CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2019 Delhi
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum marks: 70
General Instructions :
- There are 22 questions in all.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 7 are very short-answer questions carrying 1 mark each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 40
- Question numbers 8 to 13 are short-answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 80-100 words.
- Question numbers 14 to 20 are long-answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 150
- Question numbers 21 to 22 are related to identification or locating and labelling of geographical features on maps, carrying 5 marks each.
- Outline maps of the World and India provided to you must be attached within your answer-book.
- Use of templates or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2019 Delhi Set – I
Question 1.
Define the term ‘literacy’. [1]
OR
Define the term ‘Age Structure’.
Answer:
- Literacy: The percentage of population above 7 years of age, who is able to read, write and has the ability to do arithmetic calculations with understanding.
- Age Structure : Age structure represents the number of people of different age groups.
Question 2.
Differentiate between ‘Growth and Development’. [1]
Answer:
- Growth : Growth is quantitative and value neutral. It may have a positive or a negative sign,
- Development: Development means a qualitative change which is always value positive.
Question 3.
Write the meaning of ‘digital divide’. [1]
Answer:
Opportunities emerging from the Information and Communication Technology based development is unevenly distributed across the globe. There are wide ranging economic, political and social differences among countries. While developed countries in general have surged forward economically, politically and socially, the developing countries have lagged behind economically, politically and socially and this difference is known as the digital divide. Similarly digital divides exist within countries.
Question 4.
Mention any two problems of barter system of trade. [1]
Answer:
Problems of Barter system :
- Lack of double coincidence of wants : Double coincidence of wants means what one person wants to sell and buy must coincide with what some other person wants to buy and sell.
- Lack of common measure of value : In barter, there is no common measure of value. Even if the problem of double coincidence is solved, the problem that arises is in what proportion the two goods are’to be exchanged.
Question 5.
Explain why male migration is higher than females from rural to urban areas in India. [1]
OR
Explain why female migration is higher from rural to rural areas in India.
Answer:
Male migration is higher than females from rural to urban area in India due to work and employment.
OR
Female migration is higher from rural to rural areas in India because of marriage.
Question 6.
Examine the importance of ‘rain water harvesting’. [1]
Answer:
Importance of rain water harvesting :
- Checks the decline in groundwater level.
- Improves the quality of groundwater.
- It prevents flooding and arrests salt.
- It increases water availability.
Question 7.
Why is urban waste a serious problem in India ? Explain one reason. [1]
OR
Why is air pollution a serious problem in India ? Explain one reason.
Answer:
Urban waste is a serious problem in India due to :
- Generation of large quantity of waste in urban areas due to overcrowding.
- No proper disposal of waste material.
- Concentration of industries in and around the urban areas.
OR
Air pollution is a serious problem because it causes various diseases related to respiratory, nervous and circulatory systems.
Question 8.
“Physical environment has been greatly modified by human beings, it has also, in turn impacted human lives.” Explain the statement. [3]
Answer:
Human geography deals with the inter-relationship between the physical environment and socio-cultural environment created by human beings through mutual interactions with each other. “The physical environment like landforms, soils, climate, water, natural vegetation and diverse flora and fauna has been greatly modified by human beings, in turn it has also impacted human lives”. This statement absolutely makes sense because houses, villages, cities, road-rail networks, industries, farms, ports, items of our daily use and all other elements of material culture have been created by human beings using the resources provided by the physical environment.
Question 9.
Study the given diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow : [1 + 2 = 3]
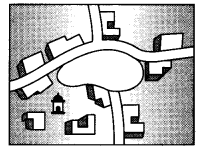
(9.1) Identify and name the pattern of rural settlement shown in the diagram.
(9.2) Explain any two characteristics of this type of pattern of rural settlement.
OR
Study the given diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow:

(9.1) Identify and name the pattern of rural settlement shown in the diagram.
(9.2) Explain any two characteristics of this type of pattern of rural settlement.
Answer:
(9.1) Circular pattern.
OR
(i) Circular pattern is developed around lakes and tanks.
(ii) Central part remains open and is used for keeping animals to protect them from wild animals.
OR
(i) Star-like pattern.
(9.2)
- Several roads coverage.
- Houses are built along the roads.
Question 10.
