Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13Amines: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Class 12 Important Questions
Amines: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Class 12 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Why is an alkylamine more basic than ammonia? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Due to electron releasing inductive effect (+1) of alkyl group, the electron density on the nitrogen atom increases and thus, it can donate the lone pair of electrons more easily than ammonia.
Question 2.
Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of basic strengths in their aqueous solutions : NH3, CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N (All India 2009)
Answer:
Basicity order (due to stability of ammonium cation)
(CH3)2 NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3 N > NH3
Question 3.
Give the IUPAC name of H2N — CH2—CH2—CH = CH2. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
IUPAC name : But-3-ene-1-amine
Question 4.
Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their solubility in water : C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2HSNH2 (Delhi & All India 2011)
Answer:
C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C22H5NH2
Question 5.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between ethylamine and aniline. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Ethylamine and aniline :
By Azo dye test: It involves the reaction of any aromatic primary amine with HNO2(NaNO2 + dil. HCl) at 273-278 K followed by treatment with an alkaline solution of 2-naphthol when a brilliant yellow, orange or red coloured dye is obtained.
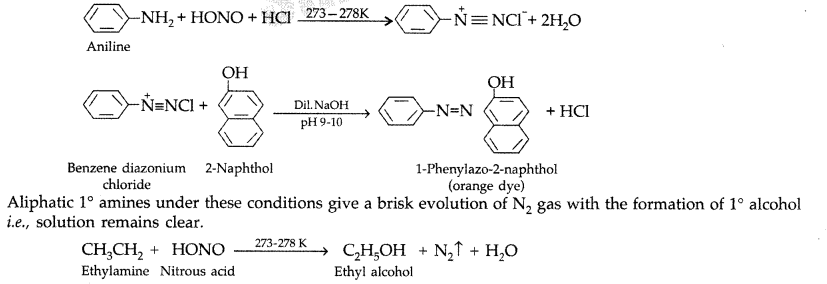
Question 6.
Arrange the following in the decreasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solutions: CH3NH2, (CH3)2 NH, (CH3)3N and NH3 (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(CH3)2 NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3 N > NH3
Question 7.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solution: CH3.NH2, (CH3)3N, (CH3)2NH (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Write the structure of 2-aminotoluene. (All India 2013)
Answer:

Question 9.
Write the structure of n-methylethanamine. (All India 2013)
Answer:
Structure of n-methylethanamine :
H3C—H2C—NH—CH2
Question 10.
Write the structure of prop-2-en-l-amine. (All India 2013)
Answer:
H2C=CH—H2C—NH2
Question 11.
How may methyl bromide be preferentially converted to methyl isocyanide? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Bit carbylamine reaction:

Question 12.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of solubility in water :
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2H5NH2 (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH,
Question 13.
Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5CH2NH2 (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5CH2NH2
Question 14.
Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5N(CH3)2 (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
C6H5N(CH3)2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C6H5NH2
Question 15.
The conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts is known as (All India 2014)
Answer:
Diazotization.
Question 16.
Out of CH3—NH2 and (CH3)3N, which one has higher boiling point? (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
CH3—NH2 has higher boiling point than (CH3)3N.
Question 17.
Complete the following reaction equation : (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:

Question 18.
Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength (Comptt. All India 2015)
Aniline, p-Nitroaniline and p-Toluidine
Answer:
![]()
Question 19.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound: (Delhi 2016)

Answer:
2, 4, 6-Tribromoaniline
Question 20.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound: (CH3CH2)2NCH3 (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
N-Ethyl-N-methylethanamine
Question 21.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: (Comptt. All India 2017)
CH3NHCH(CH3)2
Answer:
IUPAC name: N-Methylpropan-2-amine
Question 22.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: (Delhi 2017)
(CH3)2N-CH2CH3
Answer:
IUPAC name: N, N Dimethylamine
Question 23.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound : (Comptt. All India 2017)

Answer:
IUPAC name : N, N-Dimethylbutanamine.
Amines: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -I [SA – I]
Question 24.
Give the chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethyl amine and Aniline
(ii) Aniline and Benzylamine (All India 2010)
Answer:
(i) Ethylamine and aniline :
By Azo dye test: It involves the reaction of any aromatic primary amine with HNO2(NaNO2 + dil. HCl) at 273-278 K followed by treatment with an alkaline solution of 2-naphthol when a brilliant yellow, orange or red coloured dye is obtained.

