Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Science Chapter 1
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Is there any similarity in materials?
Answer:
Yes, all materials possess mass and occupy space.
Question 2.
When 50 g of sugar is dissolved in 100 mL of water, there is no increase in volume. What characteristic of matter is illustrated by this observation?
Answer:
This observation indicates that particles of water have spaces between them into which sugar particles fit.
Question 3.
What happens when an inflated air balloon is pricked with a pin? Name the property of the gaseous state exhibited by this observation.
Answer:
The balloon bursts and diffusion takes place.
Question 4.
Name the process which occurs when a drop of dettol is added to water.
Answer:
When dettol is added to water, diffusion takes place.
Question 5.
To which physical state of matter do the following statements apply?
(i) Incompressible, no fixed shape
(ii) Compressible, no definite volume
Answer:
(i) Liquid
(ii) Gas
Question 6.
Name the state of matter in which:
(i) Layers of particles can slip and slide over one another easily.
(ii) Particles just move around randomly because of very weak force of attraction.
Answer:
(i) Liquid state,
(ii) Gaseous state.
Question 7.
Define density and give its SI unit.
Answer:
Density of a substance is defined as the mass per unit volume. Its SI unit is kgm-3.
Question 8.
In which of the following, the particles have highest forces of attraction?
Water, NaCl (solid), ice or, wax.
Answer:
NaCl (solid) has particles with the highest forces of attraction.
Question 9.
Why do the gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container than the solids?
Answer:
In gases, the particles move randomly at high speed and they collide with each other and with the walls of the container.
Question 10.
Which of the following diffuses faster?
Water vapour, wax or, ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
Water vapour
Question 11.
Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice cold water?
Answer:
The water vapour present in the air comes in contact with cold surface of the glass, loses its energy and gets converted into droplets of water.
Question 12.
Can materials exist in all the three states?
Answer:
Yes, materials can exist in all the three states under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
Question 13.
Kinetic energy of particles of water in three vessels A, B and C are EA, EB and EC respectively and EA > EB > EC. Arrange the temperatures, TA, TBand TC of water in the three vessels in increasing order.
Answer:
TC < TB < TA , the kinetic energy of particles is greater at higher temperature.
Question 14.
Analyse the temperature versus time graph of water, given below.
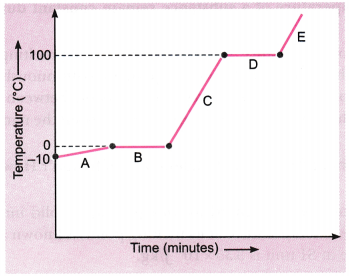
Which region contains all liquids?
Answer:
Region C
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-I
Question 1.
When a crystal of potassium permanganate is placed in a beaker containing water, its purple colour spreads throughout the water. What do you conclude from this observation about the nature of potassium permanganate and water?
Answer:
When we place few crystals of potassium permanganate in a beaker containing water, we get two distinct layers—colourless water at the top and pink colour at the bottom. After few minutes, pink colour spreads and whole solution turns pink due to diffusion. Since potassium permanganate is a solid substance, it does not possess so much space. Water molecules due to liquid state, collide with solid particles and intermix due to sufficient space between molecules.
Question 2.
Why do solids have a regular geometrical shape?
Answer:
In solids, the particles have highly ordered arrangement because the intermolecular forces between the particles are very strong. Therefore, solids have a regular geometrical shape.
Question 3.
Why are gases compressible but not liquids?
Answer:
Gases are compressible because the intermolecular space is very large in gases, whereas liquids are not compressible because in liquids, the intermolecular space is less.
Question 4.
Can a rubber band change its shape on stretching? Is it a solid?
Answer:
Yes, a rubber band changes shape under force and regains the same shape when the force is removed. It breaks on applying excessive force. Yes, it is a solid.
Question 5.
Why steam at 100°C is better for heating purposes than water at 100°C?
Answer: Steam at 100°C is better for heating purposes than water at 100°C because the energy of 1 kg of steam at 100°C is 22.6 × 105 joule which is more than that of 1 kg of water at the same temperature.
Question 6.
Give two ways in which melting points and boiling points can be useful.
Answer:
- To check whether the substance is pure or not.
- To identify and characterise the substance.
Question 7.
Alka was making tea in a kettle. Suddenly she felt intense heat from the puff of steam gushing out of the spout of the kettle. She wondered whether the temperature of the steam was higher than that of the water boiling in the kettle. Comment. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The temperature of both boiling water and steam is 100°C, but steam has more energy because of latent heat of vaporisation.
Question 8.
Why does the temperature of a substance remain constant during its melting point or boiling point? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The temperature of a substance remains constant at its melting and boiling points until all the substance melts or boils because, the heat supplied is continuously used up in changing the state of the substance by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. This heat energy absorbed without showing any rise in temperature is given the name latent heat of fusion/latent heat of vaporisation.
