Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Important Questions
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
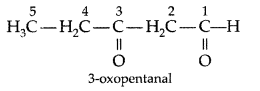
Question 1.
Write the structure of 3-oxopentanal. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Question 2.
Write the structural formula of 1-phenylpentan- 1-one. (All India 2009)
Answer:
1-Phenylpentan-1-one

Question 3.
Draw the structural formula of 1-phenyl propan- 1-one molecule. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
1-phenyl propan-1-one

Question 4.
What is Tollen’s reagent? Write one usefulness of this reagent. (All India 2010)
Answer:
Ammonical silver nitrate solution is called Tollen’s reagent.
Uses: It is used to test aldehydes. Both aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes reduce Tollen’s reagent to shining silver mirror. It is also used to distinguish aldehydes from ketones.

Question 5.
Draw the structure of 3-methylbutanal. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:

Question 6.
Draw the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one. (All India 2011)
Answer:

Question 7.
Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions : ethanal, propanal, propanone, butanone. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal
Question 8.
Write the IUPAC name of the following : (All India 2012)

Answer:
IUPAC name : Pent-2-enal
Question 9.
Write the IUPAC name of Ph – CH = CH – CHO. (All India 2012)
Answer:
IUPAC name : 3-phenylprop-2-enal
Question 10.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between Benzoic acid and Phenol. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Benzoic acid forms a brisk effervescence with NaHCO3 solution but phenol does not respond to this test.
Question 11.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between Ethanal and Propanal. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Ethanal on heating with I2 in NaOH gives a yellow ppt of iodoform but propanal does not respond to this test.
Question 12.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between Propanal and Propanone. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Propanone on reacting with I2 and NaOH gives a yellow ppt of iodoform but propanal does not respond to this test.
Question 13.
Formaldehyde does not take part in Aldol condensation. Why ? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Formaldehyde does not contain a-hydrogen atom. Therefore it does not take part in aldol condensation.
Question 14.
Write the IUPAC name of the following : (Comptt. All India 2012)

Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-methylcyclohexanone
Question 15.
Aldehydes and Ketones have lower boiling points than corresponding alcohols. Why ? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
It is due to weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of the dipole- dipole interactions.
Question 16.
Give the structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when propanone is reacted with methylmagnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:

IUPAC name : 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Question 17.
Write the structure of the product formed in the following reaction : (Comptt. All India 2012)

Answer:

Question 18.
Write the structure of 3-methyl butanal. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:

Question 19.
Write the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:

Question 20.
Write the structure of p-Methylbenzaldehyde molecule. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:

Question 21.
Rearrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points: (All India 2013)
CH3 — CHO, CH3 — CH2 — OH, CH3 — CH2— CH3
Answer:
CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH
Question 22.
Ethanal is soluble in water. Why? (All India 2013)
Answer:
Ethanal is soluble in water due to H-bonding between the polar carbonyl group and water molecules.
Question 23.
Draw the structure of the compound named 4-methylpent-3-en-2-one. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:

Question 24.
Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group. Explain why? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
The carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.

Question 25.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between benzoic acid and phenol. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbon dioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2

Question 26.
Write IUPAC name of the following : (Comptt. All India 2013)

Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-Ethyl cyclohexanone.
Question 27.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
IUPAC name : 3-Hydroxybutanoic acid
Question 28.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
IUPAC name : 3-Aminobutanal
Question 29.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
IUPAC name : 4-Hydroxypentan-2-one
Question 30.
Write the structure of p-methylbenzaldehyde. (All India 2014)
Answer:
p-methylbenzaldehyde

Question 31.
Write the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one. (All India 2014)
Answer:

Question 32.
Write the structure of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid. (All India 2014)
Answer:

Question 33.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: (Comptt. Delhi 2014)

Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-methypropanal
Question 34.
Give a test to distinguish between propan-2-one and pentan-3-one. (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
Propan-2-one and pentan-3-one can be distinguished by Iodoform test.

Question 35.
Draw the structure of 3-methylpentanal. (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:

Question 36.
Write the IUPAC name of the following: (Comptt. All India 2015)
CH3— CH2 — CHO
Answer:
IUPAC name : Propan-1-al
Question 37.
Draw the structure of 2-methylbutanaI. (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:

Question 38.
What type of aldehydes undergo Cannizaro reaction? (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Aldehydes which do not contain α-hydrogen atom undergo Cannizzaro reaction e.g. Formaldehyde (HCHO) and Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO).
Question 39.
What type of aldehydes undergo Aldol condensation? (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Aldehydes with a hydrogen atom undergo Aldol condensation.
Question 40.
Arrange the following compound groups in the increasing order of their property indicated: Propanol, Propane, Propanal (boiling point) (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Propanol > Propanal > Propane (Boiling point)
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -I [SA – I]
Question 41.
Name the reagents used in the following reactions : (Delhi 2015)

Answer:
(i) LiAlH4 (Lithium Aluminium Hydride)
(ii) KMnO4 (Alkaline Potassium Permanganate)
Question 42.
Write the reagents required in the following reactions : (All India 2015)