(ii) Distinction between Aniline and Benzylamine :
By Nitrous acid test : Benzylamine reacts with HNO2 to form a diazonium salt which being unstable even at low temperature, decomposes with evolution of N2 gas

Question 25.
Identify A and B in each of the following processes : (All India 20100
![]()
Answer:

Question 26.
Give the chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Methylamine and Dimethylamine
(ii) Aniline and N-methylaniline (All India 2010)
Answer:
(i) Methylamine and Dimethylamine :
By Carbylamine test: Methylamine being a primary amine gives this test but Dimethylamine being a secondary amine does not.

(ii) Aniline and N-methylaniline
By Carbylamine test : Aniline is a 1° aromatic amine while N-methylaniline is a secondary aromatic amine. Therefore only 1° aromatic amine gives this test.

Question 27.
Describe the following giving the relevant chemical equation in each case :
(i) Carbylamine reaction
(ii) Hofmann’s bromamide reaction (All India 2012)
Answer:
(i) Carbylamine reaction : Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic KOH form isocyanides or carbylamines which are foul smelling substances. This reaction is known as carbylamines reaction.
![]()
(ii) Hofmann’s bromamide reaction : Primary amines can be prepared by treating an amide with Br2 in an aqueous or alcoholic soln of NaOH.

Question 28.
Complete the following reaction equations : (All India 2012)
(i) C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O →
(ii) C6H5NH2 + Br2 (aq) →
Answer:

Question 29.
Give IUPAC names of the following compounds : (Comptt. Delhi 2012)

Answer:
(a) IUPAC name : Methyl prop-2-en-1-amine
(b) IUPAC name : Phenyl acetamide
Question 30.
How are the following conversions carried out :
(a) Aniline to p-hydroxyazobenzene
(b) Ethanoyl chloride to Ethanenitrile. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) Aniline to p-hydroxyazobenzene

Question 31.
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) CH3CH2Cl to CH3CH2CH2NH2
(ii) Benzene to aniline (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:

Question 32.
How would you account for the following :
(a) Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexyl amine.
(b) Methylamine in aqueous medium gives reddish-brown precipitate with FeCl3. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) In aniline, the lone pair of electrons on the N-atom is delocalised over the benzene ring. As a result, the electron density on the nitrogen decreases.
But in cyclohexylamine, the lone pair of electrons on N-atom is readily available due to absence of reelections. Hence aniline is weaker base than cyclohexylamine.
(b) Methylamine being more basic than H2O, it accepts a proton from water liberating OH– ions.

Question 33.
How would you account for the following :
(a) Electrophilic susbstitution in case of aromatic amines takes place more readily than benzene.
(b) Ethanamide is a weaker base than ethanamine. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) Aniline exists as a resonance hybrid of the following five structures :

The electron density is maximum at ortho and para positions to the – NH2 group. But in benzene there is no delocalisation of electron at any position and hence electrophilic substitution in case of aromatic amines takes place more readily than benzene.
(b) In ethanamide the lone pair of electron of N-atom is not available due to resonance structure

So it is a weaker base.
Question 34.
Illustrate the following reactions :
(a) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(b) Coupling reaction (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) Sandmeyer’s reaction : Aniline reacts with NaNO2 in HCl at 273 – 278 K giving diazonium salt which further reacts with cuprous chloride/bromide to give chloro or bromo benzene.

This reaction is Sandmeyer’s reaction.
(b) Coupling reaction : Arene diazonium salts react with highly reactive aromatic compounds such as phenols and amines to form brightly coloured azo compounds.
Ar – N = N – Ar. This reaction is known as coupling reaction.

Question 35.
Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Aniline and Ethylamine
(b) Ethylamine and Dimethylamine (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Ethylamine and aniline :
By Azo dye test: It involves the reaction of any aromatic primary amine with HNO2(NaNO2 + dil. HCl) at 273-278 K followed by treatment with an alkaline solution of 2-naphthol when a brilliant yellow, orange or red coloured dye is obtained.

(b) Ethylamine and dimethylamine can be distinguished by the carbylamine test.
Carbylamine test: Aliphatic and aromatic amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide form foul smelling isocyanides or carbylamines. Ethylamine (being an aliphatic primary amine) gives a positive carbylamine test, but dimethylamine does not.

Question 36.
Explain the following reactions :
(a) Gabriel Phthalimide reaction
(b) Coupling reaction (Comptt. Delhi, Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis : It is used to prepare 1° amine (Primary amine). The starting compound is a phthalimide. But aromatic primary amines cannot be prepared by this method because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
Example :

(b) Coupling reaction : Arene diazonium salts react with highly reactive aromatic compounds such as phenols and amines to form brightly coloured azo compounds.
Ar – N = N – Ar. This reaction is known as coupling reaction.

