Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 5 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be:
(a) Double fertilisation
(b) Self-pollination
(c) Cross fertilisation
(d) No fertilisation
Answer:
(c) Cross fertilisation
Explanation: Cross fertilisation will be the nature of the cross. Cross-fertilisation is when a plant is fertilised with pollen from another plant of the same species. Flowering plants use a sophisticated fertilisation method called double fertilisation. Fusion of a male and female gamete is required.
Question 2.
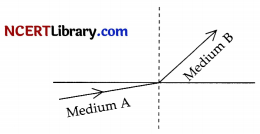
A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be:
(a) greater than unity
(b) less than unity
(c) equal to unity
(d) zero
Answer:
(a) greater than unity
Explanation: As the light ray when travelled from medium A to medium B, then they bend towards the normal which means that medium B has higher refractive index and less speed of light with respect to medium A, So, refractive index of medium B w.r.t. medium A will be greater than unity.
Question 3.
The accumulator which is used for the domestic purpose has the electromotive force of 10 V and with an internal resistance of 0.8 Ω is externally charged by 150 V of the direct current power supply using a series resistor 18 Ω. Calculate the terminal voltage of the accumulator during using.
(a) 16.8 V
(b) 17.1 V
(c) 11.3 V
(d) 15.9 V
Answer:
E = V – Ir
V = E + Ir
= 10 + \(\left(\frac{150-10}{18+0.8}\right)\)
= 15.9 V
Question 4.
In which of the following aspects does multiple fission differs from binary fission?
(i) Number of offsprings produced.
(ii) Level of genetic variation in offsprings.
(iii) Number of parents involved.
(iv) Multiple fission happens in Plasmodium whereas binary fission happens in Leishmania.
(a) Only (i) is correct
(b) Both (i) and (iv) are correct
(c) (iii) is correct
(d) (ii) is correct
Answer:
(b) Both (i) and (iv) are correct
Explanation: Multiple fission produces many offsprings whereas binary fission produces only two. Off-springs produced through multiple fission as well as binary fission are genetically identical to each other and to their parents. Both multiple fission and binary fission require only one parent. Plasmodium, the protozoan that causes malaria reproduces through multiple fission. Leishmania causes Kala-azar and it reproduces through binary fission.
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following endocrine glands is unpaired?
(a) Adrenal
(b) Pituitary
(c) Testes
(d) Ovary
Answer:
(b) Pituitary
Explanation: The pituitary gland, also known as the hypophysis, is a pea-sized endocrine gland. It is a protrusion at the base of the brain, at the bottom of the hypothalamus. It is a gland which is not paired. Adrenal, ovary and testes are paired glands.
Question 6.
If a person has five resistors each of value \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)Ω, then the maximum resistance he can obtain by connecting them is:
(a) 1 Ω
(b) 5 Ω
(c) 10 Ω
(d) 25 Ω
Answer:
(a) 1 Ω
Explanation:
Resistance of one resistor = \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)Ω
Number of resistors = 5
Maximum resistances can be obtained by combining the resistors in series:
Rs = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4 + R5
= \(\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{1+1+1+1+1}{5}=\frac{5}{5}\)
= 1 Ω
Hence, a person on combining five resistors in series gets resistance 1 Ω.
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a straight chain hydrocarbon?

Answer:

Explanation: In straight chain hydrocarbons, carbon atoms are connected through covalent bond in one continuous chain with no branches. In the structure (a), (b) and (c), all the carbon atoms are connected to each other in a continuous straight chain:

In structure (d), – CH3 group is attached to the second carbon atom of the chain forming a branch. Hence, compound in structure (d) is a branched chain hydrocarbon.

