Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 6 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 6 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section- B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section- C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section- D has 2 case-based questions of A marks each; and Section- E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A (16 Marks)
Question 1.
Why does Bt toxin not kill the bacterium that produces it, but kill the insect that ingests it?
(a) Toxin is in an inactive and crystalline form
(b) Bacteria has alkaline gut
(c) Bacteria has acidic gut
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Toxin is in an inactive and crystalline form.
Explanation: Bt toxin is produced by bacteria Bacillus thuriengiensis. During sporulation, these bacteria forms intracellular crystalline bodies thatcontain aninsecticidal protein called the endotoxin. Bt toxin does not kill the bacterium that produces it, but kill the insect that ingests it because the endotoxin that accumulates in the bacterium is an inactive precursor. It gets activated only in the alkaline gut of insect.
Question 2.
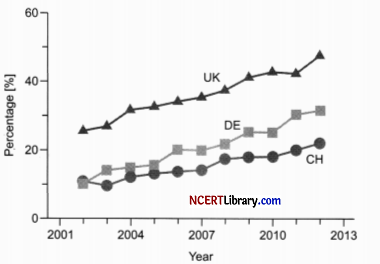
The following statements are drawn as conclusions from the above data:
I. The graph shows that the annual percentage of transgenic animals of the total animals used for scientific purposes from 2002 to 2012 in the United Kingdom is highest.
II. Equal percentage of transgenic animals are used for research in DE and CH.
III. UK has banned use of transgenics.
IV. DE favours research based on transgenics.
Choose the correct alternative from below.
(a) Only I is true
(b) I and IV are true
Answer:
(a) Only I is true
(c) III and II are true
(d) I and III are true
Explanation: The graph shows that the annual percentage of transgenic animals of the total animals used for scientific purposes from 2002 to 2012 in the United Kingdom is highest. In DE, percentage of transgenic animals are used for research is higher than CH. So, only statement I is true.
Question 3.
What is the best way to protect yourself against HIV?
(a) Get yourself vaccinated for HIV
(b) Use birth control pills
(c) Use a latex condom during sexual intercourse
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(c) Use a latex condom during sexual intercourse
Explanation: HIV is spread through semen, vaginal fluids, blood, and breast milk. The protection can be done by using condoms during sexual intercourse.
Question 4.
Sertoli cells are regulated by the pituitary hormone known as:
(a) LH
(b) FSH
(c) GH
(d) Prolactin
Answer:
(b) FSH
Explanation: Sertoli cells are regulated by FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone). FSH stimulates Sertoli cells to produce androgen-binding protein and inhibin; and together with testosterone, to promote the proliferation of Sertoli cells.
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following microbes are used for the commercial production of citric acid?
(a) Xanthomonas citri
(b) Asparagine
(c) Asparagus
(d) Aspergillus
Answer:
(d) Aspergillus
Explanation: Citric acid is the most important organic acid produced in tonnage and is extensively used in food and pharmaceutical industries. It is produced mainly by submerged fermentation using Aspergillus niger or Candida sp.
Question 6.
Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character under consideration is called:
(a) Reciprocal cross
(b) Test cross
(c) Dihybrid cross
(d) Back cross
Answer:
(b) Test cross
Explanation: A test cross is performed to determine the genotype of a dominant parent if it is a heterozygous- or homozygous-dominant. For the purpose, a dominant parent is crossed with the homozygous recessive parent.
Question 7.
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is considered safe upto how many weeks to avoid pregnancy?
(c) 18 weeks
(d) 6 weeks
(a) 8 weeks
(b) 12 weeks
Answer:
(b) 12 weeks
Explanation: Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or medical abortion is the use of abortion pills for terminating a pregnancy. MTP is feasible only up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, and after that surgical termination takes over. MTP is one of the safest methods of terminating an unwanted pregnancy
Question 8.
The method of directly injecting a sperm into ovum in assisted reproductive technology is called:
(a) GIFT
(b) ZIFT
(c) ICSI
(d) ET
Answer:
(c) ICSI
Explanation: ICSI is intra cytoplasmic sperm injection. It is one of the techniques of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) that help couples to overcome their infertility. In ICSI, sperm is directly injected into ovum in vitro to form zygote. Embryo is later implanted through ZIFT into the uterus of the woman. GIFT is Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer.
