Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 Polymers Class 12 Important Questions
Polymers Class 12 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Give an example of elastomers. (Delhi, All India 2009)
Answer:
Buna-S, Buna-N.
Question 2.
What does the part ‘6, 6’ mean in the name nylon-6, 6? (Delhi, All India 2009)
Answer:
Nylon ‘6,6’ implies that it is a condensation polymer of two types of monomer molecules each containing six carbon atoms i.e. adipic acid (HOOC (CH2)4 COOH) and hexamethylenediamine (H2N CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH2)
Question 3.
What is the primary structural feature necessary for a molecule to make it useful in a condensation polymerization reaction? (All India 2009)
Answer:
The presence of two bifunctional monomer molecules undergo condensation with the loss of simple molecule of water, alcohol to form dimer.
Question 4.
What does the designation ‘6, 6’ mean in the name nylon-6, 6? (All India 2010)
Answer:
Since both adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine contain six carbon atoms each.
Question 5.
What is meant by ‘copolymerisation’? (All India 2010)
Answer:
When two or more different monomers are allowed to polymerize together, the product formed is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerisation.
Question 6.
What are biodegradable polymers? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Biodegradable polymers : All those biopolymers which disintegrate by themselves in biological systems during certain period of time by enzymatic hydrolysis are called biodegradable polymers.
Example : Poly-p-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-p-Hydro- xyvalerate (PHBV)
Uses : These are used
- in packaging
- in orthopaedic devices
- in controlled drug release
- in bacterial degradation
Question 7.
In nylon 6, 6, what does the designation ‘6, 6’ mean? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Since both adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine contain six carbon atoms each.
Question 8.
Define the term, ‘homopolymerisation’ giving an example. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
The polymer formed by the polymerization of a single/same monomeric species is known as homopolymerization.
Example : Polythene/PVC/Polypropene.
Question 9.
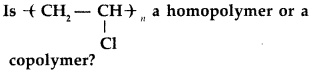
(All India 2013)
Answer:

up of some monomer units
Question 10.
Give one example of a condensation polymer. (All India 2013)
Answer:
Example : Nylon 6,6
Question 11.
Which of the following is a natural polymer?
Buna-S, Proteins, PVC (All India 2014)
Answer:
Protein is a natural polymer.
Question 12.
Based on molecular forces what type of polymer is neoprene? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Elastomers
Question 13.
Which of the following is a fibre?
Nylon, Neoprene, PVC (All India 2013)
Answer:
Nylon is a fibre.
Question 14.
How does a homopolymer differ from a copolymer? (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
Homopolymers : Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monomer units are called homopolymers. Example : Polyethene, PVC, teflon.
Copolymers : Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomer molecules are copolymers.
Example : Buna-S, Nylon 6, 6
Polymers Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type SA-I
Question 15.
Draw the structures of the monomers of the following polymers : (Delhi 2009)
(i) Teflon
(ii) Polyethene
Answer:

Question 16.
What is the repeating unit in the condensation polymer obtained by combining HO2CCH2CH2CO2H (succinic acid) and H2NCH2CH2NH2 (ethylene diamine)? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:


Question 17.
Differentiate between molecular structures and behaviours of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each type. (All India 2009)
Answer:

Question 18.
Differentiate between condensation and addition polymerisations. Give one example each of the resulting polymers. (All India 2009)
Answer:
Condensation polymerisation : In this, two or more bifunctional molecules undergo a series of independent condensation reactions with the elimination of simple molecules like H2O, alcohol, NH3, CO2, HCl etc. to form a macromolecule.
Example : Formation of nylon 6, 6

Addition polymerisation : In this, the molecules of the same or different monomers simply add on one another to form macromolecule. These molecules occur among molecules containing double and triple bonds.
Example : Formation of polyethene

Question 19.
Draw the molecular structures of the monomers of
(i) PVC
(ii) Teflon (All India 2010)
Answer:

(ii)

Question 20.
Draw the structures of the monomers of the following polymers : (All India 2010)
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Nylon-6
Answer:
(i) Bakelite : Phenol and formaldehyde ➝ Condensation polymer.
(ii) Nylon-6 : The monomeric repeating unit of Nylon-6 is

