Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 6 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
The correct path of urine flow in our body is :
(a) Kidney → Ureter → Urethra → Urinary bladder
(b) Kidney → Urinary bladder → Urethra → Ureter
(c) Kidney → Ureter → Urinary bladder → Urethra
(d) Urinary → bladder → Kidney → Ureter → Urethra
Answer:
Kidney → Ureter → Urinary bladder → Urethra
Explanation: Urine from the nephron is transported to the collecting duct, where it enters the ureters. Ureters open from kidney into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder holds urine, and as the volume of urine collected increases, so does the si∠e of the bladder. When the CNS sends a voluntary message to the bladder, the bladder muscles contract and the bladder sphincter relaxes, allowing urine to pass through the urethra.
Question 2.
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens. The shape of the image of this object on the screen would be :
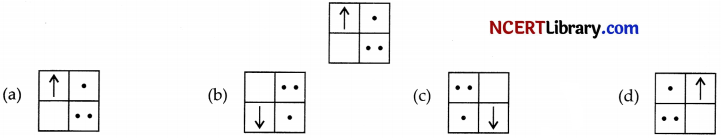
Answer:

Explanation: Since, the image formed is inverted for distant object.
Question 3.
In the following diagram the correctly marked angles are :

(a) ∠A and ∠e
(b) ∠i, ∠A and ∠D
(c) ∠A, ∠i, and ∠e
(d) ∠A, ∠r and ∠D
Answer:
(a) ∠A and ∠e
Explanation: It is clear from the ray diagram that ∠A, ∠e are correctly marked. ∠A represents the angle of prism which is correctly marked. ZD represents the angle of deviation which is formed between the emergent ray and incident ray is incorrectly marked. Zr represents the angle of refraction which is formed by the refracted ray with the normal is incorrectly marked. Zi is the angle formed by the incident ray with the normal is incorrectly marked.
Question 4.
The structural and functional unit of nervous system is:
(a) Nephron
(b) Neuron
(c) Cyton
(d) Axon
Answer:
(b) Neuron
Explanation: Neurons are the structural and functional unit of nervous system. They generate electrical signals called action potentials that allow them to quickly send information over large distances.
Question 5.
What, according to Mendel, was responsible for the inheritance of specific traits?
(a) Genes
(b) Factors
(c) Chromosomes
(d) DNA
Answer:
(b) Factors
Explanation: Mendel discovered the laws of inheritance. He attributed these traits being encoded by factors. Later studies showed that these factors are genes.
Question 6.
A student plots V-I graphs for three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3. Choose from the following statement that holds true of this graph.

(a) R1 = R2 = R3
(b) R1 > R2 > R3
(c) R3 > R2 > R1
(d) R2 > R1 > R3
Answer:
(d) R2 > R1 > R3
Explanation: As it is clear from the graph, the current for A2 conductor is less than A2 and A3 is less than A3 we can say IA2 < IA1 < IA3.
We know
R = \(\frac { V }{ I }\)
or R ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ I }\)

If I is less, then R will be more.
IA2 < IA1 < IA3.
R2 > R1 > R3.
Question 7.
C3H8 belongs to the homologous series of:
(a) Alkynes
(b) Alkenes
(c) Alkanes
(d) cycloalkanes
Answer:
(c) Alkanes
Explanation: A homologous series is a family of compounds with the same general formula, same functional group and similar chemical properties. Each family of organic compound is called a homologous series for example:
1. Homologous series of Alkanes with general formula CnH2n+2
2. Homologous series of Alkene with general formula CnH2n
3. Homologous series of Alkyne with general formula CnH2n-2
Hence, from the general formula of the homologous series of alkanes, this can be confirmed that C3H8 belongs to the homologous series of alkanes.
![]()
Question 8.
The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called:
(a) Budding
(b) Reduction division
(c) Multiple fission
(d) Binary fission
Answer:
(c) Multiple fission
Explanation: Plasmodium reproduces asexually after feeding on red blood cells, a process known as schizogony or multiple fission. Plasmodium divides into numerous cells during multiple fission.
Question 9.

