Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physical Education with Solutions Set 3 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physical Education Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 5 sections and 37 Questions.
- Section A consists of questions 1-18 carrying 1 mark each and is multiple choice questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Sections B consists of questions 19-24 carrying 2 marks each and are very short answer types and should not exceed 60-90 words. Attempt any 5.
- Sections C consists of Questions 25-30 carrying 3 marks each and are short answer types and should not exceed 100-150 words. Attempt any 5.
- Sections D consists of Questions 31-33 carrying 4 marks each and are case studies. There is an internal choice available.
- Section E consists of Questions 34-37 carrying 5 marks each and are short answer types and should not exceed 200-300 words. Attempt any 3.
Section -A
Question 1.
Which of the following is an example of Lordosis?
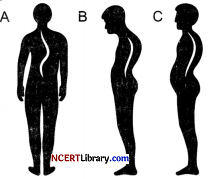
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) None of these
Question 2.
Vitamin E contributes to the production of_______ making our____system strong.
(a) Strength, digestive
(b) Antibodies, immunity
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Hormones, muscular
Answer:
(b) Antibodies, immunity
Question 3.
__________Vitamin is a group of 8 water-soluble vitamins which are important for cellular metabolism.
(a) E
(b) B Complex
(c) C
(d) D
Answer:
(b) B Complex
Question 4.
Rikli Jones test is conducted on
(a) Children
(b) Adults
(c) Adolescent
(d) Senior Citizens
Answer:
(d) Senior Citizens
Question 5.
______is the last function during an event organization.
(a) Organizing
(b) Planning
(c) Managing
(d) Feedback
Answer:
(d) Feedback
Question 6.
__________represents the smooth running of the event.
(a) Managing
(b) Feedback
(c) Organizing
(d) Planning
Answer:
(a) Managing
![]()
Question 7.
Schedules fixed for the matches to be played their time, place, date and court, etc. known as
(a) bye
(b) fixture
(c) advantage
(d) seeding
Answer:
(b) fixture
Question 8.
Allotment of the bye is on the basis of
(a) performance
(b) random draws
(c) first come first serve
(d) pre-decided sequence
Answer:
(b) random draws
Question 9.
Assertion (A): “A change in the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force producing it and inversely proportional to its mass”.
Reason (R): lighter mass will travel at a faster speed.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 10.
Which of the following food helps in sustaining a prolonged routine of exercise?
(a) Fats
(b) Proteins
(c) Vitamins
(d) Carbohydrates
Answer:
(a) Fats
Question 11.
What is Bye?
(a) It’s a method of drawing fixtures.
(b) Point system for team games.
(c) Advantage is given to a team to not play in the initial round.
(d) Placing of teams according to previous performance.
Answer:
(c) Advantage is given to a team to not play in the initial round.
Question 12.
Partial curl-up is to test:
(a) agility and speed
(b) leg strength and endurance
(c) abdominal strength and endurance
(d) upper body strength and endurance
Question 13.
Vitamin E deficiency causes:
(a) Anaemia
(b) Weakness in the heart and muscle
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Weakness in heart and muscle.
![]()
Question 14.
A tournament where every team plays with every other team once and the number of matches is
determined with the help of N(N-1) is called as:
(a) Single league tournament
(b) Double league tournament
(c) Knock-out tournament
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Single league tournament
Question 15.
A___________diet contains all the essential food constituents necessary for the growth and maintenance of our body.
(a) Strict
(b) balanced
(c) Prescribed
(d) consistent
Answer:
(b) balanced
Question 16.
Match the following:
| S. No. | LIST-I | LIST-II |
| 1. | Abrasion | A. Joint Injuries |
| 2. | Green stick fractures | B. Soft tissue injuries |
| 3. | Shoulder Dislocation | C. Cause of sport injuries |
| 4. | Lack of fitness | D. Bone injuries |
Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) 1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
(b) 1-B, 2-A, 3-C, 4-D
(c) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
(d) 1-A, 2-D, 3-B, 4-C.
Answer:
(c) 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
Question 17.
Match the following:
| S. No. | LIST-I | LIST-II |
| 1. | Technical committee | A. to provide shifting facility |
| 2. | Finance committee | B. to resolve dispute |
| 3. | Transport committee | C. to deals with money and expenditure |
| 4. | First and committee | D. to provide medical facility |
Question 18.
___________methods helps best in maintaining a healthy body weight?
(a) Leading an active lifestyle
(b) Missing at least one meal every day
(c) Eating snacks frequently but no meals
(d) Reducing calories drastically in food eaten
Answer:
(a) Leading an active lifestyle
![]()
Section -B
Question 19.