Answer:

Question 43.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated :
(i) CH3COCH3, C6H5COCH3, CH3CHO
(reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction)
(ii) Cl—CH2—COOH, F—CH2—COOH, CH3—COOH (acidic character) (All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(Reactivity towards nucleophilic addition)

Question 44.
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Wolff-Kishner reduction
(ii) Etard reaction (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Wolff-Kishner reduction

(ii) Etard reaction

Question 45.
Write the reactions involved in the following:
(i) Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction
(ii) Decarboxylation reaction (Delhi 2017)
Answer:

Question 46.
Write the reactions involved in the following reactions: (Delhi 2017)
(i) Clemmensen reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
Answer:
(i) Clemmensen reduction. The carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.

(ii) Cannizzaro reaction. Aldehydes, which do not have an a-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -II [SA – II]
Question 47.
Predict the products of the following reactions : (Delhi 2015)

Answer:

Question 48.
Predict the products of the following reactions : (All India 2015)

Answer:

Question 49.
Write structures of compounds A, B and C in each of the following reactions: (Delhi 2017)
![]()
Answer:

A = Ethanal
B = 3-Hydroxybutanal (Aldol)
C = But-2-enal
Question 50.
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps:
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Ethyl benzene to Benzoic acid
(iii) Propanone to Propene
Answer:

Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Important Questions long Answer Type [LA]
Question 51.
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions by giving example :
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(ii) Clemmensen reduction
(b) An organic compound A contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acids. Derive the possible structure of compound A. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
(a) (i) Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes, which do not have an oc-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(ii) Clemmensen reduction: The carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketones is reduced to CH, group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.

Question 52.
(a) How are the following obtained?
(i) Benzoic acid from ethyl benzene, (ii) Benzaldehyde from toluene.
(b) Complete each synthesis by giving the missing material, reagent or products : (Delhi 2009)

Answer:


Question 53.
(a) Write chemical equations to illustrate the following name bearing reactions :
(i) Cannizzaro’s reaction (ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Propanal and Propanone (ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid (All India 2009)
Answer:
(a) (i) Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes, which do not have an oc-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction : Carboxylic acid reacts with chlorine or bromine in presence of small quantities of red phosphorous to give exclusively α-chloro or α-bromo acids.
Example :

(b) (i) Propanal and propanone: Propanal gives a positive test with the Fehling solution in which a red ppt. of cuprous oxide is obtained while propanone does not respond to test
![]()
(ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone: They can be distinguished by iodoform test which is given by only acetophenone with the formation of yellow ppt. while benzophenone does not respond to iodoform test

(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid: On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbon dioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2

Question 54.
(a) How will you bring about the following conversions :
(i) Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal (ii) Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone
(b) An organic compound A has the molecular formula C8H16O2. It gets hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid and gives a carboxylic acid B and an alcohol C. Oxidation of C with chromic acid also produced B. C on dehydration reaction gives but-l-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved. (All India 2009)
Answer:
(a) (i) Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal :


Question 55.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between compounds in the following pairs of substances :
(i) Ethanol and Propanal (ii) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
(b) An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acids. Derive the structure of the compound. (All India 2009)
Answer:
(a) (i) Ethanol and Propanal :
Ethanol: Ethanol does not form silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent.
Propanal: Propanal being an aldehyde forms silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent (Silver Mirror Test).
(ii) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate :
By Iodoform test: Ethyl benzoate on boiling with excess of NaOH solution gives ethyl alcohol which on heating with iodine gives yellow ppt. of iodoform.

Benzoic acid does not show this test.

Question 56.
(a) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their indicated property :
(i) Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
(ii) CH3CH2CH (Br) COOH, CH3CH (Br) CH2COOH,
(CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength)
(b) How would you bring about the following conversions :
(i) Propanone to Propene (ii) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
(iii) Bromobenzene to 1-phenylethanol (All India 2009)
Answer:
(a) (i) 4-Methoxy benzoic acid < Benzoic acid < 4-Nitrobenzoic acid < 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid.
The order is due to increasing -I effect.


Question 57.
(a) Explain the mechanism of a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or a ketone.
(b) An organic compound (A) (molecular formula CgH16Q2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid also produced (B). On dehydration (C) gives but-1-ene. Write the equations for the reactions involved. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
(a) Mechanism of a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group
![]() is a polar group in which carbon acquires positive charge and O acquires negative charge due to more electronegativity of oxygen. The Nu~ attacks on carbon and forms a tetrahedral intermediate and then electrophile attacks on oxygen and forms a compound.
is a polar group in which carbon acquires positive charge and O acquires negative charge due to more electronegativity of oxygen. The Nu~ attacks on carbon and forms a tetrahedral intermediate and then electrophile attacks on oxygen and forms a compound.