Which of the following two combinations are correct?
| Multiple Fission | Binary fission | |
| (a) | 2 daughter cells are formed. | Many daughter cells are formed. |
| (b) | Both the nucleus and cytoplasm divide simultaneously. | First, the nucleus divides and is surrounded by cytoplasm. |
| (c) | Divides repeatedly. | Divides only once. |
| (d) | Includes a definite pattern of division. | Has no definite pattern of division. |
Answer:
(c) Divides repeatedly – Divides only once.
Explanation: Both binary fission and multiple fission are modes of asexual reproduction and occur with the presence of only one parent. In binary fission, the parent cell divides itself into two equal and identical daughter cells. It is the most common form of reproduction in prokaryotes such as bacteria. In multiple fission, a single parent cell is divided into many daughter cells. It is the most common form of reproduction in protists and in some parasitic species.
Question 10.
The instrument used for measuring electric current is:
(a) galvanometer
(b) ammeter
(c) voltmeter
(d) potentiometer
Answer:
(b) ammeter
Explanation: Ammeter is a device used for measuring electric current in amperes.
Question 11.
In which part of alimentary canal food is finally digested?
(a) Stomach
(b) Mouth cavity
(c) Large intestine
(d) Small intestine
Answer:
(d) Small intestine
Explanation: Food is broken down in the small intestine by enzymes secreted by the pancreas and bile from the liver because it contains all of the enzymes required for the digestion of every type of food, the food is finally digested in the small intestine of the alimentary canal.
Question 12.
The proper representation of series combination of cells for obtaining maximum potential is:

Answer:

Explanation: The maximum potential is obtained when cells are connected in series such that the negative terminal of the first cell is connected to the positive terminal of the second cell and so on.
Example:

Question 13.
While preparing soap a small quantity of common salt is generally added to the reaction mixture of vegetable oil and sodium hydroxide. Which one of the following may be the purpose of adding common salt?
(a) To reduce the basic nature of the soap
(b) To make the soap neutral
(c) To enhance the cleansing power of the soap
(d) To favour the precipitation of the soap
Answer:
(d) To favour the precipitation of the soap
Explanation: A small quantity of common salt is generally added to the reaction mixture of vegetable oil and sodium hydroxide to favour the precipitation of the soap because by adding salt to the suspension mixture, soap is precipitated as solid. This process is called salting out of soap.
Question 14.
Which of the following statements about binary fission is true?
(a) Some multicellular organisms also reproduce through binary fission.
(b) Binary fission produces two new organisms.
(c) Binary fission in amoeba happens only in the vertical plane.
(d) Binary fission in Leishmania can happen in any plane.
Answer:
(b) Binary fission produces two new organisms.
Explanation: Only unicellular organisms reproduce through binary fission. In binary fission, a unicellular organism (a cell) divides to form two unicellular organisms (two cells). Binary fission in Amoeba can happen in any plane. Binary fission in Leishmania happens in a definite orientation (plane) to the body because Leishmania has somewhat organised structure.
Question 15.
In the figure shown below, the point A and B are respectively:

(a) North pole, South pole
(b) South pole, North pole
(c) North pole, North pole
(d) South pole, South pole
Answer:
(b) South pole, North pole
Explanation: As magnetic field lines start from North pole and terminates at S-pole.
Question 16.
Which of the following is not controlled by genes?
(a) Eye colour
(b) Height
(c) Hair colour
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
Explanation: Characters or traits are the characteristics that a person expresses and can be seen in their phenotype. Height, eye colour, and body colour are all controlled by genes and can be inherited.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is False but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion: Iron filings are kept near a magnet it gets arranged in a particular fashion.
Reason: Magnetic field is a scalar quantity.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Magnetic field is not a scalar quantity rather it is a vector quantity which has both magnitude and direction. So, when iron filings are placed around a magnet, they get arranged in a fashion similar to that of magnetic field lines. Thus, assertion is correct, but reason is false.
Question 18.
Assertion: Voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the circuit while measuring the potential difference.
Reason: As the voltage in parallel circuits is measured to be the same.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Voltage measured in parallel circuits is always equal. As all the parallel circuits start from one point and end at another point and the potential difference between these two points will always be same. So, this is the reason why voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the circuit. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
![]()
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Sexual reproduction is more beneficial than asexual reproduction.
Reason (R): Sexual reproduction has less variation.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Sexual reproduction is more advanced than asexual reproduction as it involves the fusion of two different gametes. This leads to genetic variation which helps the organisms to evolve and survive new changes. Asexual reproduction involves the production of clones and hence evolution becomes less obvious. In sexual reproduction, evolution occurs very frequently as every combination of gametes leads to a new genetic combination. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false
Question 20.
Assertion: Photosynthesis is considered as an exothermic reaction.
Reason: Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction because sunlight energy is absorbed by green plants during this process.
Answer:
(d) A is False but R is true
Explanation: Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction because sunlight energy is absorbed by green plants during this process. Thus, assertion is false but reason is true.
Section – B
Question number 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
The following diagram displays a chemical reaction. Observe carefully and answer the following questions:

(i) Identify the type of chemical reaction that will take place and define it. How will the colour of the salt change?
(ii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
(iii) Mention one commercial use of this salt.
OR
Identify the type of chemical reaction in the following statements and define each of them.
(i) Digestion of food in the body.
(ii) Rusting of iron.
Answer:
(i) Photochemical decomposition reaction is taking place. The reactions in which a compound breaks down into simple substances in presence of light are called photochemical decomposition reaction. The colour of salt will change from white to grey.
(ii) ![]()
(iii) Silver chloride is used in photography.
OR
(i) Digestion of food is an example of decomposition reaction because the food we eat mainly contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats. These are decomposed into smaller units such as glucose, amino acids and fatty acids in the presence of enzymes present in the body.
(ii) Rusting of iron is an example of oxidation reaction. In this process, iron reacts with oxygen and moisture present in atmosphere and forms brown layer of iron oxide called rust.
Question 22.
Do genetic combinations of mother play a significant role in determining the sex of a new born?
Answer:
No, genetic combinations of mother do not play a significant role in determining the sex of a new born; because mother has only one type of sex chromosomes i.e., X chromosomes but a father has two types of chromosomes X and Y chromosomes. So, all children will inherit X chromosome from mother and whether X or Y bearing sperm from father fertilises the egg will determine the sex of new born.
Question 23.
Distinguish between metal and non-metals on the basis of physical properties.
Answer:
| Property | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Hardness | Metals are generally hard except sodium and potassium. | Non-metals are soft except diamond. |
| 2. Malleability and ductility | Metals are malleable and ductile except zinc. | Non-metals are neither malleable nor ductile. They are brittle in nature. |
| 3. Conductivity | Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity except mercury and tungsten. | Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity. |
| 4. Density | Metals have high densitv except sodium and potassium. | Non-metals have lower density as compared to metals except diamond. |
| 5. Lustre | All the metals have a brilliant shine or lustre. | Non-metals do not have luster except iodine and graphite. |
Question 24.
Give two ways in which:
(i) Biodegradable substances affect our environment.
(ii) Non-biodegradable substances affect our environment.
Answer:
(i) The two wrays in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment are:
- Decomposition of biodegradable substances results in production of foul smell.
- The area where biodegradable wastes are accumulated serves as a good breeding place for mosquitoes, flies etc. which are the main carriers of germs for diseases like cholera, jaundice, typhoid etc.
(ii) The two ways in w’hich non-biodegradable substances wrould affect the environment are:
- Non-biodegradable substances like pesticides (DDT) enter the food chain and leads to biomagnification.
- As non-biodegradable substances cannot be degraded naturally so they accumulate in the soil causing pollution and also reduces the fertility of the soil.
Question 25.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What is a lens?
(ii) Define optical centre of a thin lens.
(iii) Name the lens that has: (a) a real focus, (b) a virtual focus.
Answer:
(i) A piece of transparent glass bound by two spherical surfaces is called a lens.
(ii) Optical centre of a thin lens is a point on the principal axis of lens such that a ray of light directed towards it, passes undeviated.
(iii) (a) A convex lens has a real focus.
(b) A concave lens has a virtual focus.
Question 26.
Write one difference between sexual and asexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have better chances of survival the one reproducing asexuallv or the one reproducing sexually? Justify your answer?
OR
(i) Budding, fragmentation and regeneration, all are considered as asexual mode of reproduction. Why?
(ii) With the help of neat diagrams, explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Answer:
In sexual reproduction, male and female gametes from twro different individuals unite leading to variations in offsprings due to mixing up of genetic material w’hereas in case of asexual reproduction only single parent is involved and there is no formation of gametes. The ones that are produced sexually have better chances of survival due to mixing up of genetic material between the two different individuals as there is increase in genetic variations in the offsprings which provides maximum chances for the survival of species in the changing environment as well as under unfavourable conditions. This variation in species is also essential for evolution.
OR
(i) Budding, fragmentation and regeneration are considered as asexual mode of reproduction because only one parent is involved, no sex cells are involved.
(ii) Regeneration in Planaria.

Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
Explain why:
(i) Cone, nitric acid can be stored in aluminium container.
(ii) Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils.
(iii) 24 carat gold cannot be used for making ornaments.
Answer:
(i) When aluminium is treated with concentrated nitric acid, it becomes inert due to the formation of a thin layer of aluminium oxide on its surface which stops the reaction between aluminium and cone. HNO3. Thus, cone. HNO3 can be stored in an aluminium container.
(ii) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal but it is resistant to corrosion. The reason for this is that aluminium reacts with oxygen present in air to form a thin layer of aluminium oxide. This oxide layer is very stable and prevents further reaction of aluminium with oxygen. It is light in weight and a good conductor of heat. Therefore, it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(iii) 24 carat gold is a pure form of gold and is very soft, so it is not used for making ornaments. Due to this reason, it is alloyed with small amount of copper or silver to make it hard as required for making ornaments.
Question 28.
(i) Define catenation. Why no other element exhibits the property of catenation to the extent seen in carbon compounds?
(ii) What do you mean by homologous series? Give the general formula of the homologous series of alkenes?
(iii) What do you mean by isomers? Give an example.
Answer:
(i) Carbon can link with carbon atoms via covalent bonds to form long chains, branched chains and closed ring. Carbon shows catenation to a large extent because of small size and having C – C strong bonding.
(ii) A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH2 group.
The general formula of the homologous series of alkenes is CnH2n where n is number of carbon atoms in one molecule of alkene.
(iii) The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as isomers. n-butane and iso-butane are two isomers of butane.
![]()
Question 29.
(i) What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
(ii) The depletion of ozone layer is a cause of concern. Why?
(iii) In the following food chain, 100 J of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producer?
Plants → Deer → Lion
OR
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable?
(i) Decomposers act upon dead and decay organisms and convert them into simpler forms. These simple substances get mixed up in the soil and are used as nitrients by the producers. From producers it goes to consumers and so on. They maintain the balance in the ecosystem and provide space for the new life in the ecosystem.
(ii) Ozone layer is found in stratosphere which prevents the harmful UV rays to reach the earth’s surface. But the depletion of ozone layer allows more UV rays to pass through it and causes various harmful effects on human beings like cancer, genetic defects, cataract, etc.
(iii) Plants are able to capture only 1% of the energy of sunlight. 10% of energy is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers. So, if 100 J of energy is available to the lion, then the energy available to the producer is 10,000 J.