Study the following table and answer the questions that follow : [3]
Decadal Growth Rates in India, 1901-2011

Question 10.1.
Which decade has shown the negative trend rate of population ?
Answer:
1911-1921.
Question 10.2.
Mention any two decades in which the percentage decadal growth has shown the angular downward trend.
Answer:
Decadal growth has shown the downward trend:
- 1971-1981
- 1981-1991
- 1991-2001
- 2001-2011
Question 10.3.
Explain any two reasons for the declining trend in the population growth rate. Answer:
Reasons for the declining trend :
- Increase in the mean age at marriage.
- Improved quality of life.
- Improvement in the education of female.
- Opting family planning programmes.
Question 11.
“The prime task before any development activity in India is to maintain parity between population and resources.” Justify the statement. [3]
Answer:
The prime task before any development activity in India is to maintain parity between population and resources :
- It is true that population grows rapidly but resources expand marginally.
- The gap between population growth and resources expansion widened.
- There is no parity between population and resources and it hampers development.
- Thus, for development there should be parity between population growth and resources.
Question 12.
Describe the importance of sea routes in handling India’s foreign trade. [3]
Answer:
The sea routes offer a smooth highway traversable in all directions with no maintenance costs. Compared to land and air, sea route is a cheaper means of haulage (carrying of load) of bulky material over long distances from one continent to another. The development of refrigerated chambers for perishable goods, tankers and specialised ships has also improved cargo transport. The use of containers has made cargo handling at the world’s major ports easier.
Question 13.
Examine the level of urbanisation in India after independence. [4]
OR
“Towns flourished since prehistoric times in India.” Examine.
Answer:
Total urban population has increased eleven-fold during the twentieth century. Enlargement of urban centres and emergence of new towns have played a significant role in the growth of urban population and urbanisation in the country. But the growth rate of urbanisation ha’s slowed down during last two decades.
OR
Town flourisned since prehistorical times in India. The prehistoric towns developed along the rivers. Even at the time of Indus Valley Civilisation, towns like Harappa and Mohanjodaro were in existence.
The follow period has witnessed evolution of towns. It continued with periodic ups and downs Until the arival of Europeans in India in the 18th century. On the basis of their evolution in different periods, Indian towns may be classified as Ancient towns, Medieval towns and Modern towns.
Question 14.
Define the term ‘density of population’. Elaborate any four geographical factors the influence that distribution of population in the world. [1+4]
Answer:
Density of population is expressed as number of persons per unit area.
Formula = Density of Population = Population/Area Four geographical factors that influence the distribution of papulation in the world :
- Available of water : It is the most important factor for life. So, people prefer to live in areas where fresh water is easily available.
- Landforms : People prefer living on flat plains and gentle slopes. This is because such areas are favourable for the production of crops and to build roads and industries.
- Climate : An extreme climate such as very hot or cold deserts are uncomfortable climate, but where there is not much seasonal variation, attracts more people.
- Soil: Fertile soils are important for agricultural and allied activities. Therefore, areas which have fertile loamy soils have more people living on them as these can support intensive agriculture.
Question 15.
Describe any five characteristics of ‘Pastoral Nomadism’ in the world. [1 × 5]
Answer:
Characteristics of Pastoral Nomadism :
- It is a primitive subsistence activity,
- The herder relies on animals for food, clothing shelter, tools and transport.
- They move from one place to another with their livestock, depending on the amount and quality of pasture and water.
- Nomadic community occupies a well identified territory as a matter of tradition.
- A wide variety of animals are kept in different regions.
Question 16.
Explain any five characteristics of ‘high tech industry’ in the world. [1 × 5]
OR
Explain any five characteristics of ‘large scale manufacturing’ in the world.
Answer:
Characteristics of a high-tech industry :
- High technology, or simply high-tech, is the latest generation of manufacturing activities.
- It is the application of intensive research and development (R & D) efforts leading to the manufacture of products of an advanced scientific and engineering character.
- Robotics on the assembly line, computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing, electronic controls of smelting and refining processes, and the constant development of new chemical and pharmaceutical products are notable examples of the high-tech industry.
- Neatly spaced, low, modern, dispersed, office- plant-lab rather than massive assembly structures, factories and storage areas mark the high-tech industrial landscape. Planned business parks for high-tech start-ups have become part of regional and local development schemes.