Question 21.
Mention two important uses of each of the following :
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Nylon 6 (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
(i) Bakelite :
(i) It is used in making handles of utensils.
(ii) Also used in production of billiard balls, dominoes and pieces for games like chess.
(ii) Nylon 6 :
(i) Nylon is used in making stockings.
(ii) It is also used for making parachutes.
Question 22.
Name the sub-groups into which polymers are classified on the basis of magnitude of intermolecular forces. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
- Elastomers
- Fibres
- Thermoplastic polymers
- Thermosetting polymers.
Question 23.
Draw the structure of the monomer for each of the following polymers : (Delhi 2012)
(i) Nylon-6
(ii) Polypropene
Answer:
(i) Nylon-6 :


Question 24.
Define thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each. (All India 2012)
Answer:
Thermoplastic polymers : Linear polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction are in between those of elastomers and fibres and can be melted again and again on heating followed by moulding to give desired shape.
Example : Polyethene, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) etc.
Thermosetting polymers : These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould, undergo change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. These cannot be re-melted.
Example : Bakelite, Melamine etc.
Question 25.
What is a Bio-degardable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester. (All India 2013)
Answer:
Bio-degardable polymer : All those biopolymers which disintegrate by themselves in biological systems during certain period of time by enzymatic hydrolysis are called biodegradable polymers. Example: Poly-p-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-p-Hydro- xyvalerate (PHBV)
Uses : These are used
- in packaging
- in orthopaedic devices
- in controlled drug release
- in bacterial degradation
Question 26.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Neoprene (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Bakelite : Phenol and Formaldehyde
(ii) Neoprene : Chloroprene.
Question 27.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(i) Terylene
(ii) Nylon-6, 6 (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Monomers of terylene are : Ethylene glycol and Terephthalic acid.
(ii) Monomers of nylon-6, 6 are : Adipic acid and Hexamethylene diamine.
Question 28.
Write the name of monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(i) Teflon
(ii) Buna-N (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) Teflon : Tetrafluoroethylene.
(ii) Buna-N : Monomers of Buna-N are 1, 3- Butadiene and acrylonitrile.
Question 29.
Write the names and structures of monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Nylon-6, 6 (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:


Polymers Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type SA-II
Question 30.
Give one example each of
(i) addition polymers
(ii) condensation polymers
(iii) copolymers. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:

Question 31.
Write the name and structure of the monomer of each of the following polymers :
(i) Neoprene
(ii) Buna-S
(iii) Teflon (Delhi 2013)
Answer:

Question 32.
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Thermoplastic polymers : Linear polymers in which the intermolecular forces of attraction are in between those of elastomers and fibres and can be melted again and again on heating followed by moulding to give desired shape.
Example : Polyethene, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) etc.
Thermosetting polymers : These are semifluid substances with low molecular masses which when heated in a mould, undergo change in chemical composition to give a hard, infusible and insoluble mass. These cannot be re-melted.
Example : Bakelite, Melamine etc.
Question 33.
Draw the structures of the monomers of the following polymers :
(i) Polythene
(ii) PVC
(iii) Teflon
(All India 2011)
Answer:
![]()
(ii)

(iii)

Question 34.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers :
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Dacron
(iii) Neoprene (All India 2011)
Answer:

Question 35.
Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Give one example of each. (All India 2012)
Answer:

Question 36.
Explain the following terms giving a suitable example for each : (All India 2012)
(i) Elastomers
(ii) Condensation polymers
(iii) Addition polymers
Answer:
(i) Elastomers : These are rubber-like solids with elastic properties. The polymer chains are held together by the weakest intermolecular forces so that they can be stretched.
Example : Buna-S, Buna-N etc.
(ii) Condensation polymers :

Question 37.
(a) What are the differences between thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers ? Give one example of each.
(b) Write down the structure of monomer and one use of the polymer polystyrene. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a)

(b) Polymer polystyrene : The monomer of polystyrene is styrene and its structure is

Use : It is used in the manufacture of food containers, cosmetic bottles etc.
Question 38.
How are polymers classified on the basis of mode of polymerization? Explain with suitable examples. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Polymers can be classified on the basis of mode of polymerisation into two groups :
(i) Addition polymers : The addition polymers are formed by the repeated addition of monomer molecules possessing double or triple bonds.