Question 8.
The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires:
(a) carbon dioxide and water
(b) chlorophyll
(c) sunlight
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Explanation: In the autotropic mode of nutrition, the plants can prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight, carbon dioxide, water and chlorophyll present in the leaves of the plants.
Question 9.
When a new plant is formed as a result of cross-pollination from different varieties of a plant, the newly formed plant is called:
(a) Dominant plant
(b) Mutant plant
(c) Hybrid plant
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Hybrid plant
Explanation: The process of crossing pollen from one flower to the pistils of another flower is known as cross-pollination. When a new plant is formed as a result of cross-pollination from different varieties of a plant, the newly formed plant is called hybrid plant.
Question 10.
The equivalent resistance of a series combination of two resistances is χ ohm. If the resistances are of 10 Ω and 40 Ω respectively, the value of χ will be:
(a) 10 Ω
(b) 20 Ω
(c) 50 Ω
(d) 40 Ω
Answer:
(c) 50 Ω
Explanation:
We know that
Total Resistance
R = R1 + R2
= 10 + 40
= 50 Ω
Hence, the value of X is 50 Ω.
Question 11.
The number of chromosomes in parents and offspring of a particular species remains constant due to:
(a) doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation.
(b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation.
(c) doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation.
(d) halving of chromosomes after gamete formation.
Answer:
(b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation.
Explanation: The number of chromosomes in parents and offspring of a particular species remains constant due to halving of chromosomes during gamete formation.
The gametes are special type of cells which contain only half the amount of DNA as compared to normal cells of an organism. So, when a male gamete combines with a female gamete during sexual reproduction, then the new cell ‘zygote’ will have normal amount of DNA.
Question 12.
If we place the magnetic compass near the north pole of the magnet, which pole of the needle will point towards it?

(a) North pole
(b) South pole
(c) Keep deflecting
(d) Non of these
Answer:
(b) South pole
Explanation: As like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other. Therefore when North pole of bar magnet is brought near the compass, it gets deflected in south direction.
Question 13.
Rancidity can be prevented by:
(a) adding antioxidants
(b) storing food away from light
(c) keeping food in refrigerator
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Explanation: Rancidity can be prevented by packing fat and oil-containing foods in nitrogen gas. It can be retarded by keeping food in a refrigerator. It can also be retarded by storing food in air-tight containers and away from light in order to prevent their decomposition.
![]()
Question 14.
Bile from the liver is received in which part of the alimentary canal?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
Answer:
(b) Small intestine
Explanation: Bile is a dark green to yellowish brown fluid produced by the liver. It is stored in the 1 gall bladder and it helps in the digestion of fats in the small intestine.
Question 15.
In the circuit shown below, what is direction of the current?

(a) No current flowing
(b) Anti-clock wise
(c) Clock wise
(d) Data insufficient
Answer:
(c) Clock wise
Explanation: If the current flows from North to South the compass needle will move towards the last.

Question 16.
The opening and closing of stomatal pores depends upon :
(a) Oxygen
(b) Water in guard cells
(c) Concentration of carbon dioxide in stomata
(d) Temperature
Answer:
(b) Water in guard cells
Explanation: The entry of water into guard cells aids in the opening of guard cells, the guard cell becomes turgid as a result of this. Water going out from guard cells aids in the closing of guard cells, as a result of this the guard cells become flaccid.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is False but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion: A current carrying rod is suspended between U-shaped magnet, the rod deflects.
Reason: A force is exerted on the rod due to magnetic field.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: A force is always exerted due to magnetic field in the same way electric current flowing through any conductor produces magnetic field. And in this case, Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to predict directions of the magnetic field, current and displacement. Thus, assertion and reason both are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 18.
Assertion: Silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to sunlight.
Reason: It is because silver reacts with carbonates present in the air.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Silver reacts with sulphur present in the air and forms a layer of silver sulphide, therefore, silver articles get tarnished or becomes black after sometime when exposed to sunlight. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 19.
Assertion: Pancreatic amylase digests starch to maltose.
Reason: Pancreatic amylase breaks the peptide bond of protein.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Pancreatic amylase is a starch splitting enzyme like salivary amylase, so it cannot digest proteins. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
![]()
Question 20.
Assertion: Electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends.
Reason: Ohm’s law expression V = IR, where R (resistance) of the wire is always varying.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Ohm’s law states that the electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference across its two ends. The expression is written as :
V = IR
Here, R (resistance of the wire) is constant value then only the statement will be valid.
V ∝ I only if \(\frac { V }{ I }\) = constant
Thus, assertion is true, but reason is false.
Section – B
Question number 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
(i) What is myopia?
(ii) How can it be corrected?
OR
Draw a neat diagram to show refraction of a light ray through a triangular glass prism. Mark angle of incidence, angle of emergence, incident ray, refracted ray, emergent ray and the angle of deviation.
Answer:
(i) The defect of human eye in which a person can see the objects lying at short distances clearly but cannot see the far objects distinctly is called myopia or short-sightedness.
(ii) A myopic eye can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lens of suitable power or focal length.
OR
The labelled diagram has been shown in figure given below, in which