(b) Since the organic compound (A) with molecular formula (M.F.) C8H1602 upon hydrolysis with dil. H2S04 gives carboxylic acid (B) and the alcohol (C) therefore it must be an ester. Further since oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produces the acid (B), therefore both the carboxylic acid (B) and the alcohol (C) must ’.contain the same number of carbon atoms

Question 58.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethanal and Propanal (ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(b) How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde (ii) Ethanal to but-2-enal (iii) Propanone to propene
Give complete reaction in each case. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
(a) (i) Ethanal and Propanal : Ethanal and propanal can be distinguished by iodoform test. Warm each compound with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution in water. Ethanal gives yellow crystal of iodoform while propanal does not respond to iodoform test.

(ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid: On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbondioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2.


Question 59.
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions giving a chemical equation in each case :
(i) Clemmensen reaction (ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(b) Describe how the following conversions can be brought about :
(i) Cyclohexanol to cyclohexan-1-one (ii) Ethylbenzene to benzoic acid
(iii) Bromobenzene to benzoic acid (All India 2010)
Answer:
(a)
(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes, which do not have an oc-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(b) (i) Cyclohexanol to cyclohexan-1-one

Question 60.
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions :
(i) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction (ii) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction
(b) How are the following conversions carried out:
(i) Ethylcyanide to ethanoic acid (ii) Butan-l-ol to butanoic acid
(iii) Methylbenzene to benzoic acid
Write chemical equations for the involved reactions. (All India 2010)
Answer:
(a) (i) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction : Carboxylic acid reacts with chlorine or bromine in presence of small quantities of red phosphorous to give exclusively α-chloro or α-bromo acids.
Example :

(ii) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction : The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding hydrocarbons by heating them with hydrazine and KOH or potassium tert-butoxide in a high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol is called Wolff-Kishner reduction.


Question 61.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Propanal and Propanone, (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.
(b) How would you obtain
(i) But-2-enal from Ethanal, (ii) Butanoic acid from Butanol,
(iii) Benzoic acid from Ethylbenzene? (Delhi, All India 2011)
Answer:
(a) (i) Propanal and propanone: Propanal gives a positive test with the Fehling solution in which a red ppt. of cuprous oxide is obtained while propanone does not respond to test
![]()
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone :
By Iodoform test : Acetophenone being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH (NaOI) undergoes iodoform test to give yellow ppt. of iodoform but benzaldehyde does not.

(b) (i)

(ii)

(iii)

Question 62.
(a) Describe the following giving linked chemical equations :
(i) Cannizzaro reaction (ii) Decarboxylation
(b) Complete the following chemical equations (Delhi 2011)

![]()
Answer:
(a) (i) Cannizzaro reaction. Aldehydes, which do not have an a-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(ii) Decarboxylation using soda lime

Question 63.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following :
(i) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate (ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Complete each synthesis by giving missing reagents or products in the following : (All India 2011)

Answer:
(a) (i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate :
By Iodoform test: Ethyl benzoate on boiling with excess of NaOH solution gives ethyl alcohol which on heating with iodine gives yellow ppt. of iodoform.

(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone :
By Iodoform test : Acetophenone being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH (NaOI) undergoes iodoform test to give yellow ppt. of iodoform but benzaldehyde does not.

(b) (i)


Question 64.
(a) Illustrate the following name reactions giving suitable example in each case :
(i) Clemmensen reduction (ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(b) How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Ethylcyanide to ethanoic acid (ii) Butan-l-ol to butanoic acid
(iii) Benzoic acid to m-bromobenzoic acid (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) Clemmensen reduction. The carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.

(ii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction : Carboxylic acid reacts with chlorine or bromine in presence of small quantities of red phosphorous to give exclusively a-chloro or a-bromo acids.
Example :

Question 65.
Illustrate the following reactions giving a suitable example for each.
(i) Cross aldol condensation (ii) Decarboxylation
(b) Give simple tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) (i) Cross aldol condensation : When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and/or ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation

(ii) Decarboxylation : Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with soda lime. The reaction is known as decarboxylation.
![]()
(b) (i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
By Iodoform test:

Add I2 and NaOH in both the solutions. Pentan-2-one gives yellow coloured precipitate, but pentan- 3-one does not.
(ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Iodoform test: Warm each organic compound with I2 and NaOH solution.
Acetophenone-yellow precipitates of iodoform are formed.
Benzaldehyde does not respond to this test.
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid: On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbondioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2.

Question 66.
(a) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following :
(i) There are two – NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one such group is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(ii) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2, 4, 6-trimethylcyclohexanone does not.
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4, – DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’ reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation it gives 1, 2-benzene-di- carboxylic acid. Identify the compound. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) (i) Because one of the – NH2 in semicarbazide is involved in the resonance with -CO-group.

(b) Compound C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, so it contains a carbonyl group. Also it reduces Tollens’ reagent therefore carbonyl group is an aldehyde group. Since it undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction, aldehyde has no a hydrogen atom, so compound is C8H9-CHO. On vigorous oxidation, compound gives l, 2-benzene di-carboxylic acid hence the compound is

Question 67.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Phenol and Benzoic acid (ii) Benzophenone and Acetophenone
(b) Write the structures of the main products of following reactions : (Delhi 2012)

(a) (i)Phenol and Benzoic acid: On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbon dioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2

(ii) Benzophenone and Acetophenone :
Iodoform test. Warm each organic compound with I2 and NaOH solution.
Acetophenone-yellow precipitate of iodoform is formed. Benzophenone does not respond to this test.

