Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-Metals:
Metals are electropositive in nature as they lose electrons and form positive ions.
K → K+ + e–
Ca → Ca2++ 2e–
Non-metals are electronegative in nature as they accept electrons and form negative ions.
Cl + e– → cr
S + 2e– → S2-
Most non-metals produce acidic oxides
Examples: SO2, CO2
Most metals produce basic oxides. Examples: Na2O, CaO
Chemical Properties of Metals:
Reaction with Oxygen:
Metals combine with oxygen to form basic or amphoteric oxides.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide
Examples: 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO (Copper oxide)
4Al3O2 → 2Al2O3
Although metal oxides are basic in nature some metals show both acidic and basic nature.
Amphoteric oxides:
The metal oxides which show both acidic and basic nature are known as amphoteric oxides.
For example, aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric oxides.
The reaction of aluminium oxide with acids and bases is given below:
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Alkalies:
The oxides of most metals are insoluble in water but some of these dissolve in water to form alkalies.
Examples: Sodium oxide and potassium oxide
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq)
K2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq)
The reaction of different metals with oxygen: Different metals show different reactivities towards oxygen.
- The reaction of alkali metals such as potassium and sodium with oxygen is so vigorous that they are kept immersed in kerosene oil to prevent accidental fires in case they are kept open.
- The surfaces of metals such as magnesium, aluminium, zinc, lead, etc., are covered with a thin layer of oxide at ordinary temperature, which prevents the metal from further oxidation and is, therefore, a protective layer.
- Iron does not burn on heating but iron filings burn vigorously when sprinkled in the flame of a burner.
- Copper does not burn, but the hot metal is coated with a black coloured layer of copper (II) oxide.
- Silver and gold do not react with oxygen even at high temperatures.
Anodising:
Anodising is the process of forming a thick oxide layer of aluminium. Aluminium forms a thin oxide layer when exposed to air which makes it resistant to further corrosion. During anodising, a clean aluminium article is made the anode and is electrolysed with dil. H2SO4. The oxygen gas evolved at the anode reacts with aluminium to form a thicker protective oxide layer.
Example 1.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be:
(a) Calcium
(b) Carbon
(c) Silicon
(d) Iron
Answer:
(a) Calcium
Explanation: As the compound has a high melting point, it is an ionic compound. Since metal oxides are ionic in nature, therefore, the element could be calcium or iron.
However, it is also given that the compound is also soluble in water and as calcium oxide is soluble in water, whereas iron oxide is not soluble, the given element is calcium.
2Ca(s) + O2(g) → 2CaO(s)
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → 2Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Reaction with Water:
Metals react with water and produce a metal hydroxide or oxide and hydrogen gas is evolved.
Metal + Water → Metal oxide + H2
Metal oxides that are soluble in water dissolve in it to further form metal hydroxide.
Metal oxide + Water → Metal hydroxide
1. Metals like K and Na react violently with cold water.
2K(S) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + Heat
2Na(S) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + Heat
2. The reaction of calcium with water is less violent.
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
Calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
3. Mg does not react with cold water but reacts with hot water to form Mg(OH)2– It also starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
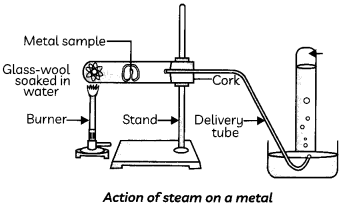
4. Metals like Al, Zn and Fe react with steam to form a metal oxide.
2Al(S) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
5. Metals like Pb, Cu, Ag and Au do not react with water at all.
Example 2.
Case-Based:
Collect the samples of the following metals: aluminium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, zinc and sodium. Put small pieces of the samples separately in beakers half-filled with cold water. Put the metals that did not react with cold water in beakers half-filled with hot water. For the metals that did not react with hot water, arrange the apparatus as shown in Figure and observe their reaction with steam.
(A) Select the metals which react with cold water:
(I) Al
(II) Mg
(III) Na
(IV) K
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (III) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) Both (III) and (IV)
Explanation: Metals like Kand Na react violently with cold water.
2K(S) + 2H2O((l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + Heat
2Na(s)+ 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + Heat
Mg does not react with cold water but reacts with hot water to form Mg(OH)2.
Al reacts with steam to form a metal oxide.
2Al(s) + 3H20(g) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
(B) A metal X when treated with cold water gives the metal hydroxide Y and starts floating.
The metal X and compound Y could be:
| Metal X | Compound Y |
| (I) Mg | Mg(OH)2 |
| (II) Ca | Ca(OH) 2 |
| (III) Na | NaOH |
| (iv) K | KOH |
Select the correct option:
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Only (II)
Explanation: Out of the metals Mg, Ca, Na and K, both Na and K react so violently with water that the hydrogen gas evolved immediately catches fire.
The reaction of Ca with cold water is less violent and calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
Mg does not react with cold water but reacts with hot water to form Mg(OH)2 and hydrogen.
(C) Name the metals which do not react either with cold or hot water.
Answer:
The metals Al, Zn and Fe do not react either with cold or hot water but they react with steam to form the metal oxide and hydrogen gas.
2Al(S) + 3H2O(g) → Al2O3(s) + 3 H2(g)
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(D) Arrange the metals aluminium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, zinc and sodium in decreasing order of their reactivity with water.
Answer:
The decreasing order of reactivity of metals with water is:
Na > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu
(E) Assertion (A): Sodium catches fire when it reacts with hot water.
Reason (R): The reaction between sodium and cold water is highly exothermic.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Explanation: Sodium reacts violently even with cold water and the reaction is such a highly exothermic reaction that the hydrogen gas evolved immediately catches fire.
Example 3.
Give reasons why copper is used to making hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
Answer:
Steel is an alloy of iron and iron reacts with steam to form Fe3O4.
3Fe(S) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
However, copper is less reactive and does not react either with cold water, hot water or steam. Therefore, copper is used to making hot water tanks being less reactive than iron.
Reaction with Acids:
1. When a metal reacts with dil HCl and dil H2SO4, a salt is formed and H2 gas is evolved.
Metal + Dil. Acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Zn(s) + ZnSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2
2. H2 gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with HNO3 (nitric acid) as HNO3 is a strong oxidizing agent and oxidizes the H2 produced to water and is itself reduced to any of the oxides of nitrogen. Exceptions: Magnesium and Manganese.
3. The reactivity of all metals towards acids is not the same and can be found out from the rate at which bubbles of hydrogen gas are formed and the amount of heat generated. Amongst Al, Mg, Fe and Zn, the reactivities towards acids is: Mg > Al > Zn > Fe
4. Aqua regia: It is a freshly prepared mixture of cones. HCl and cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1. It is a highly corrosive, fuming liquid which can even dissolve gold and platinum, even though neither of these acids can do so alone.
Important
Metals such as copper, mercury, silver and gold, which are placed below hydrogen in the reactivity series of metals, do not react with dilute acids.
Example 4.
A man went door-to-door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument, the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Answer:
The man used aqua regia which is a mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO3 acids in the ratio 3:1 and has the property of dissolving gold. When the unsuspecting Lady gave a set of gold bangles to the man, he dipped them in aqua regia solution due to which some gold dissolved in the solution bringing back the sparkle but at the same time the weight of gold bangles was reduced as it went into the solution.
Example 5.
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Answer:
Two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids are magnesium and aluminium, and two metals which will not displace hydrogen are copper and silver.
The reaction of Metals with Solutions of Other Metal Salts:
1. Reactive metals displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution or molten form. Displacement reactions give better evidence about the reactivity of metals. If metal A displaces metal B from its solution, it is more reactive than B.
Metal A + Salt solution of B → Salt solution of A + Metal B
2. If we put an iron nail in a solution of copper sulphate, we observe that the blue colour of copper sulphate solution in the test tube fades gradually and red-brown copper metal is formed. The reaction taking place is:
CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
However, no reaction takes place if a strip of copper metal is placed in iron sulphate solution because copper is less reactive than iron and hence cannot displace iron from iron sulphate solution.
Important
Some examples of reactions of metals with solutions of other metal salts.
| Example of Reaction of No. Metal with a solution of Metal Salt | Chemical Equation |
| 1. Reaction of zinc with copper sulphate solution | CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) |
| 2. Reaction of copper with a silver nitrate solution | 2AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag |
If zinc oxide, magnesium oxide and copper oxide were heated, turn by turn, with zinc, magnesium and copper metals, we can note down the displacement reactions taking place as shown:

Activity Series (The Relative Reactivities of Metals):
The metals have been arranged in order of their decreasing reactivity by using displacement reactions since all metals are not equally reactive. The activity series is shown below:

Example 6.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows:

Use the table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
(A) Which is the most reactive metal?
Answer:
We observe that A undergoes displacement reaction with Copper(ll) sulphate. Therefore, A > Cu.
Metal B displaces iron from iron(ll) sulphate. Therefore, B > Fe.
Metal C displaces silver from silver nitrate. Therefore, C > Ag.
Metal D does not undergo a reaction with any of the given salt solutions. Therefore D is the least reactive metal.
As reactivity of Fe, Cu, Zn and Ag can be written as: Zn > Fe > Cu > Ag, and B displaces Fe, therefore B is the most reactive metal.
(B) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of Copper(ll) sulphate?
Answer:
If B is added to a solution of CuSO4, it will displace copper from the solution as B is more reactive than copper.
(C) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
Metals A, B, C and D arranged in decreasing order of reactivity: B > A > C > D
Chemical Properties of Non-Metals
Reaction with Oxygen
Non-metals combine with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides which are covalent compounds.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
CO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2CO3(aq)
Examples of neutral oxides are carbon monoxide (CO), nitrous oxide (N2O).
Non-metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids as it cannot supply electrons to H+ ions.
Reaction with Hydrogen
A few active metals Like Na, K and Ca force the hydrogen atom to accept electrons to form salts called hydrides.
2Na(s) + H2(g) → 2NaH(s)
Ca(s) + H2(g) → CaH2(s)
Non-metals combine with hydrogen to form covaLent hydrides.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2N2H3(g)
Example 7.
Pratyush took a sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it, as shown in Figure below.

Collection of gas
(A) What will be the action of gas on:
(i) dry litmus paper?
(ii) moist litmus paper?
Answer:
The gas evolved when Pratyush heated sulphur powder in a spatula is sulphur dioxide, SO2.
(i) There will be no change by the action of this gas (SO2) on dry litmus paper.
(ii) When this gas acts on moist blue litmus paper, it changes the colour of litmus from blue to red as sulphur dioxide is acidic in nature since oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature but in presence of water.
(B) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Answer:
Balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place is:
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)