How physical activities can be made accessible for the CWSN?
Answer:
By adopting any of the following strategies the physical activities can be made accessible for the CWSN:
(i) Equipment: The equipment used should be according to the capability and level of children. It may vary in size, shape, color and weight.
(ii) Specific Environment: A healthy and democratic environment shall be created so that CWSN can
perform freely.
(iii) Modified Rules: According to CWSN, the rules shall be diluted and modified according to their nature of the disability.
(iv) Easy to Difficult: The exercise shall be in progression form easy to difficult.
(v) Use of All Body Parts: Physical strategies shall involve whole body parts and ensure whole body movement.
(vi) Extra Care of Concern: While deciding upon physical strategies for CWSN, extra care and concern shall be given like extra time, and to avoid stress light music.
Question 20.
Explain the method, benefits, and contraindications of the Gomukhasana.
Answer:
This asana gets its name because while doing this asana, the body resembles a cow face pose.
Pre-stage: Sit in Sukhasana pose.
Method:
(i) Sit in Sukhasana pose.
(ii) Place the ankle of left leg near the right butt.
(iii) Place the right leg over the left thigh, so that the knees should place over each other.
(iv) Sweep your left hand behind your back, facing palms upwards.
(v) Now interlock the fingers of both hands behind your back.
(vi) Stretch both hands in their respective direction, and look straight.
(vii) Repeat with changing leg position.
Benefits: Helps in curing Asthma, reduces weight, and makes body flexible.
Contraindications:
(i) People with very stiff shoulder may have to take it slow and easy.
(ii) If you have sciatica, then crossing the knee may not be too good as there will be pressure at the sciatic nerve.
Question 21.
What is the main physiological cause of Asthma?
Answer:
The physiological cause of asthma is narrowing of airway passage and a subsequent interference with airflow.
The other causes of Asthma include:
(i) Infections like colds and flu.
(ii) Allergies such as to pollen, dust mites, animal fur or feathers.
(iii) Smoke, fumes and pollution.
(iv) Medicines particularly anti-inflammatory painkillers like ibuprofen and aspirin.
![]()
Question 22.
What do you mean by soft tissue injuries?
Answer:
Soft-tissue injuries includes damage of muscles, ligaments, and tendons throughout the body. The result can be pain, swelling, bruising, and damage. Soft-tissue injuries are classified as Contusions, Sprains, Tendonitis, Bursitis, Stress injuries, Strains.
Question 23.
What kind of sports injury can be termed as “Abrasion”?
Answer:
Abrasion is injury on the surface of the skin. In this injury skin is scrapped or rubbed by friction. It causes severe pain and sometimes bleeding from the affected part. Abrasions are very common sports injuries caused by fall on hard surfaces.
Question 24.
Give the four main causes of Knock knees.
Answer:
The main causes of Knock knees are:
(i) The lack of balanced diet especially vitamin ‘D’, calcium and phosphorus.
(ii) It may also be due to rickets.
(iii) Due to growth imbalance and weakness of leg muscles and joint ligaments.
(iv) Chronic illness, obesity, flat foot, scoliosis and carrying heavy weight in early age.
![]()
Section -C
Question 25.
What is the role of spectators in creating a positive sports environment? Explain.
Answer:
A positive sports environment is the conditions and circumstances which are favorable and beneficial for the sports persons who perform sports activities. Behavior and attitude of the spectators towards coaches, players and officials should be positive. They should not pass any negative comment toward players, referees, umpires, and any other game officials.
They should not indulge themselves in any type of violence. They should try to motivate the players so that they may put up a better performance. In this way the spectators can play a vital role for creating a positive sports environment.
Question 26.
Discuss the preventive measure of sports injuries.
Answer:
“Sports injuries” are the types ofinjuries that occur during participating in sports or competitions, training sessions or sports activities. One of the important objectives of sports medicine is preventing injuries. It also prevents other physical, mental, social and financial harm accompanying sports injuries. General techniques that can prevent sports injuries are:
(i) Warm-up and Cool-down: A well-structured warm-up and cool-down is necessary to increase blood and nutrient flow and concentration. Also, it helps in relaxation, improved flexibility and recovery of muscles.
(ii) Planning a Session: Careful planning of training and rehabilitation sessions allow gradual specific adaptations. It reduces the damage to the tissues as a result of training.