Question 9.
Artificial reproductive techniques are not always applicable because:
(a) it is very expensive, hence only few people can afford it
(b) these facilities are available only in very few centres in India
(c) it has raised ethical, legal and moral issues
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation: Artificial reproductive techniques are not always applicable because, it is very expensive, hence only few people can afford it. These facilities are available only in very few centers in India. It has raised ethical, legal and moral issues.
Question 10.
DNA finger printing was developed by
(a) Francis Crick
(b) Khorana
(c) Alec Jeffrey
(d) James Watson
Answer:
(c) Alec Jeffrey
Explanation: a technique British that has geneticists revolutionized Sir AlecforensicJeffrey is science. widely considered the father of DNA fingerprinting
![]()
Question 11.
Non-directional alteration in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is:
(a) Gene flow
(b) Mutation
(c) Genetic drift
(d) Gene recombination
Answer:
(c) Genetic drift
Explanation: It is genetic drift. It is the mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population change over generations due to chance. It is non-directional and non-directive.
Question 12.
Which one of the following is a correct statement?
(a) “B” in”Bt-cotton” indicates that it is a genetically modified organism produced through biotechnology
(b) Somatic hybridization involves fusion of two complete plant cells carrying desired genes
(c) The anticoagulant Hirudin is being produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds
(d) “Flavr Savr” variety of tomato has enhanced production of ethylene which improves its taste
Answer:
(c) The anticoagulant Hirudin is being produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds
Explanation: Bt in Bt-cotton indicates that it is a genetically modified organism produced through biotechnology. Somatic hybridization involves the fusion of two complete plant cells carrying desired genes. The anticoagulant hirudin is being produced from transgenic, Brassica napus seeds. Flavr Savr variety of tomato has enhanced the production of ethylene which improves its taste.
Questions No. 13 to 16 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 13.
Assertion (A): A community with more species is more stable than that with less species.
Reason (R): More the number of species, lesser the variation in the total biomass production year after year.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Communities with higher number of species are more stable as it can resist occasional disturbances. A stable community should show less variation in productivity from year to year and resistance towards invasion by alien species. That is there is less variation in case of invasion of other species or extinction of an existing species. Thus, both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanationof assertion
Question 14.
Assertion (A): Primary transcripts in eukaryotes are nonfunctional.
Reason (R): Methyl guanosine triphosphate is attached to 5′- end of hnRNA
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The primary transcript which is produced in the prokaryotes do not contain the introns and exons. They are translated directly after transcription. There is no modification or translation stage. The eukaryotes produce the mRNA which has introns and exons. Therefore they undergo a process of splicing for removing introns and joining exons in the proper order and finally, mature mRNA is formed.
At 5 end of hnRNA, a cap is formed by modification of GTP into 7-methyl guanosine or 7mGppp. This process is called capping and it protects the mRNA from degradation by nucleases. Thus, both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): E. coli having pBR322 with DNA insert at BamHI site cannot grow in medium containing tetracycline.
Reason (R): Recognition site for Bam HI is present in tetR region of pBR322.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: pBR322 has recognition sites for several commonly used restriction enzymes. Recognition site for BamHI is present in tetr region i.e., region responsible for tetracycline resistance. When an insert is added at the BamHI recognition site the gene for tetracycline resistance becomes non-functional and the recombinant bacteria with plasmid pBR322 that has DNA insert at BamHI lose tetracycline resistance. Thus, both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 16.
When couples are unable to achieve coital pregnancy, they often turn to assisted reproductive technologies. A popular assisted reproductive technology is In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF). In the simplest case, a woman is given a course of hormone treatments to cause her ovaries to produce multiple eggs. The eggs are surgically removed just prior to ovulation.
They are then placed in a culture dish with the father’s sperm. During the next few days, the dish is periodically examined to see if fertilization has occurred. In approximately 48 hours, when the embryos reach the eight-cell stage, those that appear healthy and that are growing normally are transferred where, it is hoped, some will implant and develop full term. A woman may have to undergo several treatment cycles before she becomes pregnant.