Question 68.
(a) Write a suitable chemical equation to complete each of the following transformations :
(i) Butan-l-ol to butanoic acid
(it) 4-Methylacetophenone to benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s
reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound. (All India 2012)
Answer:

(b) Compound C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, so it contains a carbonyl group. Also it reduces Tollens’ reagent therefore carbonyl group is an aldehyde group. Since it undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction, aldehyde has no a hydrogen atom, so compound is C8H9-CHO. On vigorous oxidation, compound gives l, 2-benzene di-carboxylic acid hence the compound is

Question 69.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between :
(i) Propanol and propanone (ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their property as indicated :
(i) Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(ii) Benzoic acid, 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
(iii) CH3CH2CH (Br) COOH, CH3CH (Br) CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH (acid strength) (All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) (i) Propanone and Propanol :
It can be done by iodoform test where propanone gives yellow ppt. of iodoform while propanol does not respond to test.

(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone :
By Iodoform test : Acetophenone being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH (NaOI) undergoes iodoform test to give yellow ppt. of iodoform but benzaldehyde does not.

(b) (i) Methyl tert-butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde
(ii) 4-Methoxybenzoic acid < Benzoic acid < 3, 4-Dinitro benzoic acid

Question 70.
(a) An organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C8H8O forms an orange red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with I2 and NaOH. It neither reduces Tollen’s reagent nor Fehling’s reagent nor does it decolourize bromine water or Baeyer’s reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid ‘W having molecular formula C7H6O2. Identify the compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ and explain the reactions involved.
(b) Write the mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) (i) Molecular formula : C8H8O
(ii) Since it gives orange red ppt with 2, 4-DNP reagent Therefore it must be either aldehyde or a ketone.
(iii) Since, it does not reduce Tollen’s reagent nor Fehling’s reagent, solution ‘A’ must be a ketone,
(iv) ‘A’ on treatment with I2/NaOH gives yellow ppt

(v) It does not decolorise Br2 water or Baeyer’s reagent so the unsaturation of ‘A’ is due to benzene ring.

(b) Mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids :

Question 71.
(a) An organic compound ‘A’ which has characteristic odour, on treatment with NaOH forms two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ has the molecular formula C7H8O which on oxidation with CrO3 gives back compound ‘A’. Compound ‘C’ is the sodium salt of the acid. ‘C’ when heated with soda lime yields an aromatic hydrocarbon ‘D’. Deduce the structures of ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ and ‘D’.
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Electrophilic substitution in Benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(a) (A) gives characteristic odour which on treatment with NaOH and forms two compounds B and C.


(b) (i) The benzene ring of benzoic acid undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction such as nitration, sulphonation etc. Since the — COOH group in benzene is an electron withdrawing group, therefore it is meta directing group.
(ii) The carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.

Question 72.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Benzene amide and 4-aminobenzoic acid (ii) Methyl acetate and Ethyl acetate
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative and reduces
Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1,2- benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound and write chemical equations for the reactions. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) (i) NaHCO3 test : p-Aminobenzoic acid is an acid which decomposes NaHCO3 solution to produce effervescence due to evolution of CO2 gas while benzene amide does not give this test.
(ii) Ethyl acetate when boiled with excess of NaOH gives ethyl alcohol and if it is heated with I2 and NaOH solution, it gives yellow precipitate of iodoform.
Methyl acetate on hydrolysis with NaOH gives methyl alcohol which does not respond to iodoform test.
(b) (i) Molecular formula of compound : C9H10O
(ii) It forms a 2, 4-DNP derivative and reduces Tollen’s reagent. It must be an aldehyde.
(iii) Since it undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction, therefore CHO group is directly attached to the benzene ring.
(iv) On oxidation it gives 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, therefore it must be an ortho-substituted benzaldehyde, so the structure should be


Question 73.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C5H10O does not reduce Tollen’s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite and gives a positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation, it gives ethanoic acid and propanoic acid. Identify the compound and write all chemical equations for the reactions. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) (i) Benzoic acid is an acid which decomposes NaHCO3 solution to give effervescence of CO2 whereas phenol does not respond to this test.
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone :
By Iodoform test : Acetophenone being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2/NaOH (NaOI) undergoes iodoform test to give yellow ppt. of iodoform but benzaldehyde does not.