Question 37.
Give reasons :
(a) Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexyl amine.
(b) It is difficult to prepare pure amines by ammonolysis of alkyl halides. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) In aniline, the lone pair of electrons on the N-atom is delocalised over the benzene ring. As a result, the
electron density on the nitrogen decreases.
But in cyclohexylamine, the lone pair of electrons on N-atom is readily available due to absence of π-electrons. Hence aniline is weaker base than cyclohexylamine.
(b) Because the primary amine formed by ammonolysis itself acts as a nucleophile and produces further 2° and 3° alkyl amine.
Question 38.
Give reasons :
(i) Electrophilic substitution in aromatic amines takes place more readily than benzene.
(ii) CH3CONH2 is weaker base than CH3CH2NH2. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(i) Due to the strong activating effect of the NH2 group, aromatic amines undergo electrophilic substitution reactions readily than benzene.
(ii) In case of acetamide due to resonance, the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is delocalized over keto group which decreases electron density hence less basic while in ethylamine due to +1 effect of ethyl group electron density increases on N-atom and hence basic character increases.
Question 39.
(i) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C2H5)2NH and CH3NH2
(ii) Arrange the following compounds in a decreasing order of pKb values :
C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2NH and C6H5NH (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Increasing order of basic strength
![]()
(ii) Decreasing order of pKb values
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH
Question 40.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between each of the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethylamine and Aniline
(ii) Aniline and Benzylamine (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) Ethylamine and aniline :
By Azo dye test: It involves the reaction of any aromatic primary amine with HNO2(NaNO2 + dil. HCl) at 273-278 K followed by treatment with an alkaline solution of 2-naphthol when a brilliant yellow, orange or red coloured dye is obtained.

(ii) Distinction between Aniline and Benzylamine :
By Nitrous acid test : Benzylamine reacts with HNO2 to form a diazonium salt which being unstable even at low temperature, decomposes with evolution of N2 gas

Question 41.
Write the chemical equations involved in the following reactions: (All India 2016)
(i) Hoffmann-bromamide degradation reaction
(ii) Carbylamine reaction
Answer:
(i) Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction : In this reaction, migration of an alkyl or aryl group takes place from carbonyl carbon of the amide to the nitrogen atom. Therefore the amine so formed has one carbon atom less than that of amide.

(ii) Carbylamine reaction. This reaction is used to distinguish primary amines from 2° and 3° amines as it is only given by 1° amines with the production of a very bad smelling organic compound.
For example :

Amines: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -II [SA – II]
Question 42.
Giving an example for each describe the following reactions :
(i) Hofmann’s bromamide reaction
(ii) Gatterman reaction
(iii) A coupling reaction (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
(i) Hofmann’s bromamide reaction : When amide is treated with bromide in alkaline solution, an amide yields an amine containing one carbon less than the starting amide.

(ii) Gatterman reaction: When benzene or its derivative is treated with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride or cuprous chloride, it gives benzaldehyde or substituted benzaldehyde.

Gattermann Koch reaction : Diazonium salt reacts with hydrogen halide in presence of copper powder giving haloarene.

(iii) A coupling reaction : Arene diazonium salts react with highly reactive aromatic compounds such as phenols and amines to form brightly coloured azo compounds.
Ar – N = N – Ar. This reaction is known as coupling reaction.

Question 43.
Complete the following reaction equations: (All India 2009)

Answer:
Reduction reaction

Question 44.
Complete the following reaction equations :
(i) C6H5Cl + CH3COCl →
(ii) C2H5NH2 + C6H5SO2Cl →
(iii) C2H5NH2 + HNO2 →
Answer:

Question 45.
In the following cases rearrange the compounds as directed : (Delhi 2010)
(i) In an increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5 N(CH3)2, (C2H5)2NH and CH3NH2
(ii) In a decreasing order of basic strength :
Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine
(iii) In an increasing order of pKb values :
C2H5NH2, C6H5 NHCH3, (C2H5)2NH and C6H5NH2
Answer:
(i) Order of basic strength :

Since a stronger base has a lower pKb value therefore basic strength order.
(C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C6H5NH2
Question 46.
Complete the following chemical equations : (Delhi)

Answer:

Question 47.
(a) Explain why an alkylamine is more basic than ammonia?
(b) How would you convert
(i) Aniline to nitrobenzene (ii) Aniline to iodobenzene (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
(a) Due to electron releasing inductive effect (+1) of alkyl group, the electron density on the nitrogen atom increases and thus, it can donate the lone pair of electrons more easily than ammonia.
(b) (i) Aniline to nitrobenzene

Question 48.
Complete the following chemical equations: (Delhi 2011)

Answer:


Question 49.
State reasons for the following :
(i) pKb value for aniline is more than that for methylamine.
(ii) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not soluble in water.
(iii) Primary amines have higher boiling points than tertiary amines. (All India 2011)
Answer:
(i) Higher the pKb value, lower will be the basicity therefore aniline is less basic than methylamine because the
lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom gets delocalized over the benzene ring are unavailable for protonation due to resonance in aniline which is absent in case of alkylamine.
(ii) Ethylamine is soluble in water due to its capability to form H-bonds with water while aniline is insoluble in water due to larger hydrocarbon part which tends to retard the formation of H-bonds.
(iii) Due to presence of two H-atoms on N-atom of primary amines, they undergo extensive intermolecular H-bonding while tertiary amines due to the absence of a H-atom on the N-atom, do not undergo H- bonding. As a result, primary amines have higher boiling points than 3° amines.
Question 50.
Write chemical equations for the following conversions :
(i) Nitrobenzene to benzoic acid.
(ii) Benzyl chloride to 2-phenylethanamine
(iii) Aniline to benzyl alcohol. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) Nirtobenzene to benzoic acid :

(ii) Benzyl chloride to 2-phenylethanamine

(iii) Aniline to benzyl alcohol

Question 51.
Give the structure of A, B and C in the following reactions: (Delhi 2013)

Answer:


Question 52.
Give the structure of A, B and C in the following reactions : (Delhi 2013)

Answer:

Question 53.
Complete the following reactions : (All India 2013)

Answer:

Question 54.
Write the main products of following reactions: (All India 2013)

Answer:
![]()

Question 55.
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions : (Delhi 2014)

Answer:

Question 56.
How will you convert the following :
(i) Nitrobenzene into aniline
(ii) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
(iii) Aniline into N-phenylethanamide
(Write the chemical equations involved) (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Nitrobenzene into aniline


Question 57.
Account for the following :
(i) Primary amines (R-NH2) have higher boiling point than tertiary amines (R3N).
(ii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel – Crafts reaction.
(iii) (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution. (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) Due to presence of two H-atoms on N-atom of primary amines, they undergo extensive intermolecular H-bonding while tertiary amines due to the absence of a H-atom on the N-atom, do not undergo H- bonding. As a result, primary amines have higher boiling points than 3° amines.
(ii) Aniline being a Lewis base reacts with Lewis acid AlCl3 to form a salt.

As a result, N of aniline acquires positive charge and hence it acts as a strong deactivating group for electrophilic substitution reaction. Consequently, aniline does not undergo Freidel Craft reaction.
(iii) Due to more steric hindrance in (CH3)3N it is less basic than (CH3)2NH.
Question 58.
Account for the following:
(i) Aniline does not give Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(ii) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not.
(iii) pKb of methylamine is less than that of aniline. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Aniline being a Lewis base reacts with Lewis acid AlCl3 to form a salt.

As a result, N of aniline acquires positive charge and hence it acts as a strong deactivating group for electrophilic substitution reaction. Consequently, aniline does not undergo Freidel Craft reaction.
(ii) Ethylamine is soluble in water due to its capability to form Fl-bonds with water while aniline is insoluble in water due to larger hydrocarbon part which tends to retard the formation of H-bonds.
(iii) In aniline due to resonance lone pair of electron of nitrogen atom is delocalised due to which it is weaker base than methyl amine.
Hence Aniline has high pKb molecule i.e., methylamine has less pKb molecule.
Question 59.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C. (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
The data shows that C6H7N may be C6H5NH2 i.e. Aniline. Since it is obtained by heating with Br2 and KOH (Hoffmann bromamide reaction), then the compound ‘B’ is Benzamide C6H5CONH2 which is in turn obtained by reaction with aqueous ammonia then the compound ‘A’ can be Benzoic acid i.e. C6H5COOH

Question 60.
Write the structures A, B and C in the following : (Delhi 2016)

Answer:

Question 61.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Aniline does not undergo Friedal-Crafts reaction.
(ii) (CH3)2 NH is more basic than (CH3)3 N in an aqueous solution.
(iii) Primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines. (All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Aniline being a Lewis base reacts with Lewis acid AlCl3 to form a salt.