Assertion (A): Sterilisation methods of contraception are ineffective.
Reason (R): Sterilisation does not prevents the spread of STDs and AIDS.
Answer:
(d) A is false but R is true.
Explanation: Sterilisation does not give protection from sexually transmissible infections (STIs). It is important to practise safer sex, as well as to prevent unintended pregnancy. The best way to lessen the risk of STIs is to use barrier methods such as condoms which are more effective. Thus, assertion is false, but reason is true.
![]()
Section – B (10 Marks)
Question 17.
Explain the method to increase the competency of the bacterial cell membrane to take up recombinant DNA.
Answer:
Exposing the bacterial cells to divalent cations in cold condition may change or weaken the cell surface structure, making it more permeable to recombinant DNA. Then the heat-pulse at 42° C is thougl J create a thermal imbalance across the cell membrane, which forces the DNA to enter the cells through either cell pores or the damaged cell wall.
Question 18.
Identify ovarian hormones X and Y mentioned in the graph and specify their sources.

Answer:
X- Estrogen secreted by growing follicles on the ovaries and are also secreted by the corpus luteum after the egg has been released from the follicle and from the placenta. Y- Progesterone secreted by corpus luteum.
Question 19.
Explain the role of Ti plasmid in biotechnology.
Answer:
The Ti plasmids are actually a tumour inducing plasmids of Agrobacterium which are genetically engineered and used as vector in the cloning procedure. After genetically engineering the Ti plasmids get modified such that, they do not cause any tumours. The Ti plasmid integrates a segment of its DNA that is termed as T-DNA into the chromosomal DNA of the host cells. So being a vector it transfers the foreign genes of interest into the target cells.
Question 20.
Bt-toxins are released as inactive crystals in the bacterial body. What happens to it in the cotton bollworm body that it kills the bollworm?
Answer:
In the cotton bollworm body, Bt-toxin is converted into an active protein due to the alkaline pH of its gut. The toxin binds to the midgut cells, create pores and causes swelling and lysis of the cells. This kills the bollworm.
Question 21.
In short, explain about the exponential growth of the population.
OR
What are the characteristic features of a stable community?
Answer:
It is one of the growth models that explain the pattern of growth within the population. The model states that, if a population has a constant birth rate through time, and is never limited by the availability of food and disease outbreaks, then the population tends to grow exponentially. Through an exponential growth the birth rate alone determines the rate of growth as fast or slow.
OR
According to ecologists, stability depends upon the number of species in a community. More the species in the community more is the stability. Some important features of such community are:
1. A stable community does not show much variation in productivity from year to year.
2. Such community must be either resistant or resilient to the occasional disturbances occurred either naturally or may be manmade.
3. It should also be resistant to the invasion of alien species
Section – C (21 Marks)
Question 22.
Analyze the following given pie chart and answer the questions based on it.

(a) What conclusion can be derivedI fromI PlantsGraph 1?
(b) What does Graph 2 say?
(c) What is the ratio of fungi to animals?
Answer:
(a) As according to the graph, there is maximum population of animals as compared to plants that comprise of 70 percent of the total species population.
(b) As according to graph, in plants, the most species having its existence on earth is fungi.
(c) The existing fungal species, their population is more than the total population of Fishes, Reptiles, Amphibians and Mammals
![]()
Question 23.
Give one significant contribution of each of the following scientists:
(a) Jeffery
(b) Gamow
(c) Mendel.
Answer:
(a) Jeffrey.
Hallwasbomin1945, New York, NY, USA. Heis anAmericangeneticistand chronobiologist. Hall examined the neurological component of fly courtship and behavioral rhythms. Through his research on the neurology and behaviour of Drosophila melanogaster, Hall uncovered essential mechanisms of biological clocks and shed light on the foundations for sexual differentiation in the nervous system. He received Nobel prize in 2017 for discoveries of molecular mechanisms controlling the circadian rhythm.
(b) Antonovich Gamow, was professionally a physicist and cosmologist. He was strong supporter and developer of Lemaitre’s Big Bang theory. He gave a theoretical explanation of alpha decay via quantum tunneling and worked on radioactive decay of the atomic nucleus and molecular genetics.