(b) (i) Molecular formula of compound : C5H10O.
(ii) It gives an addition product with NaHS03 so it must be either an aldehyde or methyl ketone.
(iii) It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent so it is not an aldehyde.
(iv) It gives +ve iodoform test, therefore it is methyl ketone.
(v) On oxidation it gives a mixture of ethanoic acid and propanoic acid
Therefore, possible structure is pentan-2-one.
Reactions :

Question 74.
(a) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
(b) How will you bring about the following converstions?
(i) Propanone to propane (ii) Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde
(iii) Ethanal to but-2-enal (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol because:
(i) In the resonating structure of phenol and carboxylic acid, the negative charge on the carboxylate ion is delocalised over two oxygen atoms while they are localized on oxygen atom.

(ii) The release of a proton from carboxylic acids is much easier than from phenols,
(b) (i) Propanone to Propane

(iii)

Question 75.
(a) Complete the following reactions:

(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Ethanal and Propanal (ii) Benzoic acid and Phenol (Delhi 2013)
Answer:

(b) (i) Ethanal and Propanal : Ethanal and propanal can be distinguished by iodoform test. Warm each compound with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution in water. Ethanal gives yellow crystal of iodoform while propanal does not respond to iodoform test.

(ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid: On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbon dioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2

Question 76.
(a) How will you convert the following :
(i) Propanone to Propan-2-ol (ii) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy propanoic acid
(iii) Toluene to benzoic acid
(b) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between :
(i) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one (ii) Ethanal and Propanal (All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) (i) Propanone to Propan-2-ol


Add I2 and NaOH in both the solutions. Pentan-2-one gives yellow coloured precipitate, but pentan- 3-one does not.
(ii) Ethanal and Propanal : Add I2 and NaOH in both the solutios. Ethanal gives yellow coloured precipitate but propanal does not.
Question 77.
(a) Write the products of the following reactions :

(b) Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger? (All India 2013)

Answer:


(b) (i) Due to much stronger I-effect of F over Cl, the FCH2COO– ion is much more stable than ClCH2COO– ion and hence FCH2COOH is a stronger acid than ClCH2COOH.
(ii) Ethanoic acid is more stronger acid than phenol due to less pKa than that of phenol and the carboxylate ion is much more resonance stabilized than phenoxide ion.
Question 78.
Two moles of organic compound ‘A’ on treatment with a strong base gives two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ on dehydrogenation with Cu gives ‘A’ while acidification of ‘C’ yields carboxylic acid ‘D’ with molecular formula of CH2O2. Identify the compounds A, B, C and D and write all chemical reactions involved. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:

∴ A = Formaldehyde, B = Methyl alcohol, C = Sodium formate, D = Formic acid
Question 79.
(a) How will you carry out the following conversions?
(i) Acetylene to Acetic acid (ii) Toluene to m-nitrobenzoic acid
(iii) Ethanol to Acetone
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
(ii) pH of reaction should be carefully controlled while preparing ammonia derivatives of carbonyl compounds. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) Acetylene to Acetic acid


(b) (i) Because – I effect of Cl decreases the electron density in the O-H bond thereby making the release
of a proton easier.

(ii) In strongly acidic medium ammonia derivatives being basic will react with acids and will not react with carbonyl compound. In basic medium OH- will attack carbonyl group.
Question 80.
(a) How will you obtain the following :
(i) Benzaldehyde from Phenol (ii) Benzoic acid from Aniline
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic reagents.
(ii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids do not give the characteristic reactions of carbonyl group. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) (i) Benzaldehyde from Phenol


(b) (i) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones due to the following two reasons :
- Due to smaller +1 effect of one alkyl group in aldehydes as compared to larger +1 effect of two alkyl groups, the magnitude of positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is more in aldehydes than in ketones. As a result nucleophilic addition reactions occur more readily in aldehydes than in ketones.
- Due to presence of a H-atom on the carbonyl group, aldehydes can be more easily oxidised than ketones.
(ii) The benzene ring of benzoic acid undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction such as nitration, sulphonation etc. Since the — COOH group in benzene is an electron withdrawing group, therefore it is meta directing group.
(iii) The carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.

Question 81.
(a) State and illustrate the following :
(i) Wolff-Kishner reduction (ii) Aldol condensation
(b) An organic compound (A) which has characteristic odour, on treatment with NaOH forms two compounds (B) and (C). Compound (B) has the molecular formula C7H8O which on oxidation with CrO3 gives back compound (A). Compound (C) is the sodium salt of the acid. Compound (C) when heated with soda lime yields an aromatic hydrocarbon (D). Deduce the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write chemical equations for all reactions taking place. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) (i) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction : The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding hydrocarbons by heating them with hydrazine and KOH or potassium tert-butoxide in a high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol is called Wolff-Kishner reduction.

(ii) Aldol condensation: In this two molecules of aldehydes or ketones containing a-hydrogen atoms on treatment with dil. NaOH undergoes condensation to form β-hydroxyaldehydes or β-hydroxy ketones.