(ii) Condensation polymers : They are formed by repeated condensation reaction between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomeric units.

Question 39.
Explain the term co-polymerization and give two examples of copolymers and the reactions for their preparations. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Co-polymerization : Co-polymerization is a polymerization reaction in which a mixture of more than one monomeric species is allowed to polymerise and form a copolymer.
Example : Buna- S, Buna-N.
Equations :

Question 40.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Neoprene
(iii) Nylon-6, 6 (Delhi 2012)
Answer:

Question 41.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: (Delhi 2013)
(i) Polystyrene
(ii) Dacron
(iii) Teflon
Answer:

Question 42.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: (Delhi 2013)
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Nylon-6
(iii) Polythene
Answer:
(i) Bakelite : Monomers are
(a) Phenol Structure : (C6H5OH) and
(b) Formaldehyde Structure : (HCHO).
(ii) Nylon-6 : Monomer unit, which is derived from Caprolactum.

(iii) Polyethene : Monomer is Ethene Structure : CH2 = CH2
Question 43.
(a) Differentiate between copolymerization and homopolymerization. Give one example of each.
(b) What is the role of Benzoyl peroxide in preparation of Polythene? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Homopolymers : Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monomer units are called homopolymers.
Example : Polyethene, PVC, teflon. Copolymers : Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from two or more types of monomer molecules are copolymers.
Example : Buna-S, Nylon 6, 6
(b) Benzoyl peroxide acts as radical initiator which decomposes on mild heating to form initiator free radicals which add to double bond of ethene to form a new and larger free radical.
Question 44.
(a) How are thermosetting polymers different from thermoplastic polymers?
(b) Name the polymer which is used for making non-stick cooking utensils. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a)

(b) Teflon is used for making non-stick cooking utensils.
Question 45.
(a) Differentiate between chain growth and step growth polymerization.
(b) What is the function of sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Chain growth polymerization involves successive addition of monomer units to the growing chain carrying a reactive intermediate such as a free radical, a carbocation or a carbanion.
Example : Polyethene, Teflon, PAN etc.
In step growth or condensation polymerization, the polymer is formed in a stepwise manner with the loss of simple molecules like HzO, alcohol etc.
Example : Polyamides like Nylon 6,6, Polyesters etc.
(b) Sulphur introduces sulphur bridges or cross-links between polymer chains thereby imparting more tensile strength, elasticity and resistance to abrasion.
Question 46.
Write the monomers of the following polymers and classify them as addition or condensation polymers :
Teflon, Bakelite and Natural Rubber. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
Teflon
Monomer ➝ Tetrafluoroethylene
Type ➝ Addition polymer
Bakelite
Monomer ➝ Phenol and Formaldehyde
Type ➝ Condensation polymer Natural Rubber
Monomer ➝ Isoprene
Type ➝ Addition polymer
Question 47.
(a) Distinguish between homopolymers and copolymers. Give one example of each.
(b) What are biodegradable polymers? Give one example. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) Homopolymers : Polymers whose repeating structural units are derived from only one type of monomer units are called homopolymers. Example : Polyethene, PVC, teflon.
Copolymers : Polymers whose repeating
structural units are derived from two or more types of monomer molecules are copolymers.
Example : Buna-S, Nylon 6, 6
(b) Biodegradable polymers : All those biopolymers which disintegrate by themselves in biological systems during certain period of time by enzymatic hydrolysis are called biodegradable polymers.
Example : Poly-p-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-p-Hydro- xyvalerate (PHBV)
Uses : These are used
- in packaging
- in orthopaedic devices
- in controlled drug release
- in bacterial degradation
Question 48.
(a) What are biodegradable polymers? Give one example.
(b) Is polythene a condensation or an addition polymer? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) Those polymers which can be decomposed by microorganisms are called biodegradeable polymers.
Example : Nylon-2-Nylon-6
(b) Polythene is an addition polymer.
Question 49.
Write the names of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Polythene
(ii) Polyvinyl chloride
(iii) Bakelite (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:

(iii) Bakelite ➝ Phenol and formaldehyde ➝ Condensation polymer
Question 50.
Give names of the monomers of the following polymers :
(i) Neoprene
(ii) Polystyrene
(iii) Polypropene (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Neoprene : Monomer is Chloroprene or 2- chloro-1, 3-butadiene.