- High-tech industries which are regionally concentrated, self-sustained and highly specialised are called technopolies. For e.g., the Silicon Valley near San Francisco and Silicon Forest near Seattle.
OR
Characteristics of a large scale manufacturing :
- Large scale manufacturing involves a large market, mechanization, enormous energy, specialised workers, technological innovation, assembly-line mass production and large capital.
- Such kind of manufacturing developed in the last 200 years, in the United Kingdom, Northeastern U.S.A. and Europe.
- On the basis of the system of large scale manufacturing, the world’s major industrial regions may be grouped into—traditional large scale and high-technology large scale.
- Traditional large scale industrial regions are thickly clustered in a few more developed countries.
- High-technology large scale industrial regions have diffused to less developed countries.
Question 17.
Analyse any five points of importance of ‘pipelines’ as means of transportation. [1 × 5 = 5]
OR
Analyse the three factors that affect the development of inland waterways. Explain the significance of Rhine inland waterways. [3 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
Importance of pipelines :
- Pipelines are used extensively to transport liquid, gases and solid in the form of-slurry.
- They are used to transport liquified coal.
- In New Zealand, milk is being supplied through pipelines from farms to factories.
- About 17% of all freight per tone-km is carried through pipelines in USA.
- Pipelines are used to connect oil wells to refineries and to ports or domestic markets.
OR
Factors that affect the development of inland waterways :
- Navigable rivers
- Rivers and canals should be deep and flow throughout the year
- Use of latest transport technology Significance of Rhine inland waterways :
- It flows through a rich coalfield and the whole basin has become a prosperous manufacturing area. Huge tonnage moves along the stretch south of the Ruhr river.
- This is the world’s most heavily used waterway. Each year more than 20,000 ocean-going ships and 2,00,000 inland vessels exchange their cargoes.
- It connects the industrial area of Switzerland, Germany, France, Belgium and the Netherlands with the North Adantic Sea-route.
Question 18.
“ ‘Erratic monsoon and ‘low productivity’ are the major problems of Indian agriculture.” Substantiate the statement. [2 1/2 + 2 1/2 = 5]
Answer:
Erratic Monsoon :
- As irrigation covers only about 33 percent of the cultivated area in India, the rest of the cultivated land directly depends on the erratic monsoon.
- The rainfall in Rajasthan and other draught prone areas is too meagre and highly unreliable.
- The areas receiving high annual rainfall experience considerable fluctuations which makes them vulnerable to both drought and floods.
- Drought is a common phenomenon areas of low rainfall.
- Flash floods occured in Maharastra, Gujarat and Rajasthan.
Low Productivity:
- The agricultural productivity of the crops in India is lower than other counties like USA, Russia and Japan.
- The labour productivity is also low because of high pressure on land resources.
- The productivity in rainfed areas is particularly lower than irrigated areas.
Question 19.
Explain with examples, the factors that helped in the development of ‘Hugli industrial region. [5]
OR
Explain with examples, the factors that helped in the development of ‘Mumbai-Pune industrial region.
Answer:
Factors that helped in the development of ‘Hugli Industrial region’:
- Hugli river provides cheap transport.
- Kolkata and Haldai ports facilitate export and import.
- Power available from Damodar Valley and coal field from Chhota Nagpur region also aided the development.
- Availability of raw materials like jute, tea, iron ore deposits etc. from nearby areas contributed to the development.
- Cheap labour available from thickly populated part of Bihar, Eastern Uttar Pradesh and Odisha.
- Kolkata was well connected with interior parts by railway lines and road routes.
- Examples : Cotton textile, Jute textile, Paper textile machineries pharmacenticals etc.
OR
Factors that helped in the development of ‘Mumbai- Pune Industrial region’:
- Development started with the location of cotton textile industry in Mumbai.
- Moist climate suitable for cotton textile.
- Opening of Suez canal in 1860 provided impetus to the growth of Mumbai port.
- Hydro electricity was developed in the Western Ghat region to fulfill the requirements of this industry.
- Opening of the Mumbai high petroleum field and erection of nuclear energy plants added additional pull to this industry.