OR
There are various types of waste substances released into our environment. Those substances which are degraded into simpler form naturally by the action of microbes like bacteria or fungi are called biodegradable substances. Examples-Vegetables and fruits peels, paper, agricultural wastes etc.
Those substances which cannot be degraded into simpler forms naturally by the action of microbes are called non-biodegradable substances. Examples-Aluminium foils, plastic bottles, glass apparatus etc.
Question 30.
Define the following terms with reference to spherical mirrors:
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Principal focus
(iv) Principal axis
(v) Radius of curvature
(vi) Aperture
Answer:
(i) Pole: It is the centre of the reflecting surface of the mirror.
(ii) Centre of curvature: It is the centre of the hollow sphere of which the reflecting surface of the mirror is a part.
(iii) Principal focus: Incident rays parallel to principal axis, after reflection, either converge to or appear to diverge from a fixed point on the principal axis. This point is called principal focus of a spherical mirror.
(iv) Principal axis: It is the straight line passing through the pole and centre of curvature of a spherical mirror.
(v) Radius of curvature: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is the radius of the hollow sphere of glass of which mirror is a part.
(vi) Aperture: The portion of a mirror from which the reflection of light actually takes place is called aperture of the mirror.
Question 31.
(i) List two properties of magnetic field lines.
(ii) How is strength of magnetic field near a straight current carrying conductor is affected when:
- Strength of current in the conductor is increased?
- Direction of flow of current is reversed?
(iii) Two magnets are lying side by side as shown below. Draw magnetic field lines between them.

Answer:
(i) (a) Magnetic field lines emerge from North pole and merge at South pole outside the magnet. Inside, they flow from South to North.
(b) No two magnetic field lines can intersect each other at any point in space.
(ii) (a) The strength of magnetic field is directly proportional to the strength of current, so if the current in the conductor increases, the magnetic field around it also increases.
(b) On reversing the direction of current, direction of magnetic field will also be reversed.
(iii) Magnetic field lines between two magnets are shown below:

Question 32.
State reason for the following:
(i) Lemon is used for restoring the shine of tarnished copper vessels.
(ii) Copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
(iii) Copper wires are used in electrical appliances.
Answer:
(i) When copper vessels are exposed to moist air, they from a green coating of basic copper carbonate [CuCO3. CU(OH)2]. The sour substance such as lemon or tamarind juice contain acids. Lemon juice contains citric acid and tamarind contains tartaric acid. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxides or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and make them shining red-brown again.

(ii) Copper does not react with cold water, hot water, or steam. However, iron reacts with steam. If the hot water tanks are made of steel (an alloy of iron), then iron would react vigorously with the steam formed from hot water to corrode the tank due to the formation of iron oxide.

Therefore, copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel.
(iii) Copper metal has high melting and boiling point, good conductor of electricity and can be drawn into thin wires. This is the reason behind the use of copper metal to make electrical wires.
Question 33.
(i) What is pollination? Give its two types.
(ii) Draw a longitudinal section of female reproductive part of a flower showing germination of pollen grain. Label on it the following:
(a) Stigma.
(b) Pollen tube with a male germ cell.
(c) Female germ cell.
OR
With the help of suitable diagrams explain the various steps of budding in Hydra.
Answer:
(i) The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or different flower is known as pollination. The two types of pollination are self-pollination and cross pollination.
(ii)

OR
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction and it is the process of production of new individual from an outgrowth called bud formed on the parent body. Regenerative cells present in Hydra are used for budding. Due to repeated mitotic divisions an outgrowth called bud, develops from the parent body which enlarges in size and finally develops into a small hydra. After attaining suitable maturity the offspring get detached from the parent body and becomes an independent individual.

Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, the following observations were made by a student:
(i) Silver does not show any change.
(ii) Some bubbles of a gas are seen when lead is reacted with the acid.
(iii) The reaction of sodium is found to be highly explosive.
(iv) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium is added to the acid.
Explain these observations giving appropriate reason.
OR
Write the name, method of preparation and uses of the following:
(i) CaOCl2
(ii) CaSO4.\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)H2O
(iii) NaHCO3
Answer:
(i) Silver is covered with a thin layer of silver chloride, so it does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid.

(ii) Bubbles of hydrogen gas are evolved when lead is reacted with the acid.

(iii) The reaction of sodium is found to be highly explosive because sodium is highly reactive metal. It reacts with hydrochloric acid explosively forming hydrogen gas along with the release of large amount of heat.