PE – Incident ray ∠i – Angle of incidence
EF – Refracted ray ∠r – Angle of refraction
FS – Emergent ray ∠e – Angle of emergence
∠A – Angle of the prism ∠D – Angle of deviation
Question 22.
What are the adaptations of a leaf for photosynthesis?
Answer:
Some of the adaptations of a leaf for photosynthesis are:
- Chloroplasts are concentrated more on the upper surface of leaf than the lower surface.
- Leaves provide large surface area for maximum absorption of sunlight energy.
- More stomata are present on lower surface of leaves so that more carbon dioxide can enter for efficient photosynthesis.
- Leaves are arranged at right angles to the light source so that they can get better sunlight.
Question 23.
How can a chemical equation be made very informative and why?
Answer:
A chemical equation can be made more informative by mentioning the physical states of the reactants and products along with their chemical formula. The gaseous, liquid, aqueous, and solid states of the reactants and products are represented by the notations, (g), (1), (aq) and (s) respectively. The word aqueous is written if the reactant or product is present as a solution in water. When we use the symbol (g) with H20 it means in the reaction water is used as steam.
Example: 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
In the given chemical reaction, Fe in the solid state reacts with water in steam form and forms iron oxide in solid form and releases hydrogen gas.
Question 24.
What is parasitic mode of nutrition? Give examples of both plants and animals that are parasites.
Answer:
There are different strategies adopted by the organism for nutrition depending on how the food is available. Some organisms break down food outside the body and then absorb it. Others take in food into the body and then digest it. Some organisms get their nutrition from plants and animals without killing them. These organisms are called parasites and the organism from which they derive their food is called host. Some of the parasites are lice, ticks, mites, leeches and tapeworms among animals and orchids and Cuscuta among plants.
Question 25.
The first trophic level in a food chain is always a green plant. Why?
OR
We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned. Why?
Answer:
Green plants are the producers which prepare their own food by utilising solar energy from inorganic sources and all other living organisms depend on them for food. Herbivores and carnivores depend upon green plants either directly or indirectly for food. Hence the first trophic level in a food chain is always a green plant.
OR
Ponds or lakes are natural, self-sustaining and complete ecosystem. They have decomposers like bacteria or fungi which break down the waste material and hence they remain clean. But an aquarium is a man-made, incomplete ecosystem and they do not have decomposers to clean the waste material. So, an aquarium needs to be cleaned but we do not clean ponds or lakes.
Question 26.
While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid?
Answer:
The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is a highly exothermic in nature. The acid must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring. If water is added to a concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause bums. The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating. Hence, it is recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid.
Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
OR
(i) How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
(ii) How many pairs of chromosomes are present in human beings? Out of this how many are sex chromosomes? How many types of sex chromosomes are found in human beings?
Answer:
When Mendel crossed pure tall (TT) pea plants with pure dwarf (tt) pea plants, in F1 generation he found that all pea plants were tall (Tt). There were no dwarf plants produced in F1 generation. When he self-pollinated these F1 plants, in F2 generation he obtained tall and dwarf plants in the ratio 3: 1. Thus, as three-fourths of the plant in F2 generation are tall and one-fourth is dwarf so tall is a dominant trait whereas dwarf is a recessive trait [which expressed itself only in homozygous condition]. So he concluded that for a particular trait [here in this example height of the plant] it may be dominant or recessive.