As a result, N of aniline acquires positive charge and hence it acts as a strong deactivating group for electrophilic substitution reaction. Consequently, aniline does not undergo Freidel Crafts reaction.
(ii) In (CH3)N there is maximum steric hindrance and least solvation but in (CH3)2NH the solvation is more and the steric hindrance is less than in (CH3)3NH; although + I effect is less, since there are two methyl groups; di-methyl amine is still a stronger base than tri-methyl.
(iii) Due to presence of two H-atoms on N-atom of primary amines, they undergo extensive intermolecular H-bonding while tertiary amines due to the absence of a H-atom on the N-atom, do not undergo H- bonding. As a result, primary amines have higher boiling points than 3° amines.
Question 62.
Write major product(s) in the following reactions : (Comptt. Delhi 2016)

Answer:


Question 63.
Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemical equations of the reaction involved. (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl), which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides and tertiary amine does not react.

It does not react with tertiary amines.
Question 64.
Write the products A and B in the following : (Comptt. All India 2016)

Answer:

Question 65.
Give reasons:
(i) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect,
(ii) CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
(iii) Although —NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect because acetyl group being electron withdrawing group attracts the lone pair of electrons of the N-atom towards carboxyl group and the lone pair of electrons on N is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance.
(ii) CH3NH2 is more basic than aniline due to availability of lone pair of electrons for donation while in aniline lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is delocalised over benzene ring and thus unavailable for donation.
(iii) Because of nitration in an acidic medium, aniline gets protonated to give anilinium ion which is indirecting.
Question 66.
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
(b) CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
(c) Although —NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline. (All India 2017)
Answer:
(i) Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect because acetyl group being electron withdrawing group attracts the lone pair of electrons of the N-atom towards carboxyl group and the lone pair of . electrons on N is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance.
(ii) CH3NH2 is more basic than aniline due to availability of lone pair of electrons for donation while in aniline lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is delocalised over benzene ring and thus unavailable for donation.
(iii) Because of nitration in an acidic medium, aniline gets protonated to give anilinium ion which is indirecting.
Question 67.
Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in each of the following reactions: (All India 2017)

Answer:

Question 68.
Illustrate Sandmeyer’s reaction with the help of a suitable example. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Sandmeyer’s reaction: The substitution of diazo group of benzene diazonium chloride by Chloro, Bromo and Cyano group with the help of solution of CuCl dissolved in HCl, CuBr/HBr and CuCN/KCN respectively is known as Sandmeyer’s reaction.

Question 69.
Identify A, B and C in the following reactions : (Comptt. Delhi 2017)

Answer:

Question 70.
Identify A, B and C in the following reactions : (Comptt. All India 2017)

Answer:

Amines: Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Class 12 Important Questions Long Answer Type [LA]
Question 71.
An aromatic compound JA’ of molecular formula C7H27ON undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions : (Delhi 2015)

Answer:

Question 72.
(a) Write the structures of main products when aniline reacts with the following reagents :
(i) Br2 water (ii) HCI (iii) (CH3CO)2O/pyridine
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point :
C2H5NH2, C2H5OH, (CH3)3N
(c) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds : (CH3)2NH and (CH3)3N (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(a) (i) Br2 water

(b) Increasing order of boiling point :
(CH3)3 < C2H5NH2 < C2H2OH
(c) By Hinsberg test, secondary amines or (CH3)3NH shows precipitate formation which is insoluble in KOH. Tertiary amines or (CH3)3N do not react with Hinsberg’s reagent (benzene sulphonyl chloride).
Question 73.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ of molecular formula C7H6O3 undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions : (All India 2015)

Answer:

Question 74.
(a) Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride reacts with the following reagents :
(i) H3PO2 + H2O (ii) CuCN/KCN (iii) H2O
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their basic character in an aqueous solution :
C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C3H5)3N
(c) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds :
C6H5—NH2 and C6H5—NH—CH3 (All India 2015)
Answer:
(a) The structure of main products when aniline (benzene diazonium chloride) reacts with the following reagents :

(b) C2H5NH2 < (C3H5)3N < (C2H5)2NH
(c) Aniline and Benzylamine can be distinguished by the Nitrous acid test. Benzylamine reacts with HNO2 to form a diazonium salt which being unstable even at low temperature, decomposes with evolution of N2 gas.