Question 51.
Write the names of monomers used for getting the following polymers :
(i) Teflon
(ii) Bakelite
(iii) Neoprene (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Teflon (Tetrafluoroethylene)

(iii)

Question 52.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers:
(i) Nylon-6,6 : It has two repeating two monomers
(a) Hexa methylene diamine


(iii) Neoprene : Monomer is Chloroprene or 2- chloro-1, 3-butadiene.

Question 53.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers :
(i) Terylene
(ii) Buna-S
(iii) Neoprene (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) Terylene :
Terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol

(ii)

(iii)

Question 54.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers : (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Neoprene
(iii) Teflon
Answer:
(i)

(ii)

(iii)

Question 55.
Explain the term ‘copolymerization’ and give two examples of copolymerization. (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
When two or more different monomers are allowed to polymerize together, the product formed is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerization.
Co-polymerization is a polymerization reaction in which a mixture of more than one monomeric species is allowed to polymerize and form a copolymer. e.g. Buna- S, Buna-N.

Question 56.
(i) What is the role of t-butyl peroxide in the polymerization of ethene?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer:
![]()
(iii) Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of their intermolecular forces:
Polystyrene, Terylene, Buna-S (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(i) t-butyl peroxide acts as a radical initiator or chain initiator in the polymerization of ethene. This initiator readily decomposes on mild heating to form initiator free radicals which adds to double bond of ethene molecule to form a new and larger free radical.
(ii) Adipic acid HOOC(CH2)4—COOH and Hexamethylene diamine NH2(CH2)6NH2.
(iii) The increasing order of polymers on the basis of their intermolecular forces:
Buna-S < Polystyrene < Terylene
Question 57.
Write the mechanism of free radical polymerization of ethene. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Free radical polymerization of ethene:
This process normally occurs at high temperature and under high pressure in presence of small amounts of benzoyl peroxide as the initiator in three steps:
(i) Chain initiation step. Benzoyl peroxide undergoes homolysis and works as chain initiator.


Question 58.
(i) What is the role of Sulphur in the vulcanization of rubber?
(ii) Identify the monomers in the following polymer:

(iii) Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of their intermolecular forces:
Terylene, Polythene, Neoprene (All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Teflon is used for making non-stick cooking utensils.
(ii) The monomers in the given polymer are:
Ethylene glycol HO—CH2CH2—OH
Terephthalic acid

(iii) Neoprene < Polyethene < Terylene
Question 59.
Write two uses of each of the following polymers.
(i) Polypropylene
(ii) PVC
(iii) Nylon-66 (Comptt. Delhi & All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Polypropylene : Manufacture of ropes, toys, pipes etc.
(ii) PVC : Manufacture of raincoats, handbags, vinyl flooring, water pipes etc.
(iii) Nylon-66 : Manufacture of sheets, bristles from brushes, textiles etc.
Question 60.
Write two uses of each of the following polymers.
(i) Polyproplene
(ii) PVC
(iii) Nylon-6, 6 (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Polypropylene : Manufacture of ropes, toys, pipes etc.
(ii) PVC : Manufacture of raincoats, handbags, vinyl flooring, water pipes etc.
(iii) Nylon-6,6 : Manufacture of sheets, bristles from brushes, textiles etc.
Question 61.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Dacron
(ii) Melamine—formaldehyde polymer
(iii) Buna-N (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i)

Question 62.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Neoprene
(ii) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(iii) Buna-S (Delhi 2017)
Answer:


(iii)

Question 63.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(i) Nylon-6
(ii) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(iii) Teflon (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i)


(iii) Monomer: Tetrafluoroethene — CF2 = CF2
Question 64.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(a) Nylon-6,6
(b) Melamine—formaldehyde polymer
(c) Buna-S (All India 2017)
Answer:

(b)

(c)

Question 65.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(a) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
(b) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(c) Buna-N (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) CH2 = CH – Cl
(b)

![]()
Question 66.
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
(a) Teflon
(b) Melamine-formaldehyde polymer
(c) Neoprene (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a)

(b)

(c)