(iii) Using Protective Equipment: The use of protective equipment like proper footwear, helmets, goggles, gum shield, shin pads and gloves prevents many sports injuries.
(iv) Psychological Training: Some form of mental skills training and practice could reduce injuries by reducing anxiety and improving concentration.
(v) Adherence to the Rules: If all performers are aware of and adhere to the rules and laws of the particular sport, then injuries can be reduced to great extent.
Question 27.
What is the role of Yoga in preventing lifestyle diseases?
Answer:
Yoga places a great importance on a proper and healthy lifestyle whose main components are healthy activities, healthy relationships, healthy thoughts, healthy food, and healthy recreation. The holistic art and science of yoga is the best lifestyle ever designed and is effective in managing prevalent lifestyle disorders such as diabetes and hypertension.
There are various lifestyle diseases like Obesity, Diabetes, Asthma, Hypertension and Backache.
Through regular participation in yoga:
(i) Bones and joints become strong.
(ii) Muscles becomes stronger and flexible.
(iii) Circulation of blood becomes normal.
(iv) Respiratory organs become efficient.
(v) Efficiency of digestive system increases.
(vi) Better neuro-muscular coordination.
(vii) Strengthens the immune system
![]()
Question 28.
Explain any three principles of training in brief.
Answer:
Three principles of training are:
(i) Principle of Overload: The overload principle is a basic sports fitness training concept. It means that in order to improve, athletes must continually work harder as their bodies adjust to existing workouts. Overloading also plays a role in skill learning.
(ii) Principle of Specificity: The principle of specificity states that the more specific a training activity is to a given sport (muscle group, workload, velocity and pattern of movement, body posture, and range of motion) the more it will contribute to increasing performance in that sport.
(iii) Principle of Individualization: This could also be called the snowflake principle since it highlights that no two climbers or their optimal conditioning programs are the same. The best training program for a person will targets/her specific weaknesses, address pastor present injuries, provide sufficient time for recovery, and be structured to provide the greatest output for the available training input
Question 29.
Explain how Mental Imagery can be used in Sports.
Answer:
Mental Imagery can be used in sports to:
(i) Familiarize the athlete with a competition site, a racecourse, a complex play pattern or routine, etc.
(ii) Motivate the athlete by recalling images of their goals for that session, or of success in a past competition or beating a competitor in a competition.
(iii) Perfect skills or skill sequences the athlete is learning or refining.
(iv) Reduce negative thoughts by focusing on positive outcomes.
(v) Refocus the athlete when the need arises, e.g., if the performer is feeling sluggish, the imagery of a previous best performance or previous best event focus can help get things back on track.
(vi) See success where the athlete sees themselves performing skills correctly and the desired outcomes.
(vii) Set the stage for a performance with a complete mental run-through of their performance’s key elements to set the athlete’s desired pre-competition feelings and focus Mental imagery should not focus on the outcome but on the actions to achieve the desired outcome.
Question 30.
Give the sources of proteins and fats in our diet in brief.
Answer:
The sources of proteins and fats in our diet are:
(i) Sources of proteins: All meat and other animal products are sources of proteins. The best sources of complete proteins are eggs, milk, meat, poultry, beef and milk products. Grains, fruits and vegetables are the sources of incomplete proteins as they lack one of the essential amino acids. The plant protein can be combined to all of the essential amino acids and form a complete protein. For example, complete plant proteins are rice and beans, milk and wheat cereal, and com and beans.
(ii) Sources of fats: Saturated fats are found in foods from both animal and vegetable sources. Animal sources include meat, poultry and dairy products like milk, cream, cheese, butter and ice cream. Vegetable sources include palm, and coconut oils. Monounsaturated fat is found in large amounts in foods from plants including peanut and olive oil. Polyunsaturated fats are found in foods from plants including sunflower, com and soya-bean and also fish oil.
Section- D
Question 31

On the basis of above-given image answer the following questions:
(a) Which exercise should be done to cure this deformity?
(b) The gap between ankles goes on _______ in this deformity
(c)________should not be forced to walk at very early age.
(d) What kind of treatment is required for such deformity?
OR
_________disease process results in such deformity?
Answer:
(a) Skipping and walking on heels
(b) Increasing
(c) Babies
(d) Knock knees occurring in children often get corrected and in general, no treatment is required.
OR
Rheumatoid arthritis
![]()
Question 32.
Mr. Lakshman, aged 65 years worked as a civil engineer in a construction company. He had to walk and climb a lot as part of his job. After retirement, he settled with his son and spent time with his grandchildren. Nowadays he is experiencing difficulty in doing certain chores which involve physical movement.