OR
(i) Human beings contain 23 pairs of chromosomes-22 pairs are autosomes and one pair sex chromosomes. During meiosis process gametes are formed in sex cells where the chromosome number is halved(n). At the time of fertilisation when male gamete fuses with female gamete the diploid number (2n) is restored back in zygote. Thus, half of the chromosomes come from father and other half from mother. In this way, meiosis process ensured equal genetic contribution of male and female parents in the progeny.
(ii) There are 23 pairs of chromosomes present in human beings. One pair is sex chromosome. They are XX and XY. So there are two types of sex chromosomes.
Question 28.
What is a decomposition reaction? Give examples. What is a thermal decomposition reaction?
Answer:
Thermal decomposition is a decomposition reaction carried out by heating. The decomposition of cal¬cium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide on heating is an example of thermal decomposition. The calcium oxide formed is also called lime or quicklime.
![]()
Decomposition reactions can be regarded as opposite of combination reactions. Decomposition reac¬tions require energy in the form of heat, light or electricity to break down the reactants. Such reactions which absorb energy are called endothermic reactions. On the other hand, in combination reactions heat is given out. Such reactions are called exothermic reactions. Here is an example.
Glucose combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water with the liberation of energy.
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(aq) + 6H2O(l) + Energy
Question 29.
(i) Sometimes after a shower of rain we can see a beautiful rainbow. Can this be explained by any particular process of light?
(ii) Show the formation of a rainbow with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
(i) A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a rain shower. It is caused by dispersion of sunlight by tiny droplets present in the atmosphere. A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun. The water droplets act like small prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally and finally refract it again when it comes out of the rain¬drop. The dispersion of light and internal reflection make different colours visible to the observer’s eye. A rainbow is also seen on a sunny day when we look at the sky through a waterfall or through a water fountain with the sun behind us.
(ii) The diagram below explains how a rainbow is formed:

Question 30.
Write the molecular formula of the following compound and draw their electron dot structure.
(i) Ethane
(ii) Ethene
(iii) Ethyne
Answer:

Question 31.
What is ozone? Show the reactions of formation of ozone from oxygen in the atmosphere? Name the pollutant and its role in depletion of ozone layer.
Answer:
Ozone is a triatomic molecule made up of three oxygen atoms. It is present as a layer in our strato-sphere. It prevents the harmful UV rays of sun from reaching the surface of earth. Ozone is formed by absorption of UV rays coming from sun.
O2 ⇌ O + O
O + O2 → O3
UV radiations splits oxygen molecules to oxygen atoms and the oxygen atoms combine with oxygen molecule to form ozone.
CFCs Chlorofluorocarbons are mainly responsible for ozone layer depletion. CFCs release chlorine atoms which breaks ozone to oxygen, more amounts of CFCs thus, released will cause depletion of ozone layer.
Question 32.
(i) Write two points of difference between electric energy and electric power.
(ii) Out of 60 W and 40 W lamps, which one has a higher electric resistance when in use?
(iii) What is the commercial unit of electrical energy? Convert it into joules.
Answer:
(i)
| S. No. | Electric energy | Electric power |
| 1. | Electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance is the product of its power rating and the time for which it is used. | Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed. |
| 2. | It is measured in kWh. | It is measured in watt or kilowatt. |
(ii) We know, Power (P) = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\)
Therefore, P is inversely proportional to R as voltage remaining the same.
40 W lamp has a higher resistance.
(iii) The commercial unit of electrical energy is kWh.
⇒ 1 kWh = 1000 W x 1 hr = 1000 W x 3600s
⇒ = 36 x 105 J
⇒ = 3.6 x 106 J
![]()
Question 33.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What is the importance of pFI in everyday life?
(ii) Why does tooth decay start when the pH of mouth is lower than 5-5?
(iii) What is the change in pH value of milk when it changes into curd? Explain.
OR
Answer the following questions:
(i) Define a universal indicator. Mention one of its use.
(ii) Solution A gives pink colour when a drop of phenolphthalein indicator is added to it. Solution B gives red colour when a drop of methyl orange is added to it. What type of solutions are A and B and which one of the solutions A and B will have a higher pH value?
(iii) Name one salt whose solution has pH more than 7 and one salt whose solution has pH less than 7.
Answer:
(i) Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid which helps in digestion of food. It has pH around 1.2. If excess acid is produced, it causes pain and irritation. It can be controlled by taking antacids which controls the pH in the stomach.
(ii) Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in our body. It gets corroded slowly when pH in the mouth is below 5.5. When the pH in the mouth falls below 5.5, tooth decay starts. Bacteria present in the mouth produce acid by degradation of sugar and food particles which remain in the mouth after eating. The acid produced in the mouth attack the enamel thereby, creating tooth decay.
(iii) When milk changes into curd, the pH value will change, the pH value of milk is 6 since it is acidic in nature. When the milk is converted into curd due to the action of bacteria, lactic acid is formed which is more acidic in nature. Therefore, the pH value of the milk is reduced to the pH range 4.5-5.5 as it turns to curd.
OR
(i) Universal indicator is a mixture of many different indicators which gives different colours at different pH values of the entire pH scale. It is used to test whether a solution is an acid or a base. It changes its colour according to pH of acidic or basic medium.
(ii) A is a base and B is an acid. A will have higher pH value because pH of base is more than acids.
(iii) Ammonium chloride (pH less than 7).
Sodium carbonate (pH more than 7).
Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
(i) Describe two methods for the concentration of ores.
(ii) How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore? Explain the various steps supported by chemical equations. Draw labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper.
OR
(i) Explain any two physical properties of ionic compounds giving reasons.
(ii) List any two metals found in free state in earth’s crust.
(iii) Metals towards the top of the activity series cannot be obtained from their compounds by reducing with carbon. Why?
(iv) What will you observe when:
(a) Some zinc pieces are put in copper sulphate solution.
(b) Some silver pieces are put into green coloured ferrous sulphate solution.
Answer:
Two methods used for separation of ores are:
(i) Froth Flotation Method: It is used generally to remove gangue from sulphide ores. First of all, the ore is powdered and a suspension in water is formed. To this ore Collectors and Froth Stabilisers were added. The collectors generally used are pine oils, fatty acids etc.
The function of collectors is to increase the non-wettability of the metal part of the ore and allows it to form a froth. Froth Stabilizers (cresols, aniline etc.) sustain the froth. The oil wets the metal and the water wets the gangue. Paddles and air constantly stir up the suspension to create the froth. This frothy metal is skimmed off the top and dried, to recover the metal.