Question 82.
(a) Write the products of the following reactions :

(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid (ii) Propanal and Propanone (Delhi 2014)
Answer:


(ii) Propanal and Propanone : Propanal gives positive test with Fehling solution in which a red ppt. of cuprous oxide is obtained while propanone does not respond to test.
![]()
Question 83.
(a) Account for the following :
(i) CH3CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards reaction with HCN.
(ii) Carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions :
(i) Wolff-Kishner reduction (ii) Aldol condensation (iii) Cannizzaro reaction (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones due to the following two reasons :
- Due to smaller +1 effect of one alkyl group in aldehydes as compared to larger +1 effect of two alkyl groups, the magnitude of positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is more in aldehydes than in ketones. As a result, nucleophilic addition reactions occur more readily in aldehydes than in ketones.
- Due to presence of a H-atom on the carbonyl group, aldehydes can be more easily oxidised than ketones.
(ii) The release of a proton from carboxylic acid is much easier than phenols because carboxylate ion is much more resonance stabilized than phenoxide ion.
(b) (i) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction : The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding hydrocarbons by heating them with hydrazine and KOH or potassium tert-butoxide in a high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol is called Wolff-Kishner reduction.

(ii) Aldol condensation: In this two molecules of aldehydes or ketones containing a-hydrogen atoms on treatment with dil. NaOH undergoes condensation to form β-hydroxyaldehydes or β-hydroxy ketones.

(iii) Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes, which do not have an oc-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

Question 84.
(a) Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents :
(i) HCN (ii) H2N – OH (iii) CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Benzoic acid and Phenol (ii) Propanal and Propanone. (All India 2014)
Answer:

(b) (i) Benzoic acid and Phenol : On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbondioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2.

(ii) Propanal and Propanone : Propanal gives positive test with Fehling solution in which a red ppt. of cuprous oxide is obtained while propanone does not respond to test.
![]()
Question 85.
(a) Account for the following :
(i) Cl – CH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give reactions of carbonyl group.
(b) Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions :
(i) Rosenmund reduction (ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(c) Out of CH3CH2 – CO – CH2 – CH3 and CH3CH2 – CH2 – CO – CH3, which gives iodoform test? (All India 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) Because – I effect of Cl decreases the electron density in the O-H bond thereby making the release of a proton easier.

(ii) Carboxylic acids do not give the reactions of carbonyl group as there is no carbonyl group present due to resonance.
(b) (i) Rosenmund reduction

(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction : Aldehydes, which do not have an oe-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with conc. alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(c) CH3CH2 – CH2 – CO – CH3 gives Iodoform test.
Question 86.
(a) Describe :
(i) Aldol condensation (ii) Cannizzaro reaction
(b) Describe a chemical test to distinguish between
(i) Ethanal and Propanal (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(iii) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) Aldol condensation : Two molecules of aldehydes or ketones condense in presence of a dil.alkali to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or β-hydroxyketone respectively.

(ii) Cannizzaro’s reaction : Aldehydes, which do not have an oe-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with conc. alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(b) (i) Ethanal and Propanal : Ethanal and propanal can be distinguished by iodoform test. Warm each compound with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution in water. Ethanal gives yellow crystal of iodoform while propanal does not respond to iodoform test.

(ii) Tollen’s Test: Benzaldehyde and acetophenone can be distinguished by the Tollen’s test. Aldehydes respond to Tollen’s Test. Benzaldehyde reduces Tollen’s reagent to give a red-brown precipitate of Cu20, but aceptophenone being a ketone does not.
![]()
(iii)

Add I2 and NaOH in both the solutions. Pentan-2-one gives yellow coloured precipitate, but pentan- 3-one does not.
Question 87.
(a) Draw the structures of the following compounds:
(i) 4-chloropentan-2-one (it) But-2-en-l-al
(b) Write the product(s) in the following: (Comptt. Delhi 2014)

Answer:

Question 88.
(a) Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
(i) CH3CO(CH2)4CH3 (ii) Ph — CH = CH — CHO
(b) Describe the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(i) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal (ii) Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzyl alcohol
(iii) Propanone to Propene (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) CH3CO(CH2)4CH3 :
IUPAC name : Heptan-2-one
(ii) Ph — CH = CH — CHO :
IUPAC name : 3-phenylprop-2-en-l-al
(b) (i) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal

(ii) Benzoic acid to m-nitrobenzyl alcohol :

(iii)

Question 89.
(a) Draw the structures of the following compounds :
(i) 4-Chloropentan-2-one (ii) p-Nitropropiophenone
(b) Give tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethanal and Propanal (ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(iii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:

(b) (i) Ethanal and Propanal : Ethanal and propanal can be distinguished by iodoform test. Warm each compound with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution in water. Ethanal gives yellow crystal of iodoform while propanal does not respond to iodoform test.