(c) Gregor Mendel also known as ,Father of Modem Genetics’ was popular for the modern genetics. Mendel’s pea plant experiments conducted between 1856 and 1863 established many of the rules of heredity, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance. He wrote the experiments on hybridization of plants and explained that a specific trait would always be dominant over other traits of same species.
Question 24.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Name the scientist who suggested that the genetic code should be made of a combination of three nucleotides.
(b) Explain the basis on which he arrived at this conclusion.
(c) What does the actual structure of tRNA look like?
Answer:
(a) The scientist named George Gamow suggested that the genetic code should be made of a combination of three nucleotides.
(b) The postulation was that, there should be at least 20 different genetic codes for 20 amino acids. But the only possible combination that would meet the requirement is the combination of three bases that will give 64 codons.
(c) The actual structure of tRNA looks like an inverted L- shaped structure.
Question 25.
The relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa turns out to be a rectangular hyperbola. Give a brief explanation of the graph given below and explain the terms used in it.

Answer:
During his pioneering and extensive explorations in the wilderness of South American jungles, the great German naturalist and geographer Alexander Von Humboldt observed that within a region species richness increased with increasing explored area, but only up to a limit. In fact, the relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa (angiosperm plants, birds, bats, freshwater fishes) turns out to be a rectangular hyperbola.
Accordingly the relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa (birds, bat, angiosperms, and aquatic fishes) turns out to be a rectangular hyperbola. The relationship depicts a straight line on a logarithmic scale described by the following equation
log S = log C + Z log A
Where, ‘S’ stands for species richness, A’ is area and ‘Z’ and ‘C are slope of line (regression coefficient) and y intercept respectively
![]()
Question 26.
Genetically Engineered (GE) foods have had their DNA changed using genes fom other plants or animals. Scientists take the gene for a desired trait in one plant or animal, and they insert that gene into a cell of another plant or animal. Genetic engineering can be done with plants, animals, or bacteria and other very small organisms. Write a short note on golden rice.
Answer:
Golden rice is a Genetically Modified (GM) variety of rice, Oryza sativa, and has been developed as a fortified food for areas where there is ashortage ofdietary vitamin A. It contains a precursor of pro-vitamin A, called beta-carotene, that has been introduced into the rice through genetic engineering. The rice plant naturally produces beta-carotene pigment in its leaves.
However, it is absent in the endosperm of the seed. This is because beta-carotene pigment helps in the process of photosynthesis while photosynthesis does not occur in endosperm. Since beta-carotene is a precursor of pro-vitamin A, it is introduced into the rice variety to fulfill the shortage of dietary vitamin A. It is simple and a less expensive alternative to vitamin supplements. However, this variety of rice has faced a significant opposition from environment activists. Therefore, they are still not available in market for human consumption.
Question 27.
‘Prevention is better than cure’ is an apt slogan to safeguard adolescents from drug abuse. List any six steps that could be taken in this regard.
Answer:
The steps that can be taken in this regard are:
1. Education and awareness is the first step to avoid such things.
2. Avoid undue peer pressure as every child has his own personality and stamina to cope up with the existing society.
3. There should be regular monitoring of activities of adolescents behind them.
4. Parents must channelise the capacity of an individual into various recreational acts like sports, music and other such extracurricular activities.
5. Parents should seek professional and medical help from the experts and should insist the young generation to adopt activities like Yoga.
6. Parents must be able to identify the motivations for alcohols and drug abuse in the upcoming generation.
Question 28.
Differentiate between cancerous cell and normal cell.
OR
Cancer is one of the most dreaded diseases of humans. Explain ‘Contact inhibition’ and ‘Metastasis’ with respect to disease. Name the groups of genes which have been identified in the normal cells that could lead to cancer and how they do so? Name any two techniques which are useful to detect cancers of internal organs. Why are cancer patients often given alpha interferon as part of the treatment?