(iv) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium is added to the acid because the reaction is highly exothermic in nature.

OR
(i) CaOCl2: Its chemical name is calcium oxychloride. It is also known as bleaching powder. Preparation: Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Uses: It is used as bleaching agent in textile industry.
(ii) CaSO4.\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)H2O: It is calcium sulphate hemihydrate. It is also known as Plaster of Paris. 2
Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) Gypsum at 373K.
CaSO4.2H2O → CaSO4.\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)H2O + \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)H2O
Uses: It is used to join bones, buildings and in dentistry.
(iii) NaHCO3: Its chemical name is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). Also known as baking soda.
Preparation:
NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
Uses: It is used in food industry and bakery, as an antacid and mild antiseptic.
![]()
Question 35.
Describe the internal structure of human heart with a labelled diagram.
OR
What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer:
1. The heart is divided into a right and left side by the septum. The heart has four chambers, two relatively small upper chambers called atria or auricles and two larger lower chambers called ventricles. The walls of the ventricles are relatively thicker than atrial walls.
2. The two atria are separated from each other by a thin, muscular wall called the inter-atrial septum and the right and left ventricles are by a thick-walled, inter-ventricular septum. The inter-atrial septum and inter-ventricular septum prevent mixing of deoxygenated blood in the right side of the heart with oxygenated blood in the left side of the heart.

3. The atria and ventricle of the same side are separated by a thick fibrous tissue called the atrioventricular septum.
4. The opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle is guarded by a valve called as the tricuspid valve, whereas a bicuspid valve guards the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
5. The largest artery is the aorta which arises from the left ventricle supplies blood to all the body parts except lungs. Pulmonary artery that arises from the right ventricle carries deoxygenated blood to lungs.
6. The openings of the right and left ventricles into the pulmonary artery and the aorta respectively are provided with the semilunar valves.
7. The valves allow the blood to flow only in one direction, i.e. from the atria to the ventricles and from the ventricles to the pulmonary artery or aorta.
OR
The different methods of contraception are:
(1) Methods which create a mechanical barrier so that the sperm does not reach the egg. They include condoms on the penis or similar coverings on the vagina.
(2) A second category acts by changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released and fertilisation does not occur. These are
drugs taken as oral pills. However as they change hormonal balance they cause side effects too.
(3) There are contraceptive devices placed in the uterus such as the loop or the Copper-T to prevent pregnancy. This could cause side effects like irritation in the uterus.
(4) Surgery is used to create blocks in the vas deferens of the male so that sperm transfer is prevented. Surgery is also used to block the fallopian tube so that the egg does not reach the uterus. While surgical methods are safe in the long run surgery itself could cause infections and other problems if not done properly.
Question 36.
Due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens, a certain defect of vision arises. Write the name of this defect. Name the type of lens required by such persons to improve the vision. Explain the structure and function of such a lens.
Answer:
The defect caused due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens is presbyopia. Presbyopia is the defect of eye in which a person cannot see nearby objects comfortably and distinctly without corrective eye glasses. A presbyopic eye has its near point greater than 25 cm and is gradually increases as the eye becomes older. The type of lens required by such person to improve the vision is bifocal lens.
A bifocal lens consists of both convex lens and concave lenses. The convex lens used in bifocal lens is used to correct Hypermetropia (far sightedness) and concave lens is used to correct myopia (short sightedness).
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or fences by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. More commonly, plants respond to stimuli slowly by growing in a particular direction because this growth is directional, it appears as if the plant is moving. Let us understand this type of movement with the help of an example.
1. Fill a conical flask with water.
2. Cover the neck of the flask with a wire mesh.
3. Keep two or three freshly germinated bean seeds on the wire mesh.
4. Take a cardboard box which is open from one side.
5. Keep the flask in the box in such a manner that the open side of the box faces light coming from a window.
6. After two or three days, you will notice that the shoots bend towards light and roots away from light.
7. Now turn the flask so that the shoots are away from light and the roots towards light.
8. Leave it undisturbed in this condition for a few days.
(a) Why shoot bends towards light?
(b) Define Chemotropism. Explain with an example.
OR
(b) What can be inferred from the above activity?
Answer:
(a) Environmental triggers such as light, or gravity will change the directions that plant parts grow in. These directional, or tropic, movements can be either towards the stimulus, or away from it. The shoots usually grow upwards and away from the earth.
(b) The movement of plants in response to chemicals is called Chemotropism. One example of chemotropism is the growth of pollen tubes towards ovules.
OR
(b) The above activity shows the movement of plants in response to light.
Question 38.
Some metals are found in the earth’s crust in the Free State. Some are found in the form of their compounds. The metals at the bottom of the activity series are the least reactive. They are often found in a free state. For example, gold, silver, platinum and copper are found in the Free State. Copper and silver are also found in the combined state as their sulphide or oxide ores. The metals at the top of the activity series (K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al) are so reactive that they are never found in nature as free elements.
The metals in the middle of the activity series (Zn, Fe, Pb, etc.) are moderately reactive. They are found in the earth’s crust mainly as oxides, sulphides or carbonates. You will find that the ores of many metals are oxides. This is because oxygen is a very reactive element and is very abundant on the earth.
Thus on the basis of reactivity, we can group the metals into the following three categories-
- Metals of low reactivity
- Metals of medium reactivity
- Metals of high reactivity.
Different techniques are to be used for obtaining the metals falling in each category.
(a) Why the metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted into metal oxides prior to reduction?
(b) Write chemical equations for reduction of mercury from its ore Cinnabar?
(c) Why highly reactive metals such as sodium, calcium, aluminium, etc., are used as reducing agents? Explain with an example.
OR
Write the equations for Thermite reaction.
Answer:
(a) It is easier to obtain a metal from its oxide, as compared to its sulphides and carbonates. Therefore, metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted into metal oxides prior to their reduction.
(b) Cinnabar (HgS) is an ore of mercury. When it is heated in air, it is first converted into mercuric oxide (HgO). Mercuric oxide is then reduced to mercury on further heating.