(ii) Phenol and Benzoic acid: On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbon dioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2

(iii) Tollen’s Test: Benzaldehyde and acetophenone can be distinguished by the Tollen’s test. Aldehydes respond to Tollen’s Test. Benzaldehyde reduces Tollen’s reagent to give a red-brown precipitate of Cu20, but aceptophenone being a ketone does not.
![]()
Question 90.
(a) Describe the following giving chemical equations :
(i) De-carboxylation reaction (ii) Friedel-Crafts reaction
(b) How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde (ii) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone (iii) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) De-carboxylation reaction: When sodium salt of carboxylic acid is heated with soda lime (NaOH + CaO), then corresponding alkane and CO2 will be evolved
![]()
(ii) Friedel-Crafts reaction: The introduction of alkyl or acetyl group in the presence of anhydrous almuninium chloride (AlCl3) as catalyst to ortho and para positions of an aromatic compound is called Friedel-Crafts reaction,


Question 91.
(a) Describe the following actions
(i) Acetylation (ii) Aldol condensation
(b) Write the main product in the following equations : (Comptt. Delhi 2015)

Answer:
(a) (i) Acetylation: The addition of acyl (-COCH3) group on the ortho and para positions of acyl halide in the presence of a Lewis acid i.e. anhydrous aluminium chloride (AlCl3) which acts as a catalyst.

(ii) Aldol condensation: Those aldehydes and ketones with atleast one a-hydrogen atom condense together in presence of dil. alkali e.g. NaOH etc. to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or β-hydroxy ketone respectively which gets dehydrated in the presence of acid upon heating to form α, β -unsaturated compound.

Question 92.
(a) Draw the structure of the following :
(i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde (ii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
(b) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate, (ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone.
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid. (Comptt. All India 2015)
Answer:
(a) (i) p-Methylbenzaldehyde :


(b) (i) Distinction between Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate :
By Sodium bicarbonate test: Acids react with NaHCO3 to produce brisk effervescence due to the evolution of CO2 gas. Benzoic acid being an acid responds to this test, but ethyl benzoate does not.

(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone :
By Iodoform test: Acetophenone being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2 and NaOH (NaOI) undergoes iodoform test to give yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating whereas benzaldehyde does not.

(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid : On addition of NaHCO3 to both solutions carbon dioxide gas is evolved with benzoic acid while phenol does not form CO2.

Question 93.
(a) Draw the structures of the following derivatives :
(i) Propanone oxime (ii) Semicarbazone of CH3CHO
(b) How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds? Give the chemical equations involved. (Comptt. All India 2015)

Answer:

Question 94.
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions : (Delhi 2016)

Answer:

Question 95.
(a) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in Cannizzaro reaction.
(b) Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(c) Why pKa of F—CH2—COOH is lower than that of Cl—CH2—COOH?
(d) Write the product in the following reaction:
![]()
(e) How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes, which do not have an a-hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction on treatment with cone, alkali and produce alcohol and carboxylic acid salt.

(b)

(c) In FCH2—COOH fluorine is more electron withdrawing than chlorine in ClCH2– COOH so FCH2 – COOHis more acidic than ClCH2—COOH, hence its pKa value is lesser than ClCH2COOH.

(e) Propanal and Propanone: Propanal being an aldehyde gives positive test with Fehling solution in which a red brown ppt. of cuprous oxide is obtained while propanone being a ketone does not respond to this test.
![]()
Question 96.
(a) Write the structures of A and B in the following reactions:

(b) Distinguish between:
(i) C6H5— COCH3 and C6H5— CHO
(ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH
(c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO, CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH (All India 2016)
Answer:

(b) (i) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone :
By Iodoform test: Acetophenone being a methyl ketone on treatment with I2 and NaOH (NaOI) undergoes iodoform test to give yellow ppt. of iodoform on heating whereas benzaldehyde does not.

(ii) CH3COOH (Acetic acid) and HCOOH (Formic acid). Formic acid is the only acid which contains aldehydic group and thus shows reactions with Tollen’s reagent (silver nitrate) and Fehling’s solution which Acetic acid does not show.
Tollen’s Test:
Add ammonical solution of silver nitrate to both the compounds, HCOOH gives silver mirror but CH3COOH does not
![]()
(c) CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
Question 97.
(a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff-Kishner reduction.
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
C6H5COCH3, CH3— CHO, CH3COCH3
(c) Why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group?
(d) Write the product in the following reaction
![]()
(e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomer B forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B. (All India 2016)
Answer:
(a) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction : The reduction of aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding hydrocarbons by heating them with hydrazine and KOH or potassium tert-butoxide in a high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol is called Wolff-Kishner reduction.

(b) C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH2CHO
(c) The carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.

(e) The given compound has molecular formula C3H60. One of its functional isomer i.e., B shows iodoform test which can be only shown by compounds having methyl ketone so the compound B will be Acetone or 2-propanone. Its functional isomer A will be propanal.