Answer:
| S. No. | Normal cell | Cancerous cell |
| 1. | They exhibit the property of contact inhibition. Therefore, these stop dividing when they come into contact with other cells. | They do not exhibit the property of contact inhibition. Therefore, they continue to divide, thereby forming a mass of cells or tumour. |
| 2. | After attaining a specific growth they undergo differentiation. | They do not undergo differentiation. |
| 3. | These cells remain confined at a particular location | Do not remain confined at a particular location. They move into neighbouring tissues and disturb its function. |
OR
The contact with other cells inhibits the uncontrolled growth of the cancerous cells. The tumour cells reach the distant organs site through the blood. The group of gene is oncogenes. When activated under certain conditions there is oncogenic transformation of cells. The techniques to detect cancers are Biopsy, Radiography, CT and MRI through which the presence of cancer can be detected. The alpha interferon activates the immune system and destroys the tumours, so it is given to the cancer patients as the part of the treatment
Section – D (8 Marks)
Questions No. 29 and 30 are case based questions. Each question has subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Questions 29.
Following is the graph given about the hormonal changes occurring during menstruation
(a) According to the graph, the levels of LIT are high in which phase?
(b) In which phase is the rate of secretion of progesterone more?
(c) Name the phase in which the uterine cushion washes off?
OR
(c) In which phase is the FSH found to be minimum?
Answer:
(a) The rate of LH is maximum in the ovulation phase.
(b) progesterone is secreted more in luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
(c) The menstrual fluid is given out in the follicular phase of menstrual cycle.
OR
(c) The level of FSH is at minimum in follicular and luteal phase.
![]()
Question 30.
Analyse the below given chemical structure and answer the questions based on it:

(a) The given structure is of which chemical?
(b) What is the common name of this chemical?
(c) What are the physical attributes of this chemical?
OR
(c) This chemical is obtained from which plant?
Answer:
(a) The chemical structure is of Morphine.
(b) Heroin or Smack.
(c) It is crystalline in nature, bitter in taste, white in color and is odorless.
OR
(c) It is obtained from Papaver somniferum, commonly called as the poppy plant.
Section – E (15 Marks)
Question 31.
Identify ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘e’, and T in the table given below :
| S.No. | Syndrome | Cause | Characteristics of affected Individuals | Sex Male/Female/ Both |
| 1. | Sown’s | Trisomy of 21 | ‘a’ (i) | V |
| (ii) | ||||
| 2. | V | XXY | Overall masculine development | ‘d’ |
| 3. | Turner’s | 45 with XO | ‘e’ (i) | |
| (ii) |
OR
Answer the following questions:
(a) A tall pea plant bearing violet flowers is crossed with a tall pea plant bearing white flowers. In the Fj progeny, there were tall pea plants with white flowers, tall pea plants with violet flowers, dwarf pea plants with violet flowers and dwarf pea plants with white flowers. Work out the cross to show how is it possible.
(b) Linkage and crossing-over of genes are alternative of each other. Justify with the help of an example.
Answer:
(a) (i) Palm is broad with characteristics palm crease; short statured with small round head.
(ii) Physical, mental, psychomotor development is retarded.
(b) Both
(c) Klinefelter’s syndrome
(d) Male
(e) (i) Short stature and underdeveloped feminine character.
(ii) Such females are sterile as ovaries are rudimentary. They also do not have well developed secondary sexual characters
OR
(a) A cross of tall pea plant with violet flowers and dwarf pea plant with white flowers.

In the above cross we could notice that Ttw are tall with white flowers TtVv are tall with violet flowers ttVv are dwarf plant with violet flowers and ttw are dwarf with white flowers
(b) 1. There is some linkage between all genes located on the same chromosome. The linkage strength depends on the percentage of the distance between the two. But linkage can be easily broken by crossing over.
2. When genes are located on the same chromosome, then there is possibility of two situations, either a crossing over between the two genes or no crossing between two genes.
3. Crossing over always occurs if genes are located very far from each other – 50% recombinants, 50% parental.
Example: Morgan hybridized yellow-bodied, white-eyed females to brown-bodied, red eyed males and intercrossed their FI progeny. He found that the genes for white and yellow were very lightly linked and showed only 13% recombinant while white and miniature wing showed 37.2% recombination
![]()
Question 32.
Two plants (Snapdragon) with red flowers and white flowers are crossed and produced all pink flowers in Fj generation:
(a) What phenomenon is responsible for it?