- Examples : Engineering goods, petroleum refining, petrochemicals, leather, synthetic and plastic goods etc.
Question 20.
“India has one of the largest network of roads in the world.” Support the statement with examples. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
India has one of the largest networks of roads in the world.
- The network of roads is of a total length of 54.8 lakh km as per the economic survey 2016-17.
- 85% of passengers and 70% freight traffic are carried by roads.
- Roads are concentrated in and around urban centres, rural and remote areas.
- Under Pradhan Mantri Sadak Yojna all villages are connected with all weather roads.
- Construction of Golden Quadrilateral and North-South, East-West corridors and many super expressways have been built.
Question 21.
Identify the five geographical features shown on the given political outline map of the world as A, B, C, D and E. Write their correct names on the lines drawn near them with the help of the following information :
(A) An industrial region
(B) A major seaport
(C) The terminal station of a transcontinental railway
(D) An international airport

Answer:

Question 22.
Locate and label any five of the following geographical features with appropriate symbols on the political outline map of India : [5 × 1 = 5]
(22.1) The state with highest level of urbanisation.
(22.2) The leading state in the production of coffee.
(22.3) An oil refinery in Haryana.
(22.4) The steel plant setup in collaboration with U.K.
(22.5) An international airport in Assam.
(22.6) The major seaport in Odisha.
(22.7) The Headquarters of North-Eastern Railway.
(22.8) Singareni coal mines.
Answer:

CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2019 Delhi Set – II
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 3.
Write the meaning of ‘Tourism’. [1]
Answer:
Tourism is the travel undertaken for the purpose of recreation rather than business.
Question 4.
Mention any two ill effects of free trade and economic globalisation. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Two ill effects of free trade and economic globalisation :
- Developed countries keep their own market protected from foreign products.
- Countries also need to be cautious about dumped goods.
- It widens the gap between rich and poor counries, making rich countries more rich.
Question 6.
Examine the importance of irrigation in Indian context. [1]
Answer:
Irrigation is needed for agriculture due to uneven distribution of rainfall from time to time and place to place in the country.
Question 8.
Explain the concept of environmental determination with examples. [1 × 3 = 3]
Answer:
Concept of Environment Determinism : In the early stages of their interaction with their natural environment, humans were greatly influenced by it. They adapted to the dictates of nature. This is so because the level of technology was very low and the stage of human social development was also primitive. This type of interaction between primitive human society and strong forces of nature was termed as Environmental Determinism.
- At the stage of very low technological development one can imagine the presence of a naturalised human, who listened to Nature, was afraid of its fury and worshipped it.
- There is direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them. The physical environment for such societies becomes the “Mother Nature”.
Example : Benda, who lives in the wilds of the Abujh Maad area of Central India.
Question 15.
Describe any five characteristics of ‘subsistence agriculture’ practised in the world. ‘ [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Characteristics of subsistence agriculture :
- Farmers consume almost all of their products locally grown.
- It is classified into two types : Primitive subsistence agriculture and Intensive subsistence agriculture.
- Primitive subsistence agriculture or shifting cultivation is widely practised by many tribes in the
tropical regions. - Intensive subsistence agriculture is practised in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture is divided into intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by paddy cultivation and intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy.
Question 18.
“Lack of ‘land reforms’ and ‘degradation of cultivable land’ are the major problems of Indian agriculture.” Substantiate the statement. [21/2 + 21/2 = 5]
Answer:
Major problems of the Indian Agriculture :
- Lack of Land Reforms :
- Due to exploitative revenue systems such as Mahalwari, Ryotwari and Zamindari, operational since the British era, Indian farmers were exploited for a long time.
- Even when the land reforms were made top priority after independence, the reforms were not carried out as many state governments avoided taking politically tough decisions which went against the wealthy zamindars.
- Degradation of Cultivable Land :
- Faulty strategy of agricultural development has led to degradation of cultivated land.
- Alkalisation and salinization of soils and waterlogging has also made agriculture lands less fertile.
- Excessive use of chemicals such as pesticides and insecticides has accumulated in huge amounts in the soil.
Question 20.
“Waterways is an important mode of transport for both passenger and cargo traffic in India.” Support the statement with examples. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Importance of water transport in India :
- It is the cheapest mode of transport.