Question 98.
(a) Write the product(s) in the following :

(b) Give simple tests to distinguish the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethanal and Propanal
(ii) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(iii) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:

(b) (i) On heating with NaOH and I2, ethanal forms yellow ppt of CHI3 whereas propanal can not.
CH3CHO + 3I2 → NaOH -4 CHI3 + 3NaI + HCOONa + 3H2O
(ii) On heating with NaOH and I2, aceptophenone forms yellow ppt of CHI3 whereas benzaldehyde does not.
C6H5COCH3 + 3NaOI → C6H5COONa + CHI34 + 2NaOH
(iii) On adding NaHCO,, benzoic acid produces brisk effervescence of C02 gas whereas ethylbenzoate does not.
![]()
Question 99.
(a) Give reasons :
(i) CH3—CHO is more reactive than CH3COCH3 towards HCN.
(ii) 4-nitrobenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid.
(b) Describe the following :
(i) Acetylation (ii) Cannizzaro reaction (iii) Cross aldol condensation (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) (i) Because carbonyl carbon of CH3—CHO is more electrophilic than CH3COCH3 due to only one electron donating CH3– group.
(ii) Because of electron withdrawing nature of -NO2 group.
(b) (i) Acetylation : Introduction of an acetyl group/CH3CO- by heating an organic compound with acetyl chloride/acetic anhydride.

(ii) Cannizzaro reaction : Aldehydes having no a-hydrogen atom when treated with cone. NaOH, undergoes self-oxidation and self-reduction simultaneously

(iii) Cross Aldol Condensation : When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes or ketones, it is called cross aldol condenstation.

Question 100.
(a) Complete the following equations : (Comptt. All India 2016)

Answer:

(b) (i) On adding NaHCO3, CH3COOH produces brisk effervescence of CO2 gas whereas phenol does not.
(ii) On heating with Tollen’s reagent, CH3CHO forms silver mirror whereas CH3COCH3 does not.
Question 101.
(a) What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
(i) Aldol (ii) Semicarbazone
(b) Complete the following : (Comptt. All India)

Answer:
(a) (i) Two molecules of aldehyde and ketones containing a-hydrogen atom react in the presence of
aqueous alkali giving product known as Aldol.
Example :

Question 102.
Write the product(s) in the following reactions. (Delhi 2017)

Answer:

Question 103.
(a) Write the product(s) in the following reactions:

(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Butanal and Butan-2-one (ii) Benzoic acid and Phenol (All India 2017)
Answer:

(b) (i) Pollen’s reagent test. Add ammoniacal solution of sliver nitrate (Tollen’s Reagent) in both the solutions. Butanal gives silver mirror whereas Butan-2-one does not. Therefore Butanal gives Tollen’s test.
(ii) Ferric chloride test. Add neutral FeCl3 in both the solutions, phenol reacts with neutral FeCl3 to form an iron-phenol complex giving violet colour but benzoic acid does not.
Question 104.
(a) Write the reactions involved in the following:
(i) Etard reaction (ii) Stephen reduction
(b) How will you convert the following in not more than two steps:
(i) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde (ii) Acetophenone to Benzoic acid
(iii) Ethanoic acid to 2-Hydroxyethanoic acid (All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) (i) Etard reaction

(ii) Stephen reduction:

(b) (i) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde

(ii) Acetophenone to Benzoic acid

Question 105.
(a) How will you convert:
(i) Benzene to acetophenone (ii) Propanone to 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(ii) Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
(iii) Propanal is more reactive than propanone in nucleophilic addition reactions. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) Benzene to acetophenone

(b) (i) Because -COOH group is electron withdrawing group and deactivates the benzene ring. As a result of this ortho and para position acquires positive charge but only meta does not, so electrophile can attack on rneta position.
(ii) Because -COOH group of carboxylic acids is capable to do intermolecular hydrogen bonding forming a dimer while alcohols, aldehydes and ketones can not.

(iii) Because of smaller +1 effect of one alkyl group in propanal as compared to larger + I effect ol 2 alkyl groups of propanone, the magnitude of positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is more in propanal than propanone.
Question 106.
(a) Write the products of the following reactions :

(b) Write simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds
(i) Propanal and propanone (ii) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:


(b) (i) Propanal and propanone: Propanal gives a positive test with the Fehling solution in which a red ppt. of cuprous oxide is obtained while propanone does not respond to test
![]()
(ii) Distinction between Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid: Benzaldehyde has no alpha hydrogen atom. Therefore, it undergoes Cannizaro’s reaction as follows :

Question 107.
(a) Account for the following :
(i) Propanal is more reactive than propanone towards nucleophilic reagents.
(ii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta position.
(iii) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group.
(b) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Acetophenone and benzaldehyde
(ii) Benzoic acid and ethylbenzoate. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) (i) Due to steric and + I effect of two methyl groups in propanone.
(ii) The benzene ring of benzoic acid undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction such as nitration, sulphonation etc. Since the — COOH group in benzene is an electron withdrawing group, therefore it is meta directing group.
(iii) The carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.

(b) (i) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Iodoform test: Warm each organic compound with I2 and NaOH solution.
Acetophenone-yellow precipitates of iodoform are formed.
Benzaldehyde does not respond to this test.
(ii) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate :
By Iodoform test: Ethyl benzoate on boiling with excess of NaOH solution gives ethyl alcohol which on heating with iodine gives yellow ppt. of iodoform.

Benzoic acid does not show this test.
Question 108.
(a) Write structures of A, B, C and D in the following reaction sequence :

(b) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points :
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3COOH. (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
