Motion
- Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
- Chapter 10 Gravitation
- Chapter 11 Work and Energy
- Chapter 12 Sound
- Chapter 13 Why do we Fall ill
- Chapter 14 Natural Resources
- Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.