(ii) Magnetic ore Separation: This method is used in those cases where either ore or the impurities are of magnetic nature. In this method, the powdered impure ore in the form of thin layer is allowed to fall on a rubber belt which moves horizontally over two rollers, one of which has electromagnet attached to it. As the ore particles roll over the belt, the magnetic component in the ore gets attracted towards the magnet. It gets collected in a heap while the non – magnetic component forms a separate heap.

(iii) Copper is extracted from sulphide ore by the process of roasting. It is done in presence of air:

Electrolytic Refining of Copper:

OR
(i) The two physical properties of ionic compounds are:
- Ionic compounds are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and forms a regular crystal structure.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because ionic compounds are made up of oppositely charged positive and negative ions which are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction. Therefore, a large amount of energy is required to overcome these forces.
(ii) Gold and Platinum are the two metals that are found in free state in the earth’s crust. These metals are located at the bottom in the activity series.
(iii) Metals such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, aluminium high up in the reactivity series are very reactive and cannot be obtained from their compounds by heating with carbon. This is because these metals have more affinity for oxygen than carbon.
(iv) (a) The blue solution will become colourless and reddish brown copper metal will be deposited.

(b) When some silver pieces are put into green coloured ferrous sulphate solution, there will be no reaction because Ag is less reactive than iron:
Ag(s) + FeSO4(aq) → No reaction
Question 35.
What is “dispersion of white light”? Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate the recombination of the spectrum of white light. Why is it essential that the two prisms used for this purpose should be identical and placed in an inverted position with respect to each other?
Answer:
The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours on passing through a prism is known as the dispersion of white light. This splitting of the light rays occurs because of the different angles of bending for each colour and this different angles of bending occurs because different component of light faces different refractive indices when passing through the glass prism.

It is essential that the two prisms used for this purpose should be identical and placed in an inverted position with respect to each other so that the second prism completely nullifies the dispersion caused by the first prism and we get pure white light.
Question 36.
Describe the significance of spore formation in Rhizopus.
OR
What is vegetative propagation in plants? Name the plants where it is seen.
Answer:
Rhizopus is a fungus that commonly grows on bread, pickle and jam when conditions are favourable for its growih. It is a simple multicellular organism but shows specific reproductive parts. The thread like structure that can be seen on moist left-over bread pieces are the hyphae of the bread mould.
They are not the reproductive parts. The tiny round headed structures on a thin stalk are the reproductive parts. The round blobs are the sporangia inside which are a large number of tiny cells or spores that help in giving rise to new’ Rhizopus individuals. These spores have thick walls that protect them till they find a moist surface to grow. Hence, these spores are a means of asexual reproduction in Rhizopus.