(b) Write the genotype of Fr
(c) What would be the phenotype and genotype ratio of the F2 generation?
OR
Answer:
(a) Incomplete Dominance: Sometimes the Fj generation has a phenotype that did not resemble either of the two parents and is between the two. Incomplete dominance is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. This results in a third phenotype in which the expressed physical trait is a combination of the phenotypes of both alleles. Unlike complete dominance, one allele does not dominate or mask the other. Incomplete dominance occurs in the polygenic inheritance of traits such as eye colour and skin color.
(b) In this monohybrid cross, the allele that produces the red colour (R) is not completely expressed over the allele that produces the white colour (r). The resulting offspring are all pink.
The genotypes are : Red (RR) x White (rr) = Pink (Rr).
(c) When the FI was self-pollinated the F2 resulted in the following ratio1 (RR) Red: 2 (Rr) Pink: 1 (rr) White.
Phenotypic ratio :
\(\begin{array}{ccccc}
\text { red } & : & \text { pink } & : & \text { white } \\
1 & : & 2 & : & 3
\end{array}\)
Genotypic ratio:
\(\begin{array}{ccccc}
\mathrm{RR} & : & \mathrm{Rr} & : & \mathrm{rr} \\
1 & : & 2 & : & 1
\end{array}\)
Here the genotype ratios were exactly as we would expect in any Mendelian monohybrid cross, but the phenotype ratios had changed from the 3 : 1 dominant: recessive ratio. In incomplete dominance, the intermediate trait is the heterozygous genotype. In the case of snapdragon plants, the pink plants are heterozygous with the (Rr) genotype. The red and white plants are both homozygous for plant colour with genotypes of (RR) red and (rr) white.
OR
Hemophilia is a condition in which a person’s blood does not clot properly. It is a bleeding disorder caused by deficiency of clotting factor VIII. In most of the cases it is an inherited disorder but it can also be caused due to development of auto antibodies against factor VIII.
Symptoms : The symptoms include :
1. Primary abnormal bleeding and bruises.
2. Tingling, cracking, warmth, pain, and stiffness in joints.
3. Headache, stiff neck, vomiting, lethargy and irritability.

![]()
Type of hemophilia: There are three types of hemophilia :
1. Hemophilia A: This type of hemophilia is found in most of the cases also known as classic hemophilia, caused by deficiency of blood clotting factor VIII.
2. Hemophilia B : It is also known as Christmas disease. It is caused by the deficiency of factor IX.
3. Hemophilia C : It is also known as acquired hemophilia and caused by deficiency of coagulant factor XI
Inheritance of hemophilia : Mostly males are affected because it is transmitted from mother to son. It is X- linked recessive inheritance

Question 33.
Explain the structure of the mature ovum.
OR
Analyze the diagrams given below and answer the questions based on them:

(a) Figure 1 to figure 5 are the stages of development. What does they specify?
(b) The two, four and eight celled structure shown in figure 3, 4 and 5 are known scientifically as?
(c) What is an embryo with eight to sixteen blastomeres called as?
(d) What does figure 2 specify?
(e) What are spermatids?
Answer:
The ovum is female reproductive cell and probably the largest cell in human body. Ovum is spherical in shape and is non-motile. It contains yolky cytoplasm and has one or more egg envelops. It has the following parts :

![]()
1. Follicle Cells: It provides nourishment to the developing eggs.
2. Zona Pellucida: It is a middle, thick, transparent and non-cellular layer. It is secreted partly by follicular cells and partly by the oocyte. It consists of glycoprotein that protects the entry of sperm.
3. Cortical Granules: After fertilization, they make zona pellucida impermeable to sperm to prevent polyspermy.
4. Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is known as ooplasm and it provides nutrients to a fertilized eggs.
5. Nucleus: It is haploid and contains 23 chromosomes.
OR
(a) Fig 1 to 5 specify the passage of a growing embryo, the stages occurring through the fallopian tube.
(b) Blastomeres.
(c) It is known as morula.
(d) It represents the act of fertilization.
(e) They are four haploid cells formed when the secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division. Such haploid cells are called spermatids