(c) Highly reactive metals such as sodium, calcium, aluminium, etc., are used as reducing agents because they can displace metals of lower reactivity from their compounds. For example, when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, the following reaction takes place.
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(s) + Heat
OR
(d) The reaction of iron (III) oxide (Fe203) with aluminium is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts. This reaction is known as the Thermite reaction.
Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
Question 39.
The region surrounding a magnet, in which the force of the magnet can be detected, is said to have a magnetic field. The lines along which the iron filings align themselves represent magnetic field lines. Take a small compass and a bar magnet. Place the magnet on a sheet of white paper fixed on a drawing board, using some adhesive material.
Mark the boundary of the magnet. Place the compass near the north pole of the magnet. How does it behave? The south pole of the needle points towards the north pole of the magnet. The north pole of the compass is directed away from the north pole of the magnet.
Mark the position of two ends of the needle. Now move the needle to a new position such that its south pole occupies the position previously occupied by its north pole. In this way, proceed step by step till you reach the south pole of the magnet. Join the points marked on the paper by a smooth curve.
This curve represents a field line. Repeat the above procedure and draw as many lines as you can. These lines represent the magnetic field around the magnet. These are known as magnetic field lines. Observe the deflection in the compass needle as you move it along a field line. The deflection increases as the needle is moved towards the poles.
(a) What is a magnetic field?
(b) What is the direction of magnetic fields inside the magnet?
(c) What does the closeness of magnetic lines represents?
OR
(c) If magnetic fields are produced by a straight conductor, what happens to the deflection of the compass needle placed at a given point if the current in the copper wire is changed?
Answer:
(a) The region surrounding a magnet, in which the force of the magnet can be detected, is said to have a magnetic field.
(b) Inside the magnet, the direction of field lines is from its south pole to its north pole.
(c) The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines. The field is stronger, that is, the force acting on the pole of another magnet placed is greater where the field lines are crowded.
OR
(c) If the current is increased, the deflection also increases.