- It is suitable for carrying heavy and bulky material.
- It is fuel efficient and eco friendly.
- India contributes 1% of the country’s transportation through inland waterways. It comprises rivers, canals backwaters, creeks etc.
- Ocean routes will help in doubling India’s foreign trade.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2019 Delhi Set – III
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set.
Question 3.
Write the meaning of ‘Trading Centres’. [1]
Answer:
Trading Centres : Places where buying and selling of commodities and services take place are known as trading centres.
Question 4.
Mention any two features of ‘Commercial Ports’. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
Answer:
Features of commercial ports :
- These ports handle general cargo and manufactured goods.
- They also handle passenger traffic.
Question 6.
Examine the importance of ‘Lagoons and Backwaters’. [1]
Answer:
They are used for fishing and irrigating certain varieties of paddy crops coconut, etc.
Question 8.
Examine the concept of ‘Possibilism’ with suitable examples. [1 × 3 = 3]
Answer:
With the passage of time, people begin to understand their environment and the forces of nature. With social and cultural development, humans develop better and more efficient technology. They move from a state of necessity to a state of freedom. They create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment. The human activities create cultural landscape. Human activities take place everywhere—health resorts on highlands, huge urban sprawls, fields, orchards and pastures in plains and rolling hills, ports on the coasts, oceanic routes on the oceanic surface and satellites in the space.
Nature provides opportunities and human beings make use of these and so gradually nature gets humanised and starts bearing the imprints of human endeavour.
Question 15.
Describe any five features of ‘plantation agriculture’ practised in the world. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
- Plantation agriculture was introduced by the Europeans in colonies situated in the tropics. Some of the important plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, oil palm, sugarcane, bananas and pineapples.
- The characteristic features of this type of farming are large-estates or plantations, large capital investment, managerial and technical support, scientific methods of cultivation, single crop specialisation, cheap labour, and a good system of transportation which links the estates to the factories and markets for the export of the products.
- The French established cocoa and coffee plantations in West Africa. The British set up large tea gardens in India and Sri Lanka, rubber plantations in Malaysia and sugarcane and banana plantations in West Indies.
- Spanish and Americans invested heavily in coconut and sugarcane plantations in the Philippines. The Dutch once had monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia. Some coffee fazendas (large plantations) in Brazil are still managed by Europeans.
- Today, ownership of the majority of plantations has passed into the hands of the government or the nationals of the countries concerned.
Question 18.
“After independence various important strategies were adopted for agricultural development in India.” Substantiate the statement. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Indian agricultural economy was largely subsistence in nature after Independence. During partition about one-third of the irrigated land in undivided India went to Pakistan.
- After Independence, the immediate goal of the Government was to increase food-grains production by:
- Switching over from cash crops to food crops.
- Intensification of cropping over already cultivable land.
- Increasing cultivation by bringing cultivate land and fallow land under plough.
- This strategy helped in increasing food grains production. But it stagnated during late 1950s. Intensive Agricultural District Programme and Intensive Agricultural Area Programme were launched to overcome to this problem.
- New seed varieties of wheat and rice known as HYVs were available for cultivation by mid-1960. Package technology including HYVs was introduced in Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat.
- This strategy of agricultural development led to increase in production of the food grains at very fast rate and this agricultural growth came to be known as Green Revolution. This strategy of agricultural development made the country self-reliant in food grain production.
- Planning Commission of India initiated agro-climatic planning in 1988 to induce regionally balanced agricultural development in the country. It also emphasised the need for diversification and harnessing of resources for development of dairy farming, poultry, horticulture etc.
Question 20.
“Pipelines have become the most convenient and efficient mode of transporting liquids and gases over long distances in India.” Support the statement with examples. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Pipelines have become the most convenient and efficient mode of transporting liquids and gases over long distances in India.
- Solids can be transported in the form of slurry by pipelines.
- Oil and natural gas are transported to the thermal power stations and fertilizer plants.
- Pipelines have been constructed like Hazira, Vijaypur and Jagdishpur (HVJ Pipeline).
- Its initial cost is high but in the long run it is very cheap.
- Pipelines can be laid over difficult terrain as well as under water.
- Their operation and maintenance costs are lower and involve very low energy consumption.