OR
Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual reproduction in plants where new plants are produced from vegetative parts of plants like root, stem and leaves. While animals cannot use this method of re¬production, plants can. This method is used to produce new plants by layering or grafting as in rose, jasmine, sugarcane and grapes for agriculture purposes. It has both benefits and some drawbacks. Some examples of vegetative propagation are shown below:

(i) Propagation by buds on leaf margins in Bryophyllum leaf. The buds that develop along the leaf margin fall on the soil and each of them develops into a new plant.
(ii) A small cutting of a money plant when kept in water in a glass container or in a pot with soil grows into a new plant.
(iii) Buds in potato and ginger can grow into new plants under suitable conditions.
(iv) In sweet potato, the roots bear adventitious buds which can grow into new plants under favourable conditions.
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
The reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralization reaction. In general, a neutralization reaction can be written as –
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
1. Take about 2ml of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube.
2. Add two drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution.
3. It turns to red or pink colour.
4. Add dilute HC1 solution to the above solution drop by drop.
5. Pink colour disappears due to the reaction of NaOH (base) with HC1 (acid).
6. Now add one or two drops of NaOH to the above mixture.
In the above Activity, we have observed that the effect of a base is nullified by an acid and vice-versa.
(a) Write a chemical equation for above reaction.
(b) What conclusion can be drawn from the observation that phenolphthalein indicator turns NaOH solution to pink?
OR
(b) What happens when NaOH is again added to mixture?
Answer:
(a) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
(b) It shows that NaOH is basic in nature.
OR
(b) Pink colour reappears on adding NaOH again to the mixture.
Question 38.
There are many plants in which parts like the root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions. Unlike in most animals, plants can indeed use such a mode for reproduction. This property of vegetative propagation is used in methods such as layering or grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes for agricultural purposes.
Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. Such methods also make possible the propagation of plants such as banana, orange, rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds. Another advantage of vegetative propagation is that all plants produced are genetically similar enough to the parent plant to have all its Characteristics.
1. Take a potato and observe its surface. Can notches be seen?
2. Cut the potato into small pieces such that some pieces contain a notch or bud and some do not.
3. Spread some cotton on a tray and wet it. Place the potato pieces on this cotton. Note where the pieces with the buds are placed.
4. Observe changes taking place in these potato pieces over the next few days. Make sure that the cotton is kept moistened.
(a) Which parts of plants are used for vegetative propagation?
(b) Give any one advantage of vegetative propagation.
(c) Give an example of plant which shows vegetative propagation.
OR
(d) What observation can be seen in above activity?
Answer:
(a) There are many plants in which parts like the root, stem and leaves are used for vegetative propagation.
(b) Advantage of vegetative propagation is that all plants produced are genetically similar enough to the parent plant to have all its characteristics.
(c) Rose shows vegetative propagation.
OR
(d) The potato pieces having buds gradually grows and develops. But there is no growth and development in potato pieces without bud.
Question 39.
Complete an electric circuit consisting of a cell, an ammeter, a nichrome wire of length 1 [say, marked (1)] and a plug key, as shown

1. Now, plug the key. Note the current in the ammeter.
2. Replace the nichrome wire by another nichrome wire of same thickness but twice the length, that is 21 [marked (2) in the Figure],
3. Note the ammeter reading.
4. Now replace the wire by a thicker nichrome wire, of the same length 1 [marked (3)]. A thicker wire has a larger cross-sectional area. Again note down the current through the circuit.
5. Instead of taking a nichrome wire, connect a copper wire [marked (4) in Figure] in the circuit.
6. Let the wire be of the same length and same area of cross-section as that of the first nichrome wire [marked (1)]. Note the value of the current.
(a) What happened to ammeter reading when the length of the wire is doubled?
(b) How ammeter reading should be increased?
(c) If a wire of different material of same length and the same area of cross-section is used then how does ammeter reading affected?
OR
(c) On what factors resistance of a conductor depends?
Answer:
(a) It is observed that the ammeter reading decreases to one-half when the length of the wire is doubled.
(b) The ammeter reading is increased when a thicker wire of the same material and of the same length is used in the circuit.
(c) A change in ammeter reading is observed when a wire of different material of the same length and the same area of cross-section is used.
OR
(c) Resistance of a conductor depends on (i) on its length, (ii) on its area of cross-section, and (iii) on the nature of its material.