Question 9.
What do you understand by the term ‘latent heat of fusion’? How much is the latent heat of fusion of ice?
Answer:
The amount of heat that is required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure without any change in temperature at its melting point, is known as latent heat of fusion. The latent heat of fusion of ice in SI unit is 3.35 × 105 J/kg.
Question 10.
Which gas is called dry ice? Why?
Answer:
Solid CO2 is known as dry ice. This is because it directly gets converted into gaseous state without passing through liquid state on decreasing the pressure to 1 atmosphere.
Question 11.
A glass tumbler containing hot water is kept in the freezer compartment of a refrigerator (temperature <0°C). If you could measure the temperature of the content of the tumbler, which of the following graphs would correctly represent the change in its temperature as a function of time? [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer:
(a). The water will cool initially till it reaches 0°C, the freezing point. At this stage, the temperature will remain constant till all the water will freeze. After this, temperature would fall again.
Question 12.
Why do the doctors advise to put strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person having high fever?
Answer:
When a person has fever, his body temperature becomes more than the normal body temperature. If we put strips of wet cloth on the forehead of a person suffering from high fever, the water evaporates taking heat from the body. Thus, moist strips will lower his body temperature.
Question 13.
Look at the following figures and suggest in which of the glass containers, i.e., A, B, C or D, the rate of evaporation will be the highest? Explain. [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer:
(C). The rate of evaporation increases with an increase in surface area because evaporation is a surface phenomenon. Also, with the increase in air speed, the particles of water vapour will move away with air, which will increase the rate of evaporation.
Question 14.
Why do wet clothes dry quickly in the sun than in the shade?
Answer:
The temperature in the sunny area is higher than in the shade and evaporation takes place at a faster rate at high temperature. Hence, wet clothes dry quickly in the sun.
Question 15.
Why do trees acquire more leaves during summer?
Answer:
During summer the temperature is generally very high. In order to keep cool, a tree must transpire (transpiration is a phenomenon of evaporation of water from the leaves) more to keep itself cool. More transpiration requires more leaves. Hence, a tree acquires more leaves during summer.
Question 16.
Why do we feel comfortable under a fan when we are perspiring?
Answer:
The sweat is readily evaporated from the body by the air from the fan. As a result, we feel comfortable under a fan.
Question 17.
Why do people sprinkle water on the roof after a hot sunny day?
Answer:
Water sprinkled on the roof evaporates by taking the large latent heat of vaporisation from the ground. This makes the place cool and comfortable.
Question 18.
It is a hot summer day, Priyanshi and Ali are wearing cotton and nylon clothes respectively. Who do you think would be more comfortable and why? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Priyanshi would be more comfortable because cotton is a good absorber than nylon. It absorbs sweat from the body and provides large surface area for evaporation which causes cooling effect. As a result, body feels cool and comfortable.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-II
Question 1.
Substance ‘A’ has high compressibility and can be easily liquefied. It can take up the shape of any container. Predict the nature of the substance. Enlist four properties of this state of matter.
Answer:
‘A’ is a gas.
Properties of gases:
- They do not have fixed shape and fixed volume.
- They have large interparticle space.
- They have least forces of attraction between the molecules.
- They are highly compressible.
Question 2.
Suggest an activity to show that the rate of diffusion of liquids decreases with increase in density of the liquid.
Answer:
- Take two beakers filled with water.
- Put a drop of blue ink slowly along the sides of the first beaker and honey in the same way in another beaker.
- Leave it undisturbed.
- We observe that honey diffuses slowly as compared to ink.
This experiment shows that lesser the density, faster the rate of diffusion.
Question 3.
Classify the following into osmosis/diffusion
- Swelling up of a raisin on keeping in water.
- Spreading of virus on sneezing.
- Earthworm dying on coming in contact with common salt.
- Shrinking of grapes kept in thick sugar syrup.
- Preserving pickles in salt.
- Spreading of smell of cake being baked throughout the house.
- Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
- Osmosis
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Osmosis
- Osmosis
- Diffusion
- Diffusion
Question 4.
Explain what happens to the molecular motion and energy of 1 kg of water at 273 K when it is changed into ice at same temperature. How is the latent heat of fusion related to the energy exchange that takes place during this change of state?
Answer:
- Molecular motion decreases as water gets converted into ice.
- Latent heat of solidification is given off.
Latent heat of solidification is equal to latent heat of fusion.
Question 5.
Design an experiment to show that ammonium chloride undergoes sublimation.