(a) The test shown in the picture is performed to assess which component.
(b) Give one coordination and agility test for the senior citizens.
(c) The best time of the two trials to the nearest___________of a second is taken.
(d) For mens age 60-64 years the average score will be____________.
Answer:
(a) Agility
(b) The ‘8 Foot Up and Go’
(c) 1/10*
(d) 5.6 to 3.8
Question 33.
In relation to the picture, answer the following questions:

(a) The given image is the source of _______component of the food.
(b) They provide quick energy to the body and are not __________in the body for long.
(c) In the diet provide about____________of the total energy required by our body.
(d) Name two simple sugars.
OR
What is the main difference between the types of the diet component given in the figure above?
Answer:
(a) Carbohydrate
(b) Stored
(c) 60-80%
(d) Glucose and fructose
OR
The main difference between the types of carbohydrates is the difference between their chemical compositions.
![]()
Section -E
Question 34.
Explain the general principles for the prevention of disability.
Answer:
General Principles for the Prevention of Disability are:
Prevention at three levels is essential:
(i) Primary Prevention: Action was taken before the onset of the disability, which removes the possibility that a disability will occur.
(ii) Secondary Prevention: Action, which halts the progress of the disability at its incipient stage and prevents complications. The specific interventions are early diagnosis and adequate treatment.
(iii) Tertiary Prevention: All measures available to reduce or limit impairments and disabilities, and minimise suffering caused by existing disability. This phase is also called rehabilitation, which includes physical, psychosocial, and vocational measures taken to restore the patient to normal or near-normal condition. It is extremely important that the women undertake adequate and effective preventive measures during their pregnancy and immediate postnatal period and also for their children especially during the early childhood period, to significantly reduce the incidence of impairment and disabilities in them.
Question 35.
What are the responsibilities of the finance committee in the sports events?
Answer:
The finance committee is responsible for making of the budget for the event. The financial functioning of the game is done by this committee. It works for getting and managing the sponsorship of this event and makes all the payments.
(i) Pre-responsibilities:
1. It attempts and functions to get the expenses from various other committees.
2. It plans for collecting the funds and getting sponsorship for providing financial assistance to conduct the tournament smoothly.
3. To get approvals and other major financial sanctions from the higher concerned authority.
(ii) During responsibilities:
1. To provide funds to various other committees for different kinds of activities on the day of the event.
2. To keep record of the officiating fees paid by the teams prior to playing the match.
3. To provide traveling and diet allowances to the teams or players participating in the tournaments.
(iii) Post-responsibilities:
1. To fetch the expenditure from the various committees after the completion of the event.
2. It plays the lead role in settling the bills of the expenses made throughout the event.
3. It prepares the exact financial report covering the total expenditures of the tournament.
Question 36.
What is flexibility? Explain its types in brief.
Answer:
It is the ability to move joints and use muscles through their full range of motion. Commonly, flexibility is known as stretchability, elasticity, and mobility, etc. Flexibility varies from joint to joint due to its structure, surrounding or adjoining ligaments, tendons and muscles. The sit and reach test is a good measure of flexibility of the lower back and backs of the upper legs. Gymnastic players need this component most.
Flexibility is of two types that are given below:
(i) Passive flexibility: The ability to carry out movements to a greater distance with external help is called passive flexibility, e.g., stretching exercises with the help of a partner. Passive flexibility is always more than active flexibility. In fact, passive flexibility is the foundation for active flexibility.
(ii) Active flexibility: Active flexibility is the ability to carry out movements to a longer distance without
any external help, e.g., to do a stretch without the help of a partner. Active flexibility can further be
divided into two parts, such as static and dynamic flexibility.
![]()
Question 37.
Explain the steps involved in talent identification.
Answer:
The three steps for talent identification are the following:
(i) Step-1: Aim screening of children for the basic training stage.
1. Health and physique
2. General physical performance capacity.
3. Motives, interests, mental capabilities etc.
4. Interest of parents etc.
(ii) Step 2: After 3-4 years of basic training advanced training stage
1. Physique
2. Motor Abilities
3. Performance
4. Cognitive, emotional and motivational factors and personality
5. Ability to tolerate load
(iii) Step-3: High-performance training stage.
1. Physique
2. Performance and the potential for performance
3. Talent indicators
4. Cognitive, emotional and motivational factors and personality traits
5. Experimentation by training for a limited period in a sport.