Answer:
- Take crystals of ammonium chloride in a china dish.
- Put the china dish on a tripod stand with wire gauze.
- Put an inverted funnel on the china dish and insert a cotton plug in the stem of the funnel.
- Heat the china dish on a low flame.
- In the inside of the funnel white deposits of ammonium chloride is seen which directly converts into gaseous state and then solidifies.
Question 6.
Explain interconversion of three states of matter with the help of flow chart. Name the process of each interconversion.
Answer:

Question 7.
A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the content of the beaker as a function of time. Which of the following (shown in figure given below) would correctly represent the result? Justify your choice. [NCERT Exemplar]

Answer:
Since ice and water are in equilibrium, the temperature would be zero. When we heat the mixture, energy supplied is utilised in melting the ice and the temperature does not change till all the ice melts because of latent heat of fusion. On further heating, the temperature of the water would increase. Therefore, the correct option is (d).
Question 8.
Explain how the rate of evaporation of a liquid is affected with:
- Increase in temperature of the liquid.
- Decrease in exposed surface area.
- Increase in moisture in the surrounding air.
- Increase in wind speed.
Answer:
- Rate of evaporation increases with rise in temperature.
- Evaporation is less when exposed surface area decreases.
- Less evaporation if moisture content is high in the air.
- Rate of evaporation increases if wind speed increases.
Question 9.
You want to wear your favourite shirt to a party, but the problem is that it is still wet after a wash. What steps would you take to dry it faster? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Conditions that can increase the rate of evaporation of water are:
- An increase in the surface area by spreading the shirt.
- An increase in the temperature by putting the shirt under the sun.
- Increase in the wind speed by spreading it under the fan.
Question 10.
How does evaporation differ from boiling?
Answer:
| Evaporation | Boiling |
| 1. Evaporation takes place at all temperatures. | 1. Boiling takes place only at the boiling point of the liquid. |
| 2. Temperature changes during evaporation. | 2. The temperature does not change during boiling. |
| 3. It is a very slow process. | 3. It is a fast process. |
| 4. Evaporation takes place only at the surface of the liquid. | 4. Boiling takes place in the entire body of the liquid. |
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe the continuous motion of particles of matter with the help of an activity.
Answer:
(a) To demonstrate motion of particles in air:
- Place few lighted incense sticks in a corner of a room.
- Move about the room and smell the fragrance of the incense sticks.
The fragrance produced due to burning of incense sticks is due to movement of vapours produced
rapidly in all directions.
(b) To demonstrate motion of particles of solid matter:
- Drop a crystal of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate into a glass of hot water.
- Do not stir the solution and allow the crystals to settle at the bottom.
- The colour of the solid is seen spreading slowly. This is because the solid particles diffuse in the water.
Question 2.
Describe an activity to determine the boiling point of water and melting point of ice.

Answer:
Determination of boiling point of water:
- In a beaker take some water and insert a thermometer in it with the help of a clamp.
- Put the beaker on a tripod stand and heat the apparatus with the help of kerosene burner slowly.
- Observe what happens to water.
- You will observe a steady stream of bubbles. This temperature is the boiling point of water.
Determination of melting point of ice:
- Take crushed ice in a beaker and insert a thermometer in the beaker by hanging it from the clamp of the stand in such a way that the bulb of the thermometer is completely inside the ice.
- Wait for some time and keep recording the temperature after small intervals of time.
- Note down the temperature when ice just starts melting.
- Let the bulb of the thermometer remain in mixture of ice and water for some more time and keep recording the temperature. This temperature is the melting point of ice.
Question 3.
While heating ice in a beaker with a thermometer suspended in it, a student recorded the following observations:

Based on the above observations, answer the following questions:
(a) State the change(s) observed between 2-3 min. and name the process involved.
(b) Between 30-35 min., the temperature remains constant. State the reason for this. Name the heat involved in the process and define it.
Answer:
(a) Between 2-3 min, ice converts into water. This process is known as fusion.
(b) Between 30-35 min, the temperature remains constant because the heat supplied is used up in overcoming the intermolecular forces of liquid to change into vapours. The heat involved in the process is latent heat of vaporisation. It is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of liquid into gas at its boiling point.
Question 4.
Discuss the various factors which affect the rate of evaporation. Latent heat of evaporation of two liquids A and B is 100 J/kg and 150 J/kg respectively. Which one can produce more cooling effect and why?
Answer:
Factors affecting the rate of evaporation:
- Surface area: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in surface area.
- Temperature: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in temperature.
- Humidity: The rate of evaporation decreases with increase in humidity.
- Wind speed: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in wind speed.
- Nature of the liquid: The volatile compounds evaporate faster than less volatile compounds (liquids).
B will produce more cooling effect because it will absorb more heat from the surroundings for evaporation.
Question 5.
Comment on the following statements:
(a) Evaporation causes cooling.
(b) Rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with increase in humidity.
(c) Sponge though compressible is a solid.
(d) Ice is solid at 0°C, while water is liquid at room temperature.
(e) Sugar crystals dissolve faster in hot water than cold water. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) Evaporation produces cooling as the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the
surroundings and change into vapour, thereby producing a cooling effect.
(b) Air around us cannot hold more than a definite amount of water vapour at a given temperature which is known as humidity. So, if the air is already rich in water vapour, it will not take up more water; therefore, rate of evaporation of water will decrease.
(c) A sponge has minute holes in which air is trapped. Also the material is not rigid. When we press it, the air is expelled out and we are able to compress it. But it is a solid because it has definite shape and volume and does not change its shape unless compressed.
(d) Ice is solid at 0°C because it has a definite volume and definite shape due to strong intermolecular forces. Water is liquid at room temperature because it has definite volume and no definite shape due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction.
(e) Sugar crystals dissolve faster in hot water than cold water because hot water molecules have more kinetic energy. Due to this, they strike faster on the particles of sugar than cold water molecules. As a result, hot water will dissolve them faster than cold water.
Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Extra Questions Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
Question 1.
The diagram below shows burning of an oil lamp.

Draw the arrangement of particles of position ‘X’ and ‘Y’ when the lamp is burning.
Answer:

Question 2.
‘A small volume of water in a kettle can fill a kitchen with steam’. Explain why.
Answer:
The liquid form of water converts into gaseous form in steam.
Its particles move very rapidly in all the directions and fill the kitchen as gases completely fills the vessel.
Question 3.
A sample of water under study was found to boil at 102°C at normal temperature and pressure. Is the water pure? Will this water freeze at 0°C? Comment. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Its freezing point will be below 0°C due to the presence of a non-volatile impurity in it.
Question 4.
You are given the following substances with their melting and boiling points.
| Substance | Melting point (°C) | Boiling point (°C) |
| X | -219 | -183 |
| Y | 119 | 445 |
| Z | – 15 | 78 |
Identify the physical states of X, Y and Z at room temperature (30°C).
Answer:
‘X’ is gas at room temperature.
‘Y’ is solid at room temperature.
‘Z’ is liquid at room temperature.
Question 5.

(a) Name the changes in the terms of process P, Q, R and S?
(b) Which of the changes are exothermic and endothermic?
Answer:
(a) ‘P’ is fusion (melting), ‘0’ is boiling, ‘R’ is condensation and ‘S’ is sublimation.
(b) ‘P’, ‘0’ and ‘S’ are endothermic and ‘R’ is exothermic.
Question 6.
The temperature-time graph given alongside shows the heating curve for pure wax.

From the graph answer the following:
(a) What is the physical state of the substance at the points A, B, C and D?
(b) What is the melting point of the substance?
(c) What is its boiling point?
(d) Which portions of the graph indicates that change of state is taking place?
(e) Name the terms used for heat absorbed during change of states involved in above process.
Answer:
(a) A-Solid state,
B—Both solid and liquid states,
C—Both liquid and gaseous states
C—liquid state,
(b) 15°C
(c) 110°C
(d) A1B1 and D1D2
D1D2—Latent heat of vaporisation
(e) A1B1—Latent heat of fusion.
Question 7.
Water as ice has a cooling effect, whereas water as steam may cause severe burns. Explain these observations. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
In case of ice, the water molecules have low energy while in case of steam the water molecules have high energy. The high energy of water molecules in steam is transformed as heat and may cause burns. On the other hand, in case of ice, the water molecules take energy from the body and thus, give